You’ll find historical societies in all five boroughs of New York; as you’ll see, they are architecturally interesting in themselves, and are valuable resources for learning more about the boroughs’ history.
Here are some capsule reviews of each, with contact info. Be sure to get current visitor and exhibit information – some sites have very limited hours of operation.
New York Historical Society

The New York Historical Society is both the oldest and among the youngest museums in New York. It was founded in 1804, but the building was renovated and reopened in November 2011. It now includes state-of-the-art interactive displays on three exhibit floors and a spectacular multimedia show – “New York Story” – which by itself is almost worth the price of admission. (The 18-minute show screens every half hour.) The Society is also young in its approach to history – it has a sense of humor that pops up and keeps the exhibits fresh. Where else would you find a “Beer Here” exhibit?
The permanent collection is displayed on the fourth floor (which has its own mezzanine); changing exhibits are on the first and second floors; a children’s museum, library and classrooms are on the lower level. The first floor also contains the auditorium, gift/book shop and cafe. New York Historical Society goes to great lengths to make its collection accessible to all – mobility, sight and hearing impairments are all accommodated.
The New York Historical Society museum and library covers all of New York City – unlike the other societies, which focus on single boroughs. Consequently, there’s some overlap between this museum and the Museum of the City of New York on Fifth Avenue.
Note that the Society’s library closes earlier than its museum – 3 p.m. Tuesday-Friday and 1 p.m. on Saturday (closed Sunday).
Google map
Museum of the City of New York

This is not one of the historical societies, strictly speaking – it’s a New York City-operated museum which serves many of the same purposes.
You might also be interested in the Queens Museum of Art (which has a massive city panorama, updated from the original 1964 NY World’s Fair).
Google map
Bronx County Historical Society
The Museum of Bronx History operates out of the Valentine-Varian House, a fieldstone farmhouse built in 1758. The Society also maintains a separate archive/library and the nearby Poe House (see below). In addition, the society operates tours.
Google map
Poe Cottage

(Operated by Bronx County Historical Society)
This is where Edgar Allan Poe spent his last years; where his wife died and where he wrote some of his most memorable works. The docent gives an excellent talk about Poe, his life and times; there’s also an informative video shown in an upstairs bedroom. In the adjacent park, the Parks Department operates an educational center.
And if you need another reason to visit, the immediate neighborhood is rich in architectural treasures – including Kingsbridge Armory, two blocks west.
Google map
Brooklyn Historical Society

Founded as the Long Island Historical Society in 1863; changed its name to Brooklyn Historical Society in 1985. The building is still going through restoration – the main floor gallery is the current (as of September 2012) project; most other areas, inside and out, are stunningly beautiful. In addition to the exhibit galleries, the Society houses an impressive research library.
Google map
Queens Historical Society

The Queens Historical Society operates out of Kingsland Homestead in Flushing, next to the historic Bowne House (currently closed for restoration). It’s a small operation, open only a few hours on just three days a week. But they do have a good selection of publications – books and pamphlets – about other historic sites in Queens. And, it’s a part of the Flushing “Freedom Mile” walking tour that includes 10 other significant buildings. (Kingsland Homestead was a part of the “Underground Railroad.”)
Google map
Staten Island Historical Society

