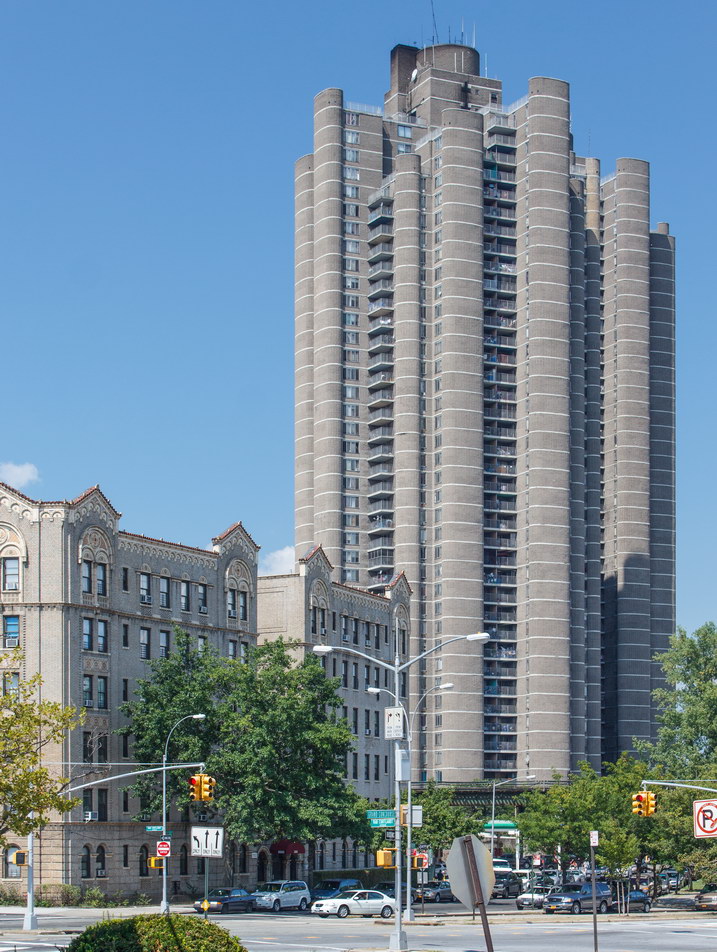
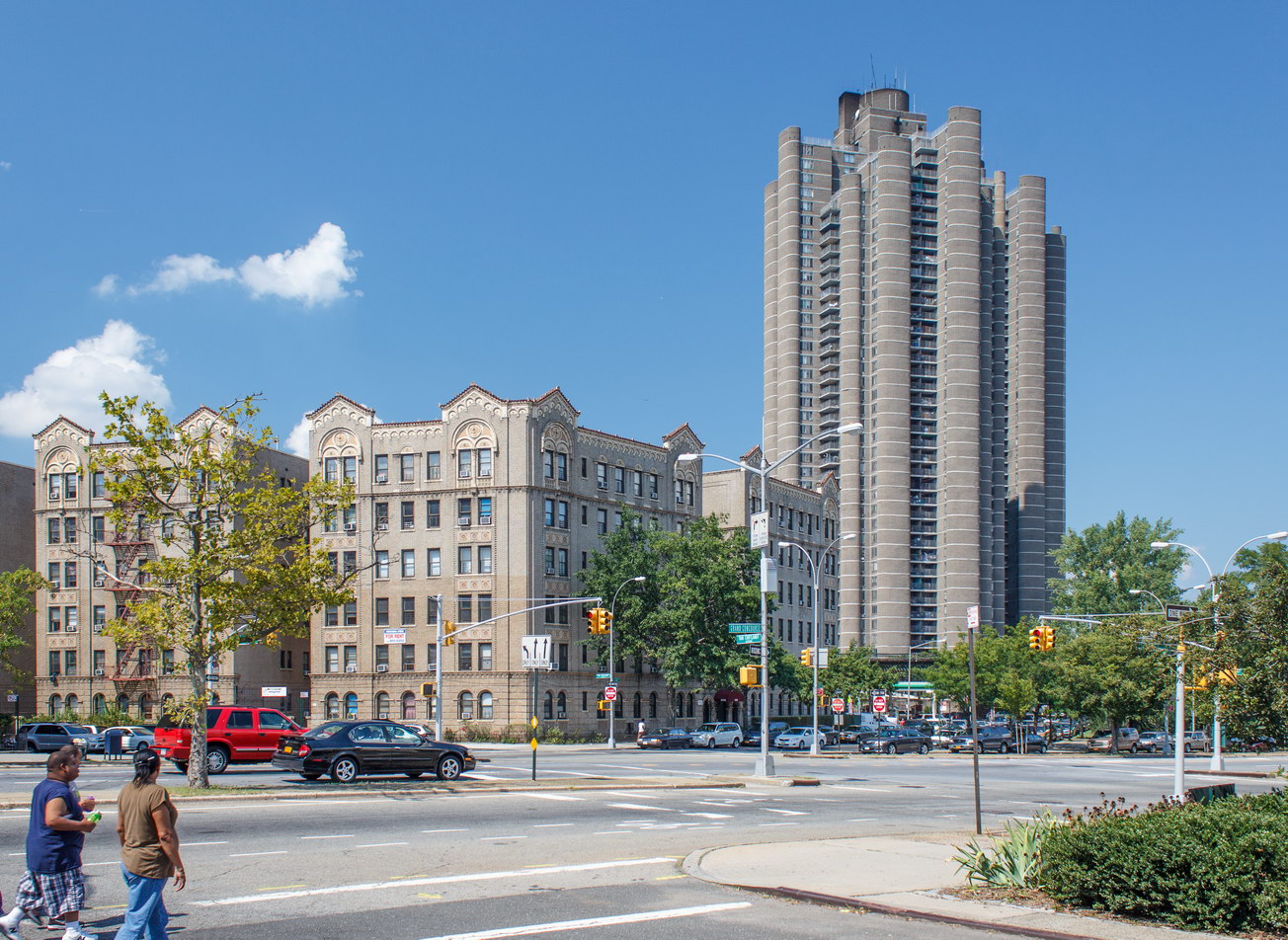
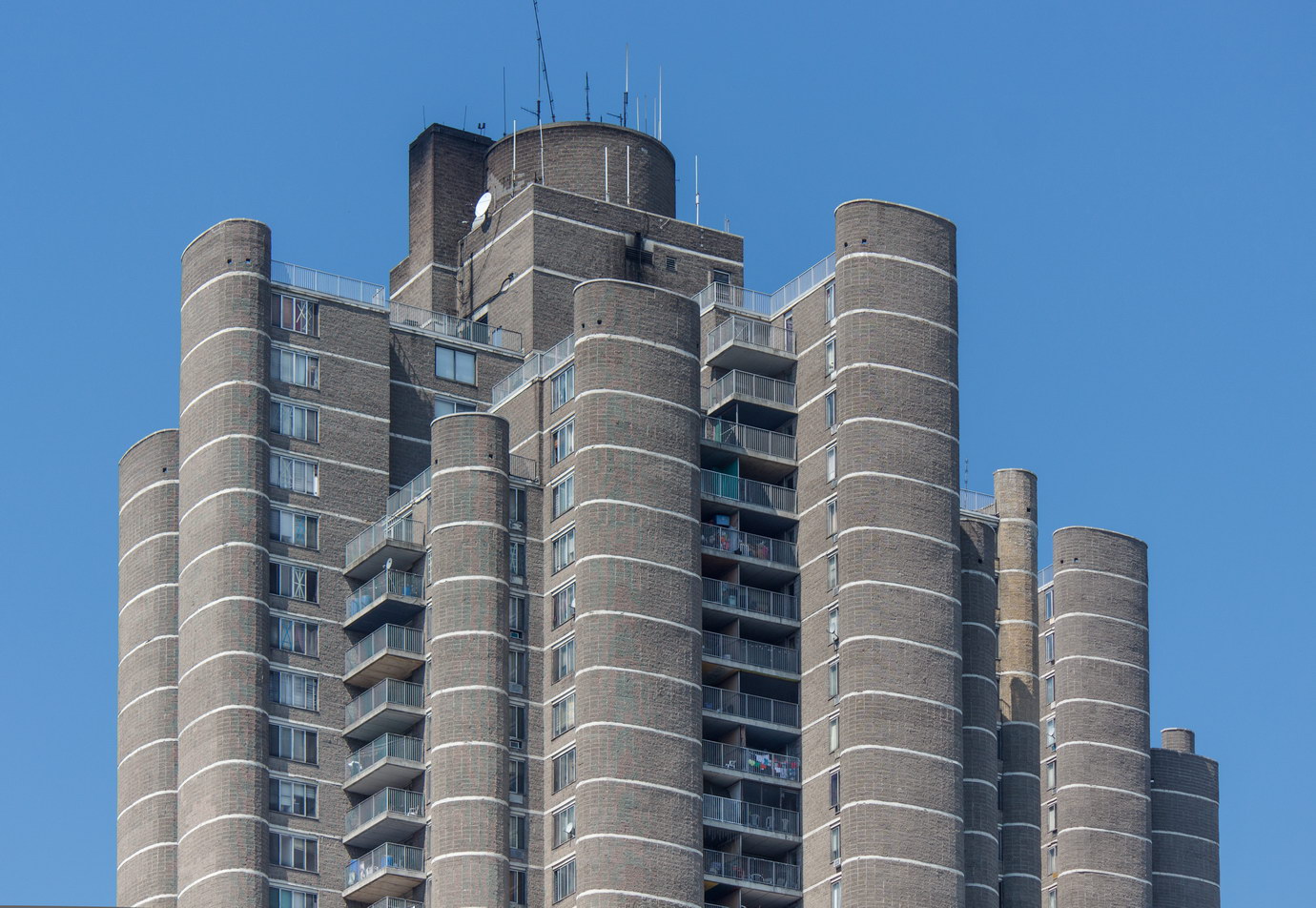
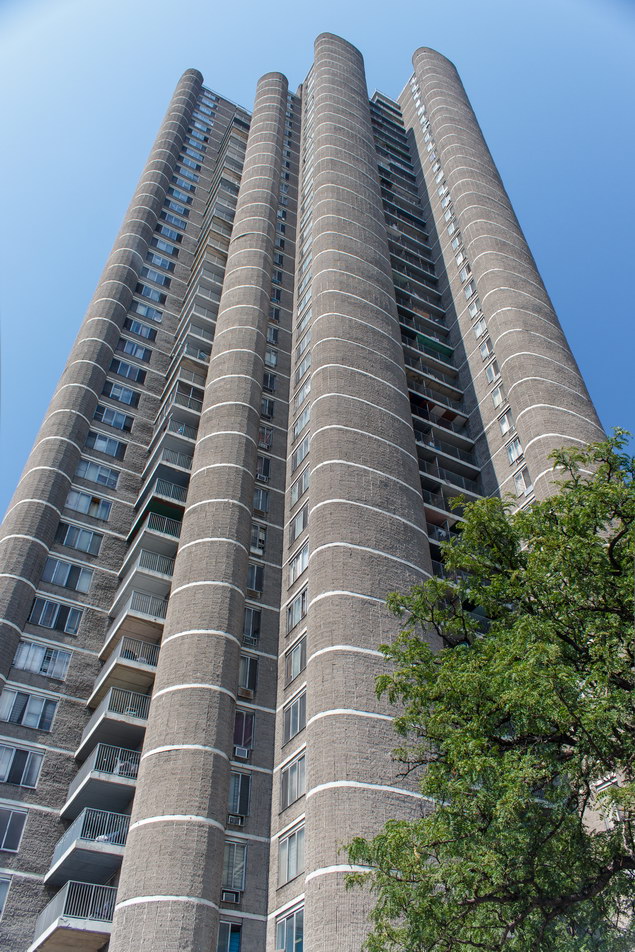