Historic Richmond Town is a score of restored/reconstructed homes, farms, businesses, schools and churches, dating from the 1700s and 1800s. It’s quite rural compared to the rest of the city and very popular for school outings. There are several themed tours – consider this an all-day trip – or several trips!
If you’re very ambitious, there’s a Frank Lloyd Wright-designed home (see “The Wright Stuff” gallery.) and a lighthouse at the top of the hill overlooking Historic Richmond Town, and a beautiful church and cemetery across the street.
Google map
Other Sites of Interest
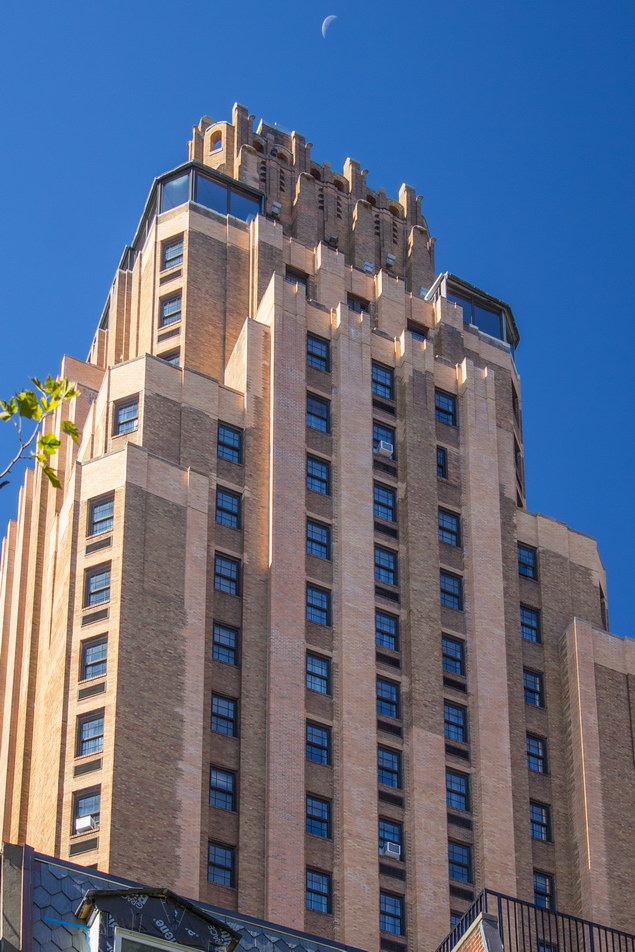


![[Beekman Tower Hotel] B_1421 [9/10/2012 10:13:35 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] B_1421 [9/10/2012 10:13:35 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/B_1421_resize.jpg)
![[Beekman Tower Hotel] C_1490 [9/10/2012 10:50:29 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] C_1490 [9/10/2012 10:50:29 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/C_1490_resize.jpg)
![[Beekman Tower Hotel] D_1746 [9/11/2012 8:35:51 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] D_1746 [9/11/2012 8:35:51 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/D_1746_resize.jpg)
![[Beekman Tower Hotel] E_1428 [9/10/2012 10:20:35 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] E_1428 [9/10/2012 10:20:35 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/E_1428_resize.jpg)
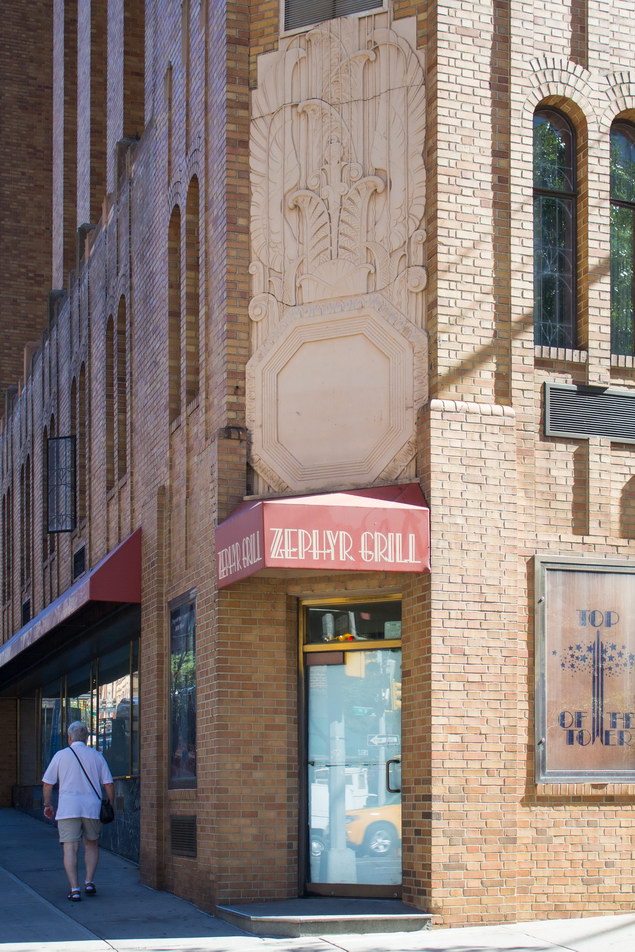

![[Beekman Tower Hotel] G_1443 [9/10/2012 10:27:56 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] G_1443 [9/10/2012 10:27:56 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/G_1443_resize.jpg)
![[Beekman Tower Hotel] H_1449 [9/10/2012 10:30:47 AM] [Beekman Tower Hotel] H_1449 [9/10/2012 10:30:47 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/beekman-tower-hotel/H_1449_resize.jpg)