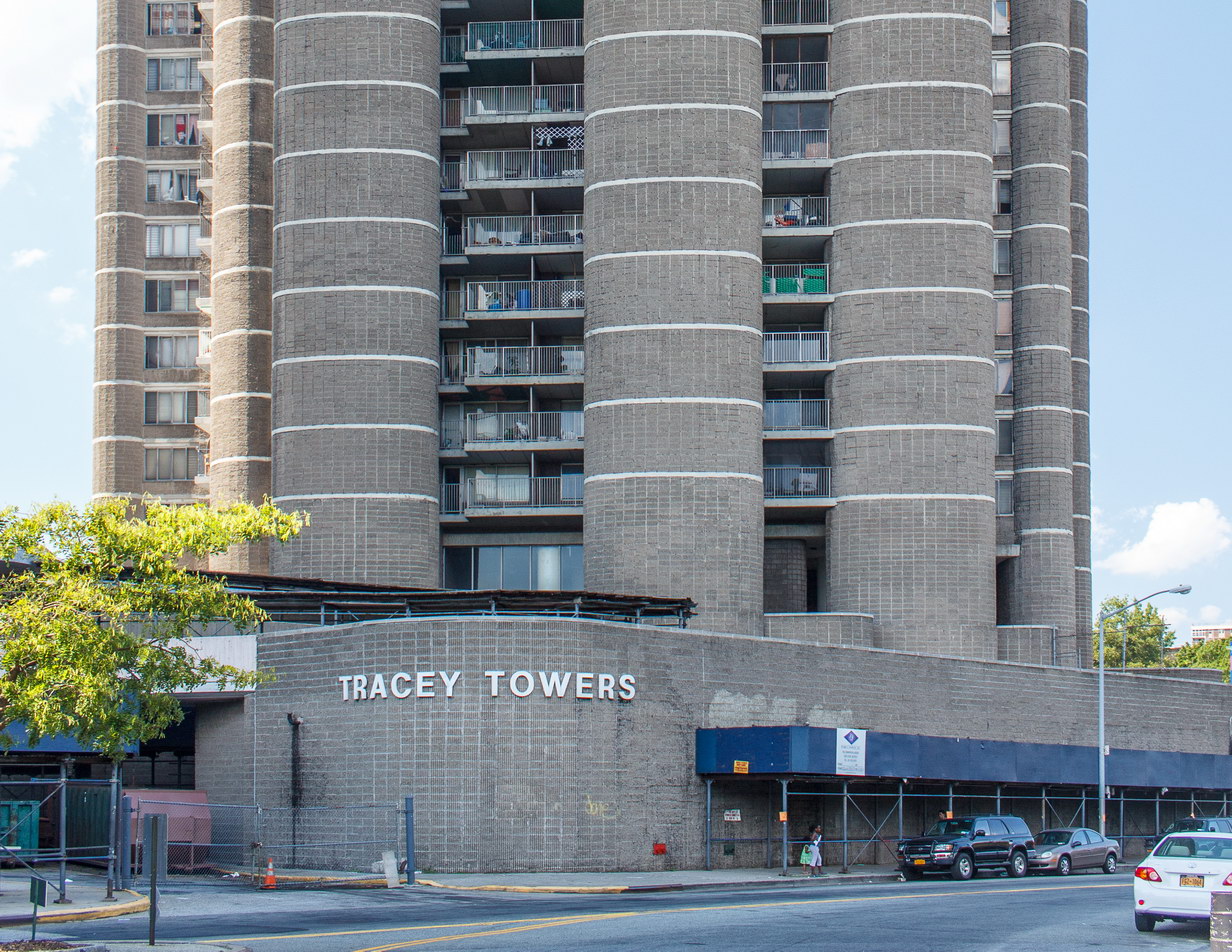
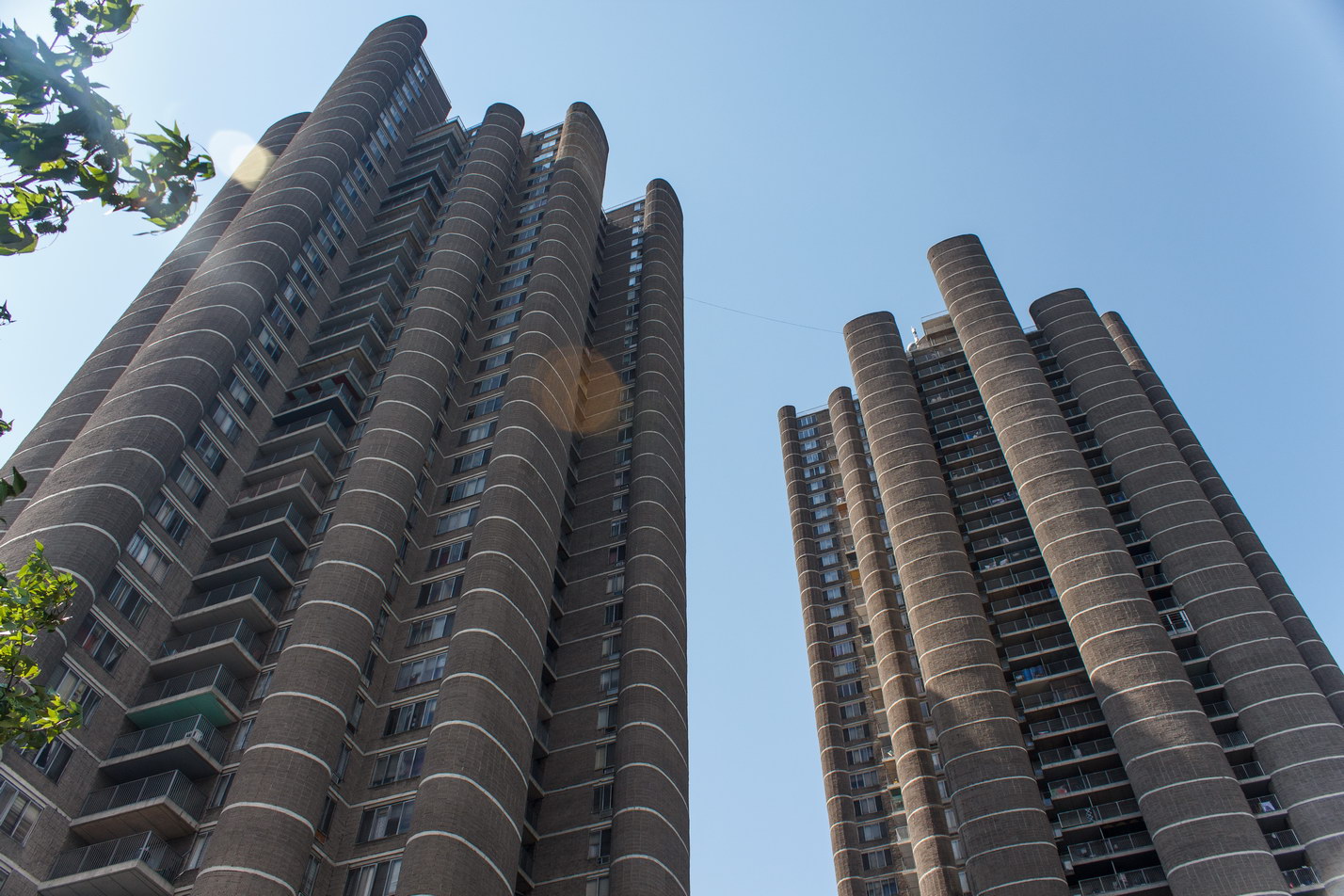
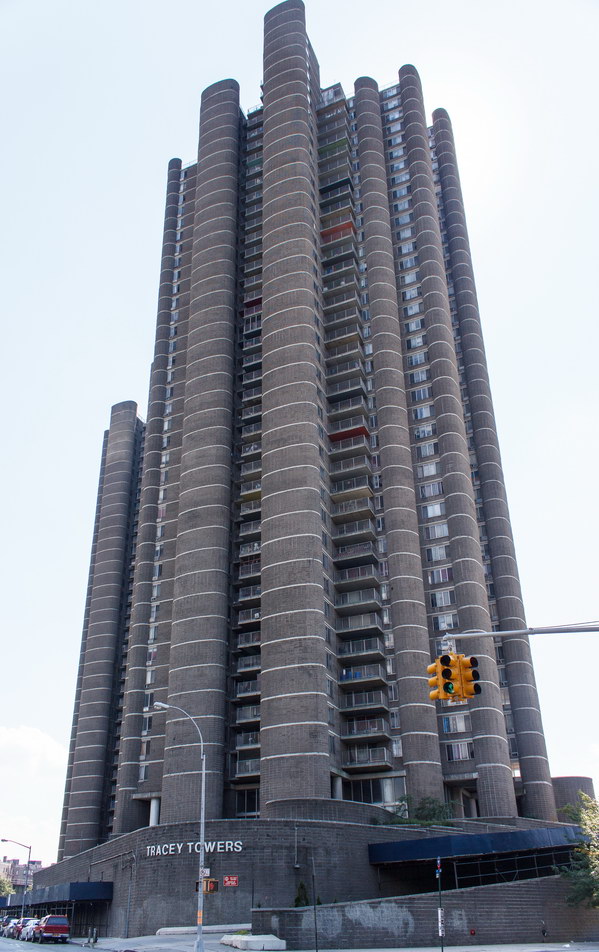
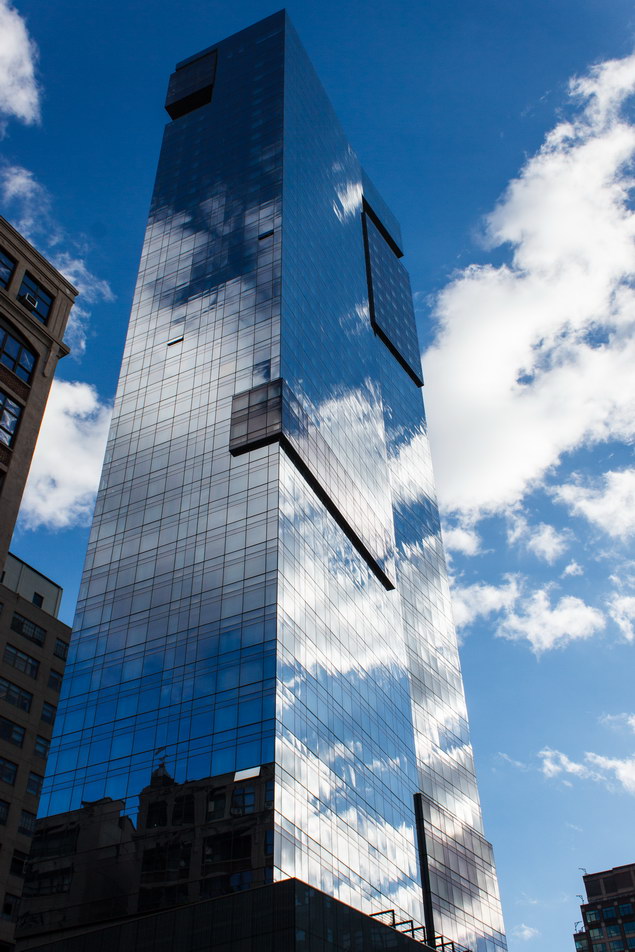