![[General Electric Building] K_1639 [9/10/2012 11:58:39 AM] [General Electric Building] K_1639 [9/10/2012 11:58:39 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/K_1639_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] V_1684 [9/10/2012 12:22:29 PM] [General Electric Building] V_1684 [9/10/2012 12:22:29 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/V_1684_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] U_1678 [9/10/2012 12:20:19 PM] [General Electric Building] U_1678 [9/10/2012 12:20:19 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/U_1678_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] T_1681 [9/10/2012 12:21:16 PM] [General Electric Building] T_1681 [9/10/2012 12:21:16 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/T_1681_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] Q_1566 [9/10/2012 11:35:38 AM] [General Electric Building] Q_1566 [9/10/2012 11:35:38 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/Q_1566_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] P_1359 [9/10/2012 9:27:37 AM] [General Electric Building] P_1359 [9/10/2012 9:27:37 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/P_1359_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] O_1569 [9/10/2012 11:36:13 AM] [General Electric Building] O_1569 [9/10/2012 11:36:13 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/O_1569_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] N_1655 [9/10/2012 12:04:23 PM] [General Electric Building] N_1655 [9/10/2012 12:04:23 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/N_1655_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] M_1653 [9/10/2012 12:03:58 PM] [General Electric Building] M_1653 [9/10/2012 12:03:58 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/M_1653_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] L_1642 [9/10/2012 12:00:09 PM] [General Electric Building] L_1642 [9/10/2012 12:00:09 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/L_1642_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] A_1970 [9/12/2012 1:34:03 PM] [General Electric Building] A_1970 [9/12/2012 1:34:03 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/A_1970_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] J_1645 [9/10/2012 12:00:52 PM] [General Electric Building] J_1645 [9/10/2012 12:00:52 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/J_1645_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] I_1638 [9/10/2012 11:58:06 AM] [General Electric Building] I_1638 [9/10/2012 11:58:06 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/I_1638_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] H_1635 [9/10/2012 11:57:35 AM] [General Electric Building] H_1635 [9/10/2012 11:57:35 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/H_1635_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] G_1632 [9/10/2012 11:56:13 AM] [General Electric Building] G_1632 [9/10/2012 11:56:13 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/G_1632_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] F_1623 [9/10/2012 11:53:05 AM] [General Electric Building] F_1623 [9/10/2012 11:53:05 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/F_1623_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] E_1613 [9/10/2012 11:50:30 AM] [General Electric Building] E_1613 [9/10/2012 11:50:30 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/E_1613_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] D_1602 [9/10/2012 11:45:41 AM] [General Electric Building] D_1602 [9/10/2012 11:45:41 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/D_1602_resize.jpg)
![[General Electric Building] B_1953 [9/12/2012 1:17:45 PM] [General Electric Building] B_1953 [9/12/2012 1:17:45 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/general-electric-building/B_1953_resize.jpg)

![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1345 [9/10/2012 9:21:26 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1345 [9/10/2012 9:21:26 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1345_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1346 [9/10/2012 9:24:23 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1346 [9/10/2012 9:24:23 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1346_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1375 [9/10/2012 9:45:06 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1375 [9/10/2012 9:45:06 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1375_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1403 [9/10/2012 10:04:23 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1403 [9/10/2012 10:04:23 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1403_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1461 [9/10/2012 10:37:13 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1461 [9/10/2012 10:37:13 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1461_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1462 [9/10/2012 10:37:40 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1462 [9/10/2012 10:37:40 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1462_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1500 [9/10/2012 10:55:51 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1500 [9/10/2012 10:55:51 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1500_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1501 [9/10/2012 10:56:15 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1501 [9/10/2012 10:56:15 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1501_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1520 [9/10/2012 11:05:12 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1520 [9/10/2012 11:05:12 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1520_resize.jpg)
![[100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1523 [9/10/2012 11:06:14 AM] [100 United Nations Plaza] IMG_1523 [9/10/2012 11:06:14 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/100-united-nations-plaza/IMG_1523_resize.jpg)









![[Seagram Building] IMG_1688 [9/11/2012 8:01:40 AM] [Seagram Building] IMG_1688 [9/11/2012 8:01:40 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_1688_resize.jpg)
![[Seagram Building] IMG_1696 [9/11/2012 8:03:47 AM] [Seagram Building] IMG_1696 [9/11/2012 8:03:47 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_1696_resize.jpg)
![[Seagram Building] IMG_1698 [9/11/2012 8:04:36 AM] [Seagram Building] IMG_1698 [9/11/2012 8:04:36 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_1698_resize.jpg)
![[Seagram Building] IMG_1997 [9/12/2012 2:17:13 PM] [Seagram Building] IMG_1997 [9/12/2012 2:17:13 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_1997_resize.jpg)

![[Seagram Building] IMG_2768 [9/26/2012 8:03:52 PM] [Seagram Building] IMG_2768 [9/26/2012 8:03:52 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_2768_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_2778 [9/26/2012 8:09:10 PM] [Lever House] IMG_2778 [9/26/2012 8:09:10 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_2778_resize.jpg)
![[Seagram Building] IMG_2783 [9/26/2012 8:12:10 PM] [Seagram Building] IMG_2783 [9/26/2012 8:12:10 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/seagram-building/IMG_2783_resize.jpg)



![[Lever House] IMG_1911 [9/11/2012 10:29:32 AM] [Lever House] IMG_1911 [9/11/2012 10:29:32 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_1911_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_1915 [9/11/2012 10:30:53 AM] [Lever House] IMG_1915 [9/11/2012 10:30:53 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_1915_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_1917 [9/11/2012 10:31:44 AM] [Lever House] IMG_1917 [9/11/2012 10:31:44 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_1917_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_1961 [9/12/2012 1:25:55 PM] [Lever House] IMG_1961 [9/12/2012 1:25:55 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_1961_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_2788 [9/26/2012 8:18:18 PM] [Lever House] IMG_2788 [9/26/2012 8:18:18 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_2788_resize.jpg)
![[Lever House] IMG_2790 [9/26/2012 8:20:56 PM] [Lever House] IMG_2790 [9/26/2012 8:20:56 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/lever-house/IMG_2790_resize.jpg)

![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2823 [9/26/2012 8:51:38 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2823 [9/26/2012 8:51:38 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2823_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9086 [8/16/2012 2:49:46 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9086 [8/16/2012 2:49:46 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9086_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9082 [8/16/2012 2:47:58 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9082 [8/16/2012 2:47:58 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9082_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9062 [8/16/2012 2:36:06 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9062 [8/16/2012 2:36:06 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9062_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9059 [8/16/2012 2:35:32 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9059 [8/16/2012 2:35:32 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9059_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9047 [8/16/2012 2:27:51 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9047 [8/16/2012 2:27:51 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9047_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9040 [8/16/2012 2:22:22 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9040 [8/16/2012 2:22:22 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9040_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9036 [8/16/2012 2:20:59 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9036 [8/16/2012 2:20:59 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9036_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9030 [8/16/2012 2:18:37 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_9030 [8/16/2012 2:18:37 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_9030_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2795 [9/26/2012 8:30:21 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2795 [9/26/2012 8:30:21 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2795_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2815 [9/26/2012 8:46:40 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2815 [9/26/2012 8:46:40 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2815_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2812 [9/26/2012 8:44:29 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2812 [9/26/2012 8:44:29 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2812_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2811 [9/26/2012 8:43:49 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2811 [9/26/2012 8:43:49 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2811_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2808 [9/26/2012 8:40:40 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2808 [9/26/2012 8:40:40 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2808_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2802 [9/26/2012 8:37:13 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2802 [9/26/2012 8:37:13 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2802_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2801 [9/26/2012 8:35:20 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2801 [9/26/2012 8:35:20 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2801_resize.jpg)
![[Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2798 [9/26/2012 8:31:51 PM] [Bloomberg Tower] IMG_2798 [9/26/2012 8:31:51 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/bloomberg-tower/IMG_2798_resize.jpg)