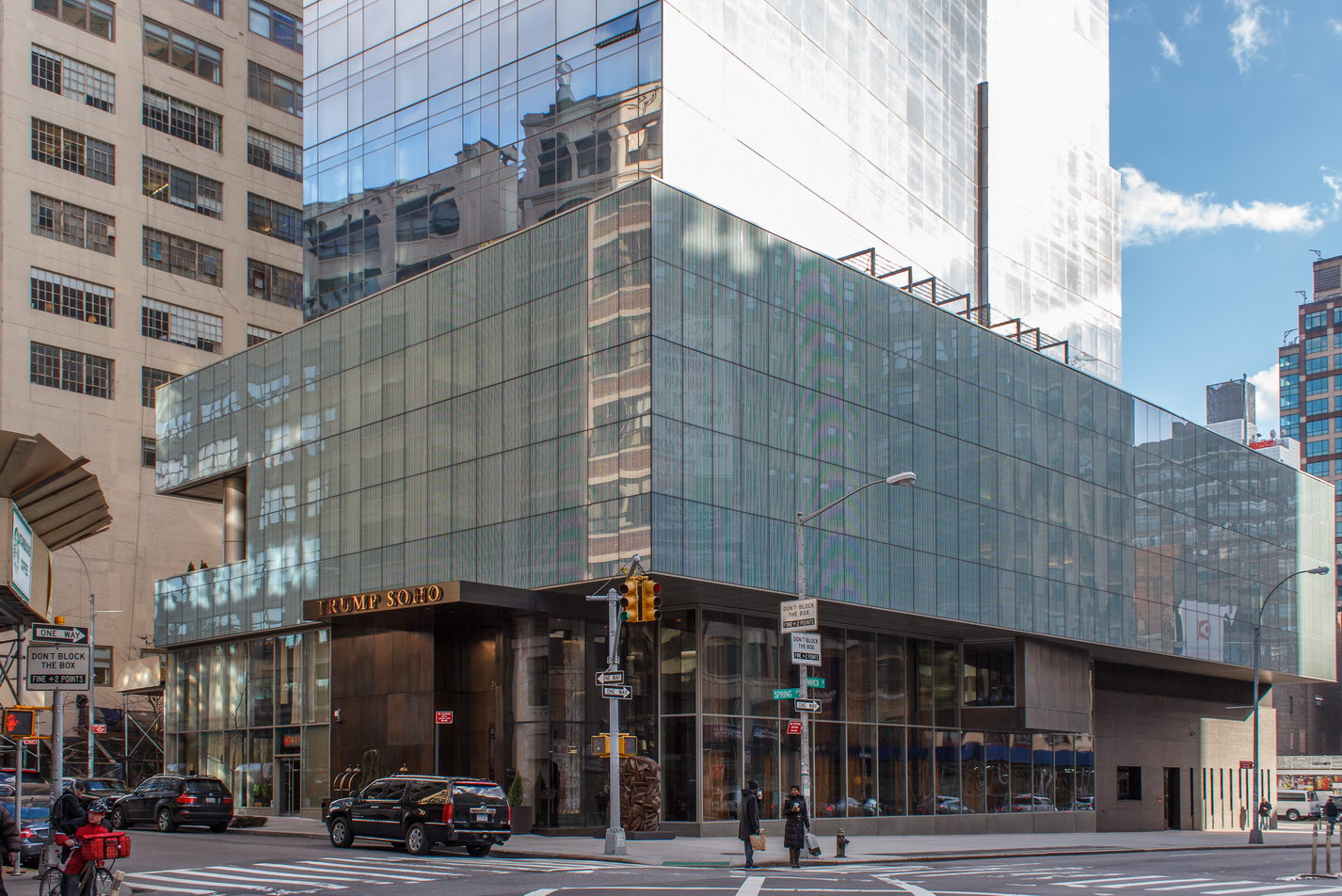
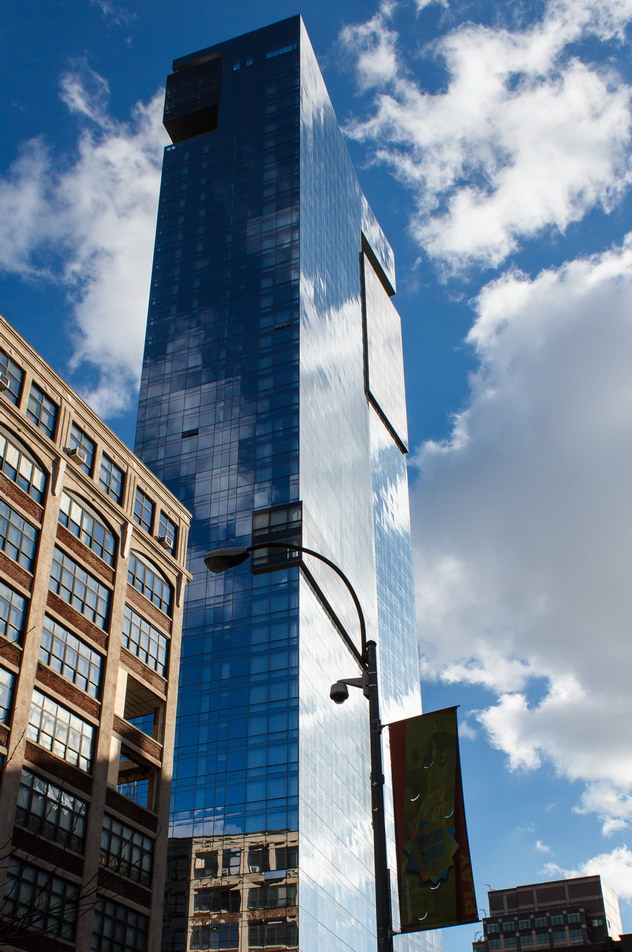
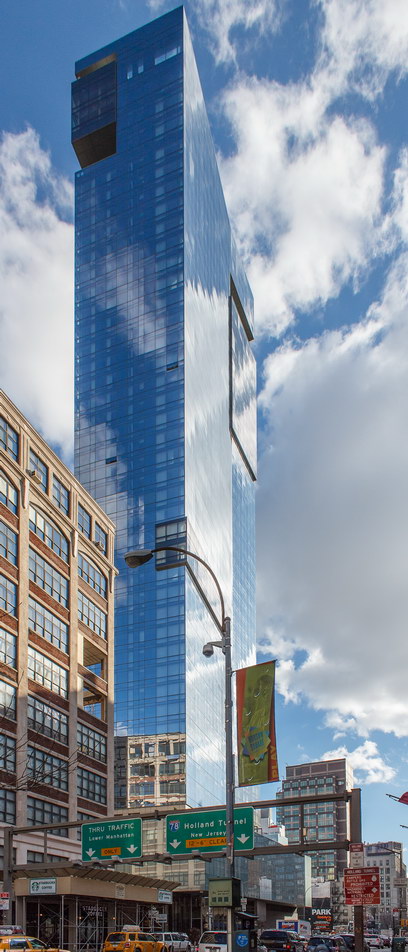
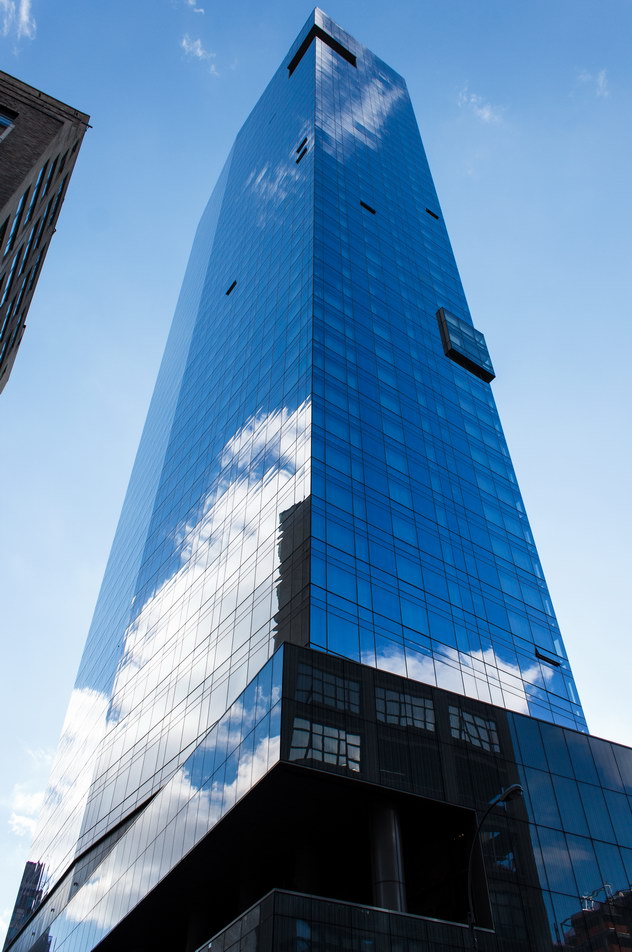
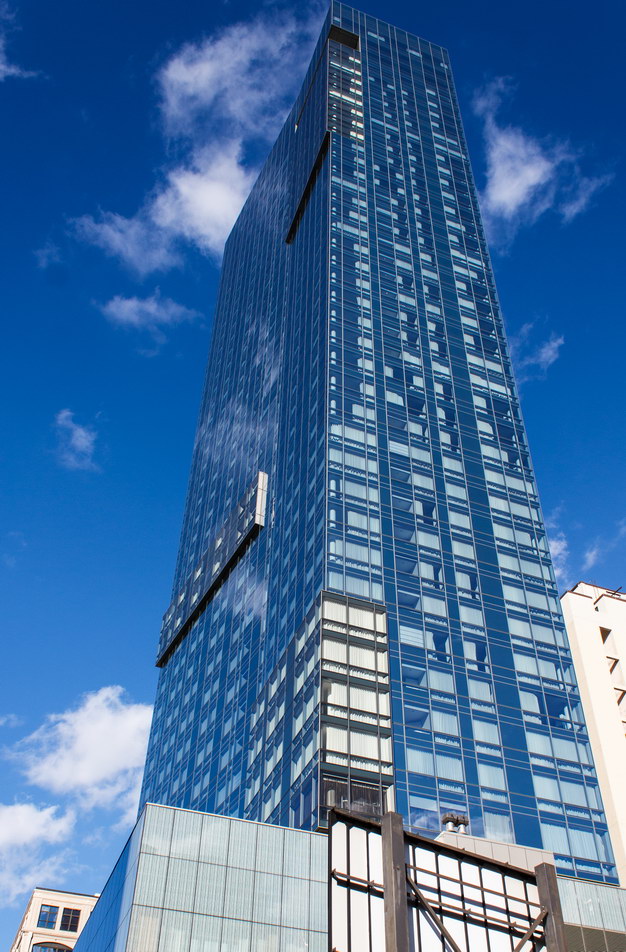
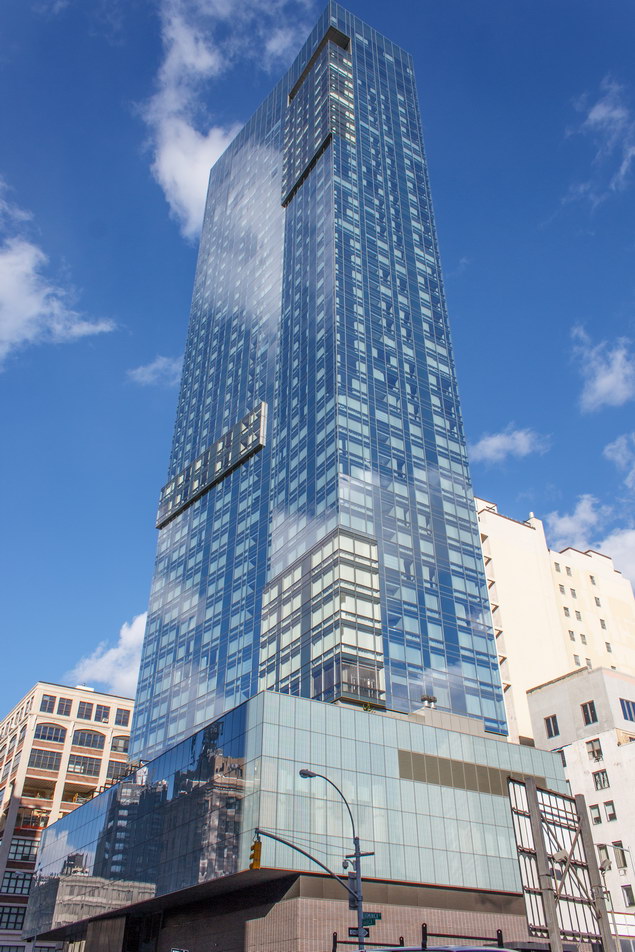
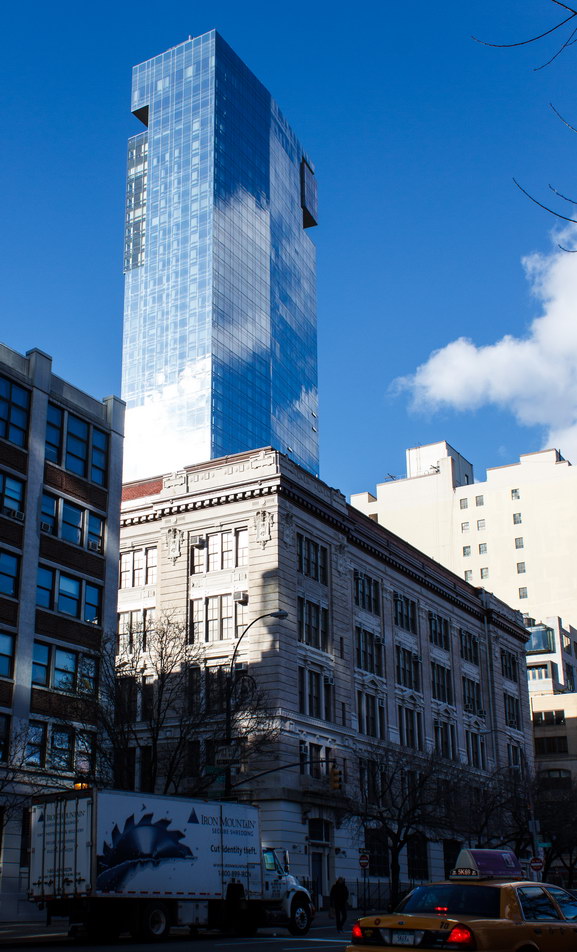
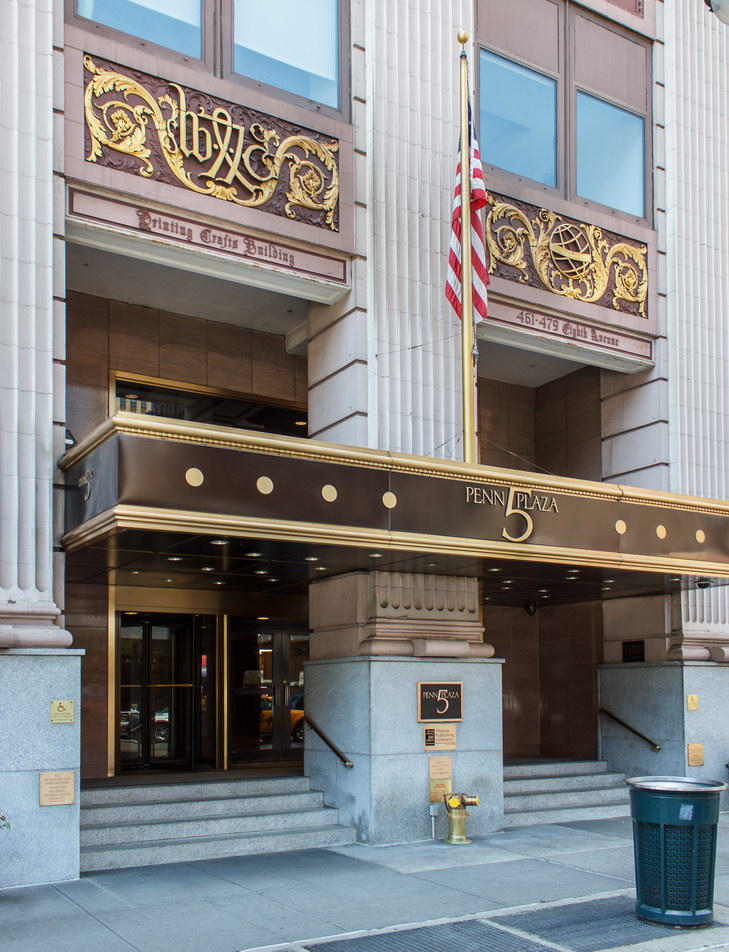
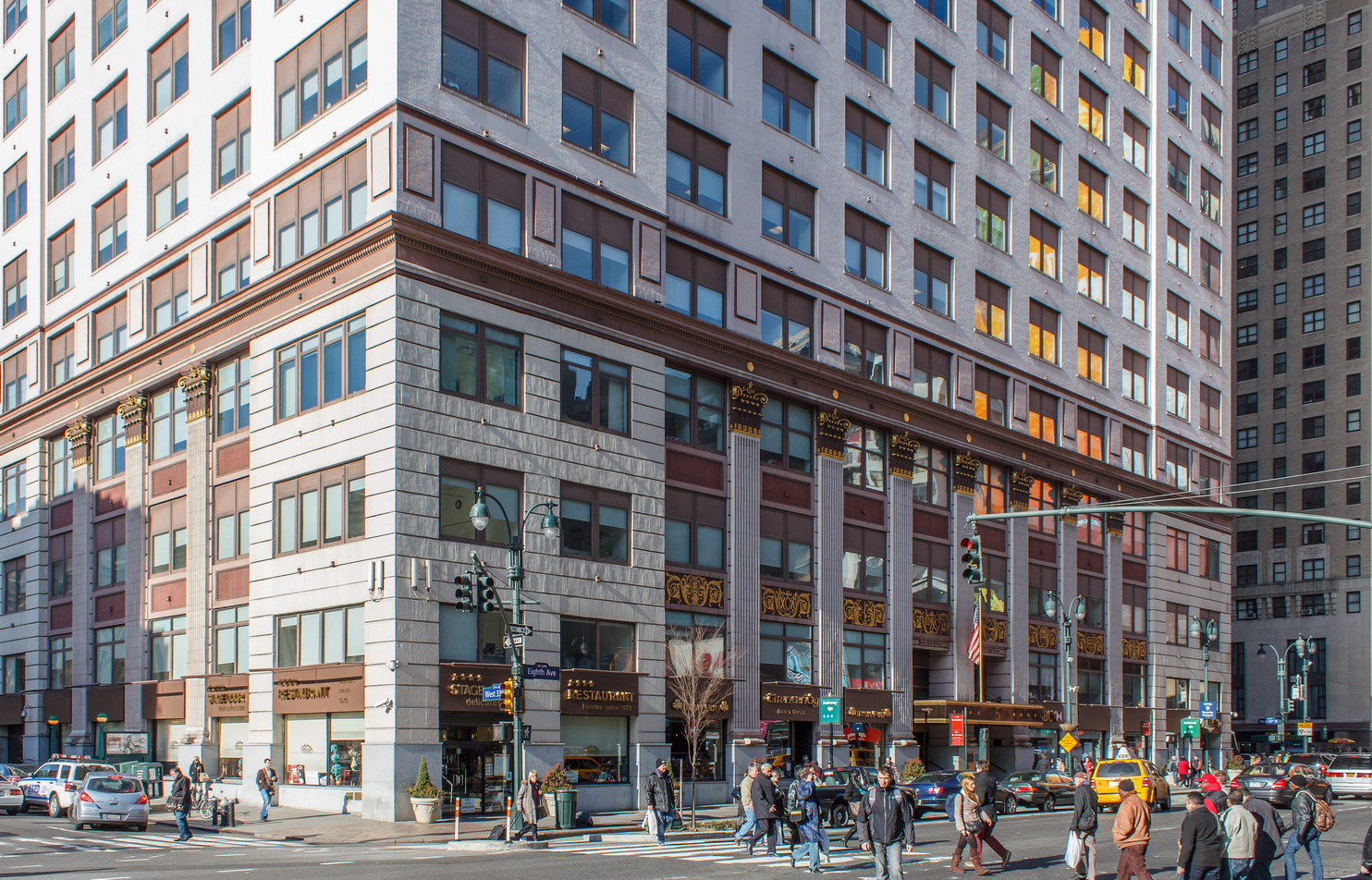
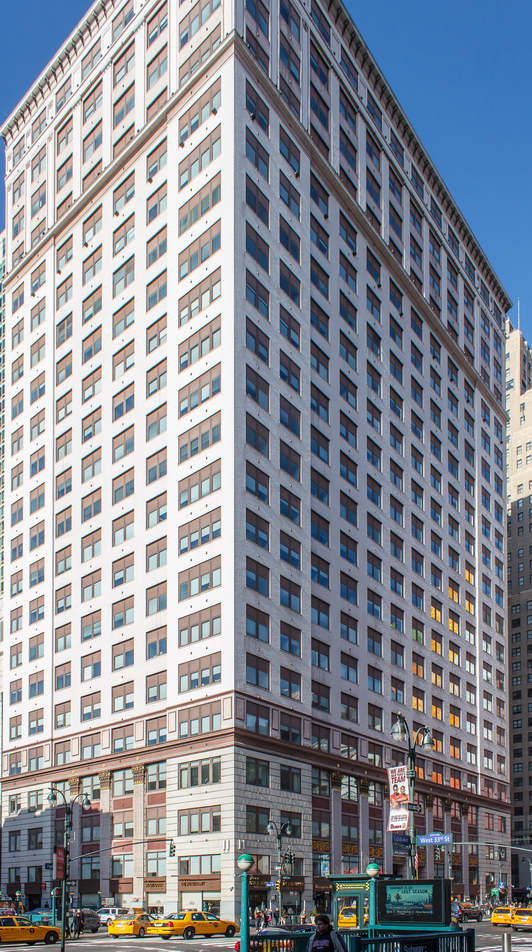
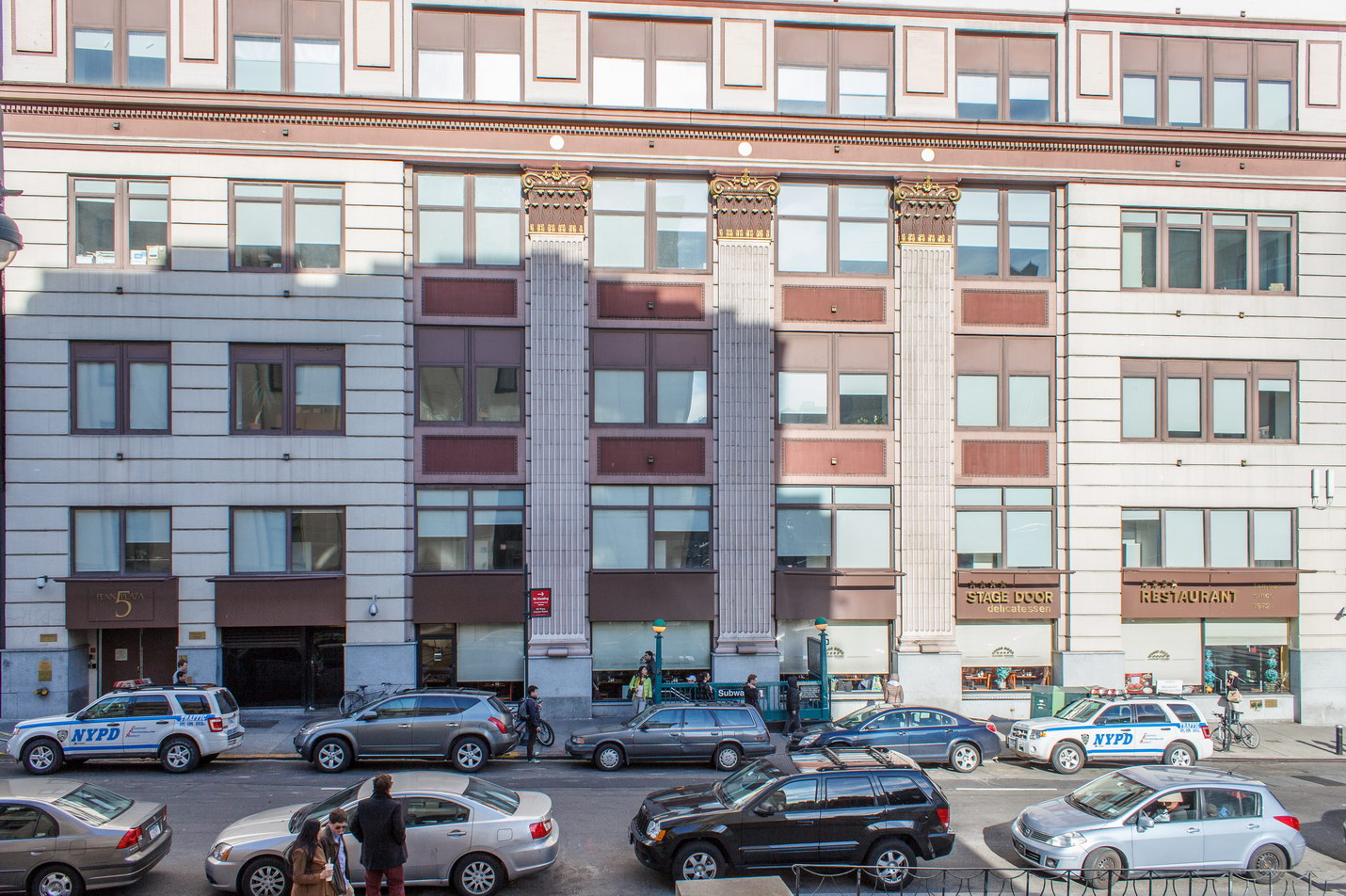
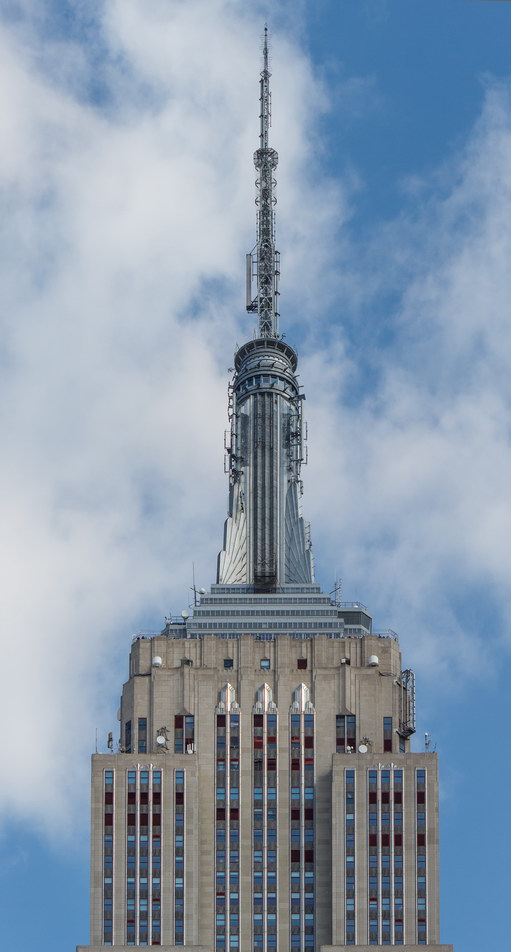
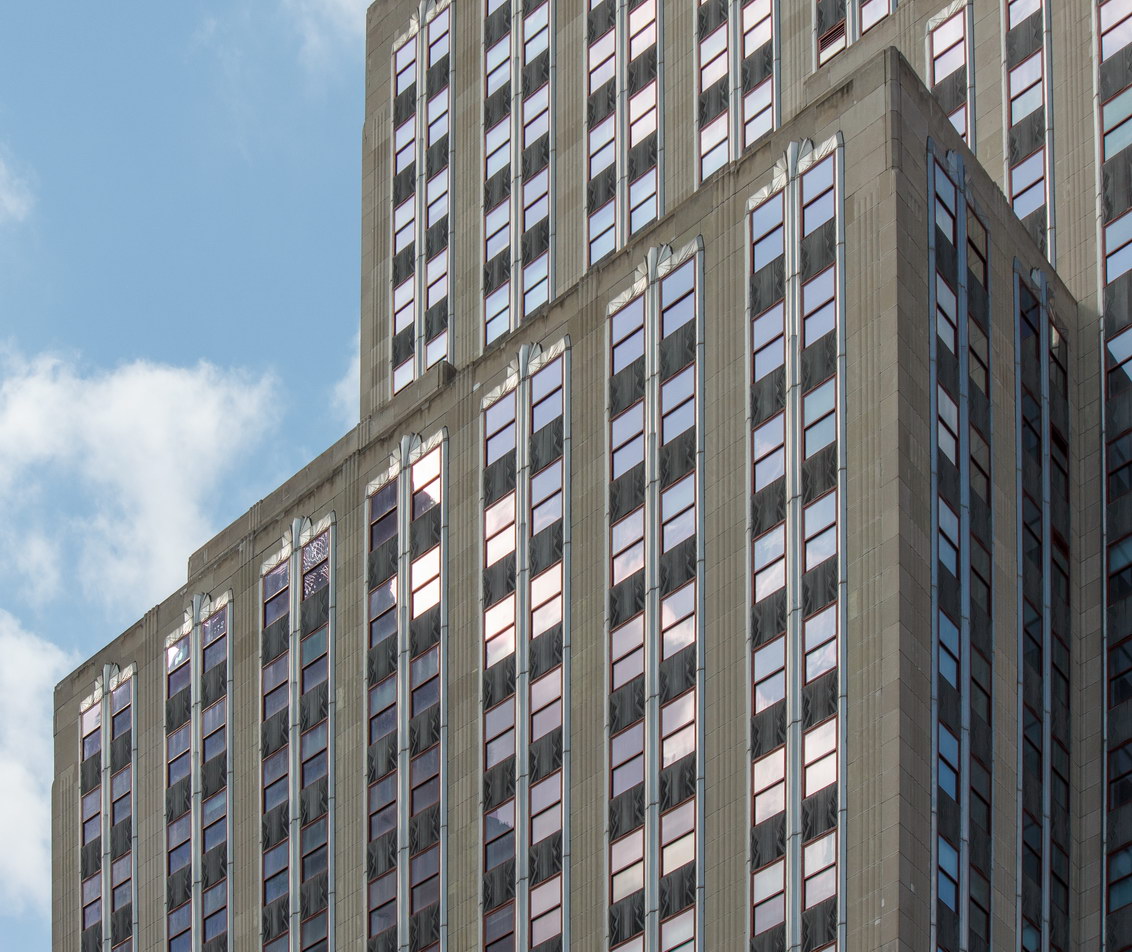
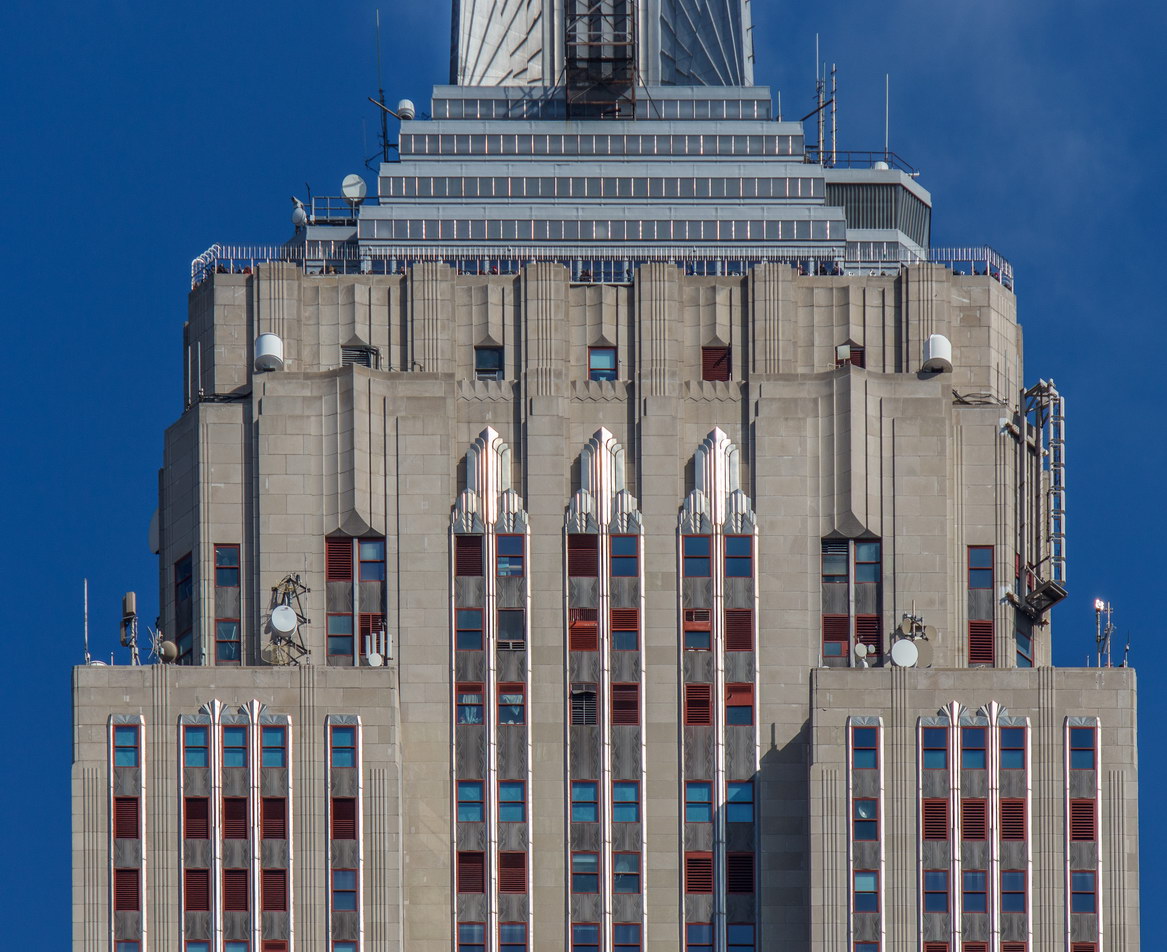
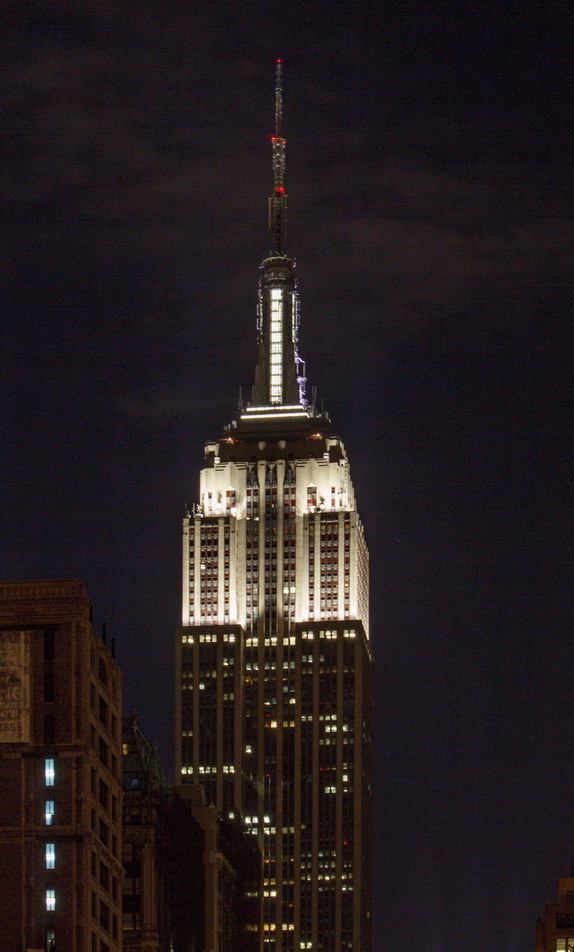
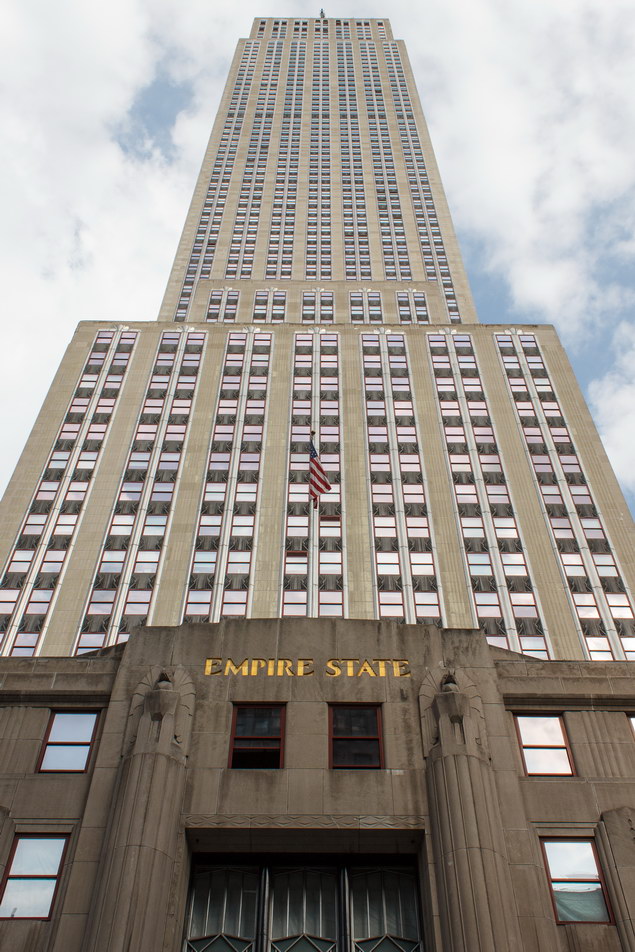
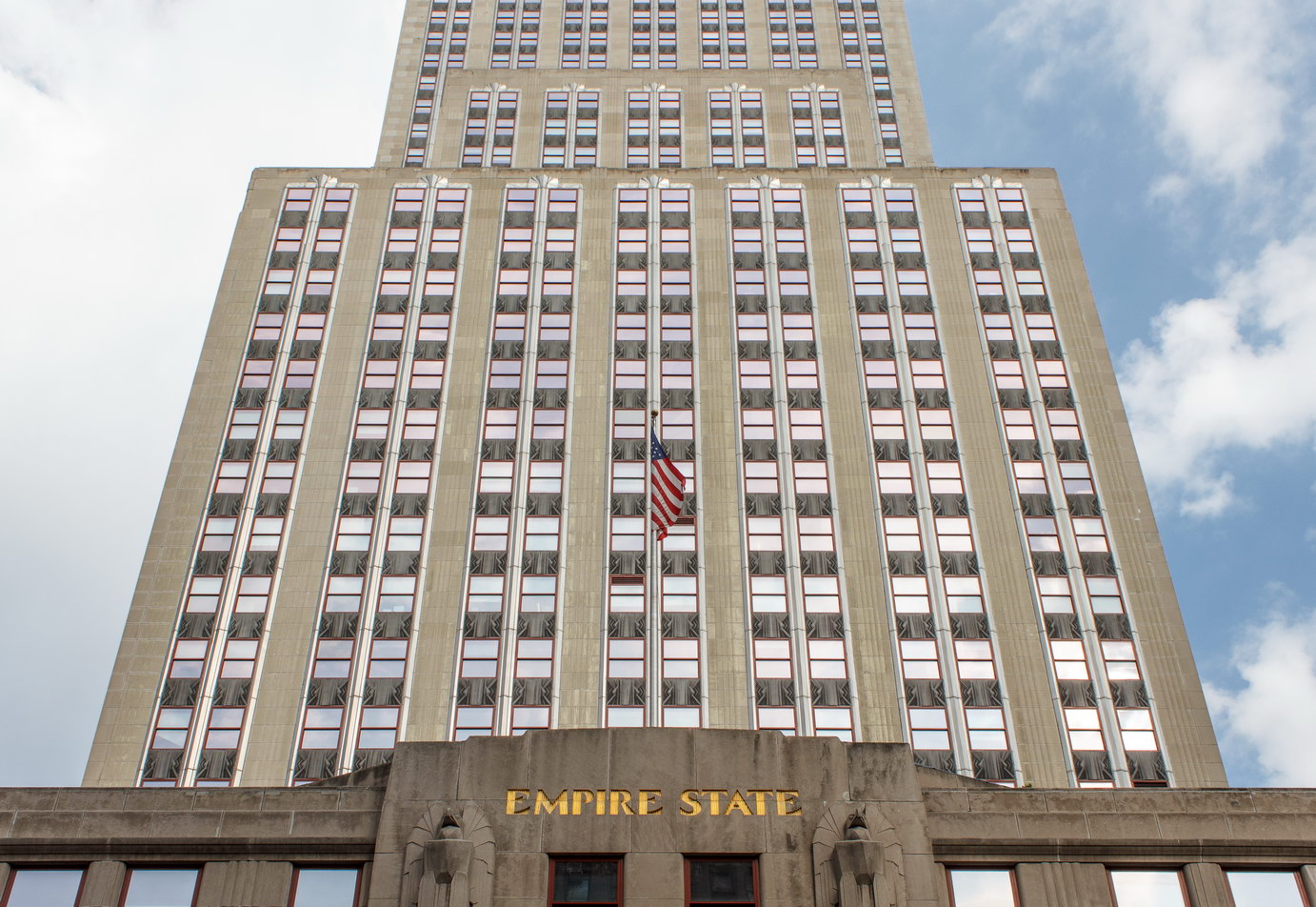
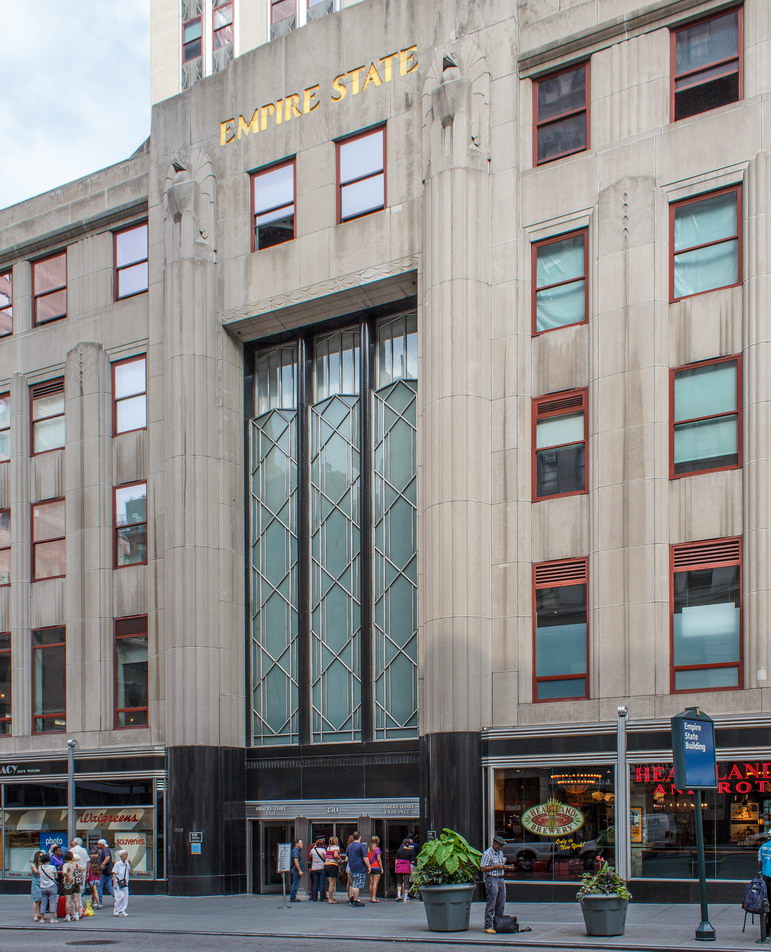
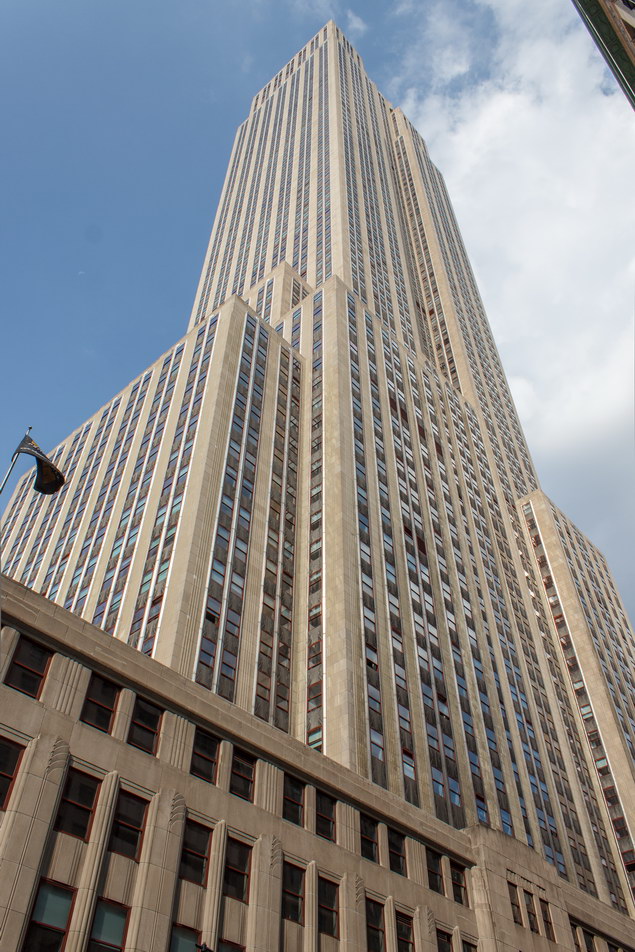
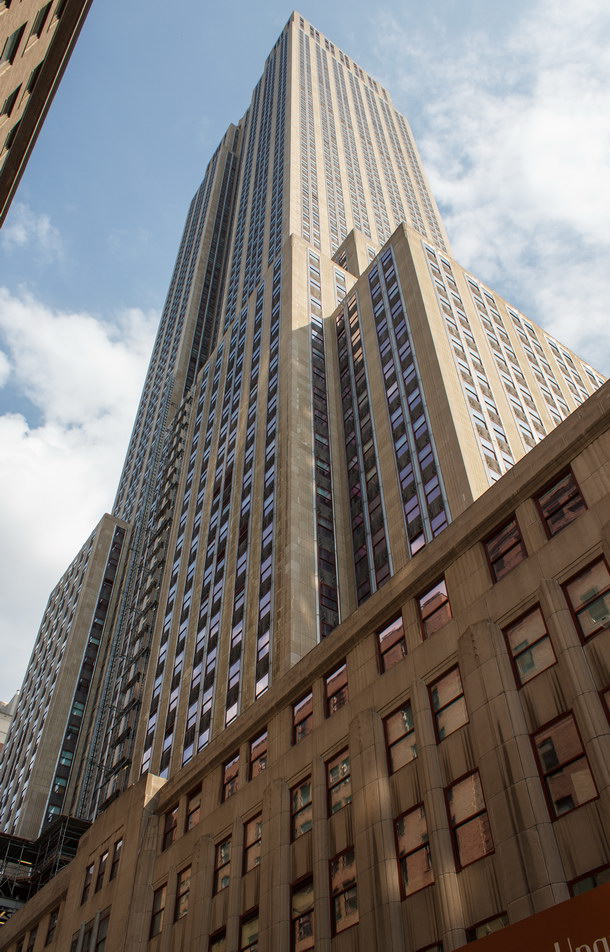
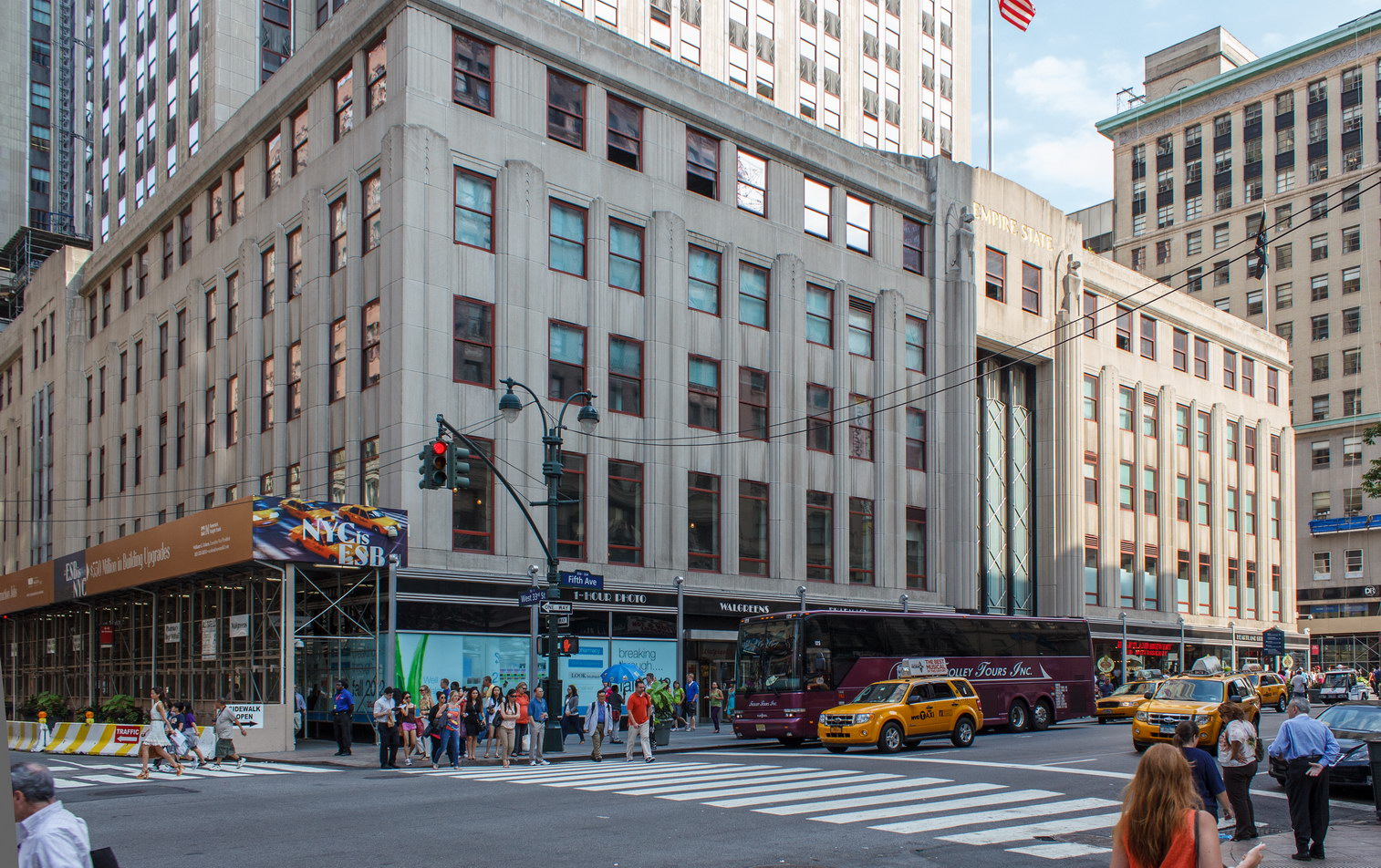
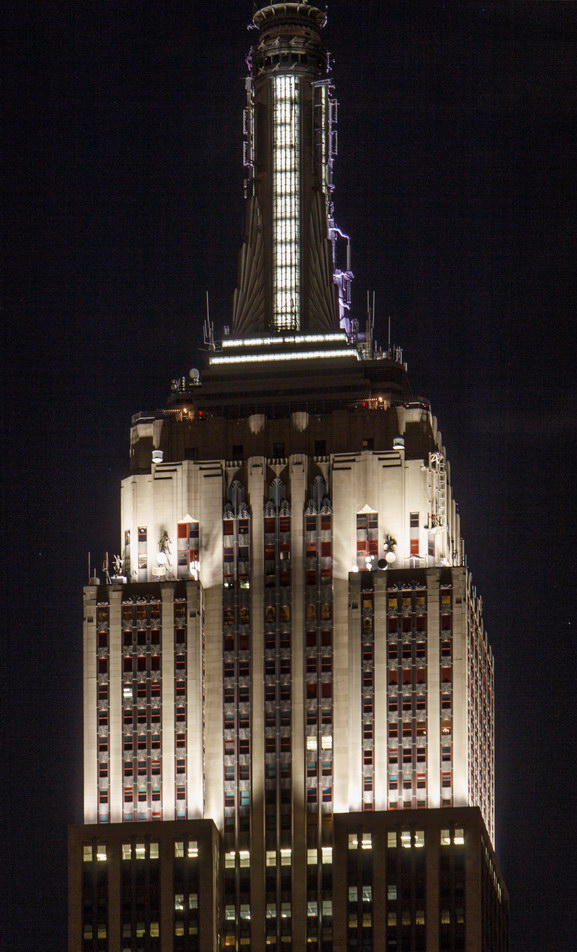
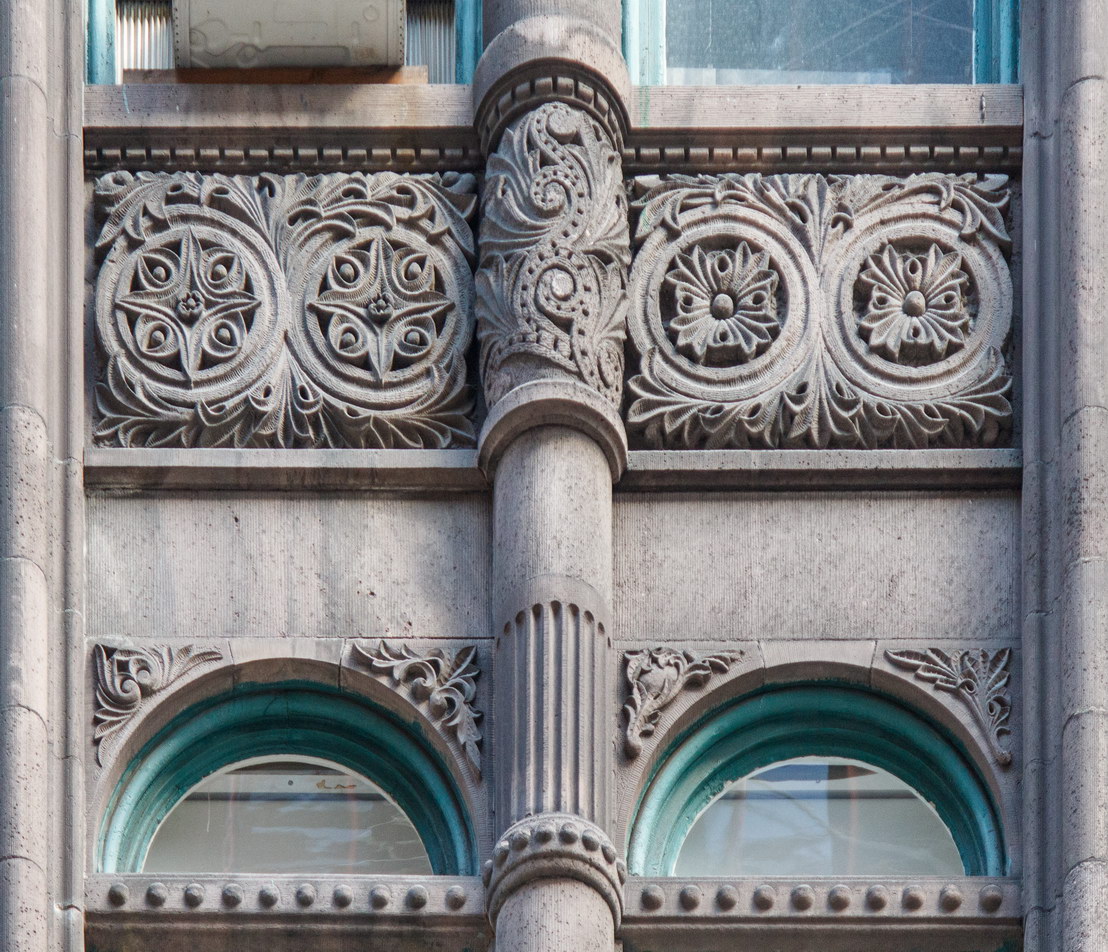