![[9 W57th Street] IMG_3538 [6/15/2012 8:44:05 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_3538 [6/15/2012 8:44:05 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_3538_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4683 [7/3/2012 10:31:24 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4683 [7/3/2012 10:31:24 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4683_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4684 [7/3/2012 10:31:42 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4684 [7/3/2012 10:31:42 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4684_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4695 [7/3/2012 10:34:43 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4695 [7/3/2012 10:34:43 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4695_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4696 [7/3/2012 10:35:32 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4696 [7/3/2012 10:35:32 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4696_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4701 [7/3/2012 10:39:35 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4701 [7/3/2012 10:39:35 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4701_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4707 [7/3/2012 10:46:22 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4707 [7/3/2012 10:46:22 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4707_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4713 [7/3/2012 10:47:42 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4713 [7/3/2012 10:47:42 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4713_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4719 [7/3/2012 10:50:49 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4719 [7/3/2012 10:50:49 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4719_resize.jpg)
![[9 W57th Street] IMG_4725 [7/3/2012 10:53:31 AM] [9 W57th Street] IMG_4725 [7/3/2012 10:53:31 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/solow-building/IMG_4725_resize.jpg)


![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_3046 [6/11/2012 9:27:45 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_3046 [6/11/2012 9:27:45 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_3046_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_3050 [6/11/2012 9:30:07 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_3050 [6/11/2012 9:30:07 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_3050_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4460 [6/21/2012 10:05:33 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4460 [6/21/2012 10:05:33 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4460_resize.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4668 [7/3/2012 10:20:41 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4668 [7/3/2012 10:20:41 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4668_resize1.jpg)
![[Sherry Netherland] IMG_4791 [7/3/2012 11:34:29 AM] [Sherry Netherland] IMG_4791 [7/3/2012 11:34:29 AM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/sherry-netherland/IMG_4791_resize.jpg)

![[Morgan Library] IMG_2951 [10/1/2012 2:49:23 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2951 [10/1/2012 2:49:23 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2951_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3173 [10/5/2012 12:10:21 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3173 [10/5/2012 12:10:21 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3173_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3171 [10/5/2012 12:09:41 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3171 [10/5/2012 12:09:41 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3171_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3170 [10/5/2012 12:09:20 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3170 [10/5/2012 12:09:20 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3170_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3167 [10/5/2012 12:07:45 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3167 [10/5/2012 12:07:45 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3167_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3162 [10/5/2012 12:04:46 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3162 [10/5/2012 12:04:46 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3162_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3159 [10/5/2012 12:02:27 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3159 [10/5/2012 12:02:27 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3159_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3158 [10/5/2012 12:02:04 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3158 [10/5/2012 12:02:04 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3158_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_3157 [10/5/2012 12:01:36 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_3157 [10/5/2012 12:01:36 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_3157_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2960 [10/1/2012 2:52:36 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2960 [10/1/2012 2:52:36 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2960_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2959 [10/1/2012 2:51:59 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2959 [10/1/2012 2:51:59 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2959_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2955 [10/1/2012 2:50:45 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2955 [10/1/2012 2:50:45 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2955_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2954 [10/1/2012 2:50:18 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2954 [10/1/2012 2:50:18 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2954_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2859 [10/1/2012 2:07:10 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2859 [10/1/2012 2:07:10 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2859_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2949 [10/1/2012 2:47:05 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2949 [10/1/2012 2:47:05 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2949_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2946 [10/1/2012 2:46:13 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2946 [10/1/2012 2:46:13 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2946_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2939 [10/1/2012 2:44:39 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2939 [10/1/2012 2:44:39 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2939_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2938 [10/1/2012 2:44:11 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2938 [10/1/2012 2:44:11 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2938_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2936 [10/1/2012 2:43:45 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2936 [10/1/2012 2:43:45 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2936_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2934 [10/1/2012 2:43:16 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2934 [10/1/2012 2:43:16 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2934_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2929 [10/1/2012 2:41:23 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2929 [10/1/2012 2:41:23 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2929_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2928 [10/1/2012 2:41:05 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2928 [10/1/2012 2:41:05 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2928_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2878 [10/1/2012 2:18:24 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2878 [10/1/2012 2:18:24 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2878_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2876 [10/1/2012 2:17:38 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2876 [10/1/2012 2:17:38 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2876_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2874 [10/1/2012 2:16:57 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2874 [10/1/2012 2:16:57 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2874_resize.jpg)
![[Morgan Library] IMG_2860 [10/1/2012 2:07:54 PM] [Morgan Library] IMG_2860 [10/1/2012 2:07:54 PM]](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/morgan-library/IMG_2860_resize.jpg)
You must be logged in to post a comment.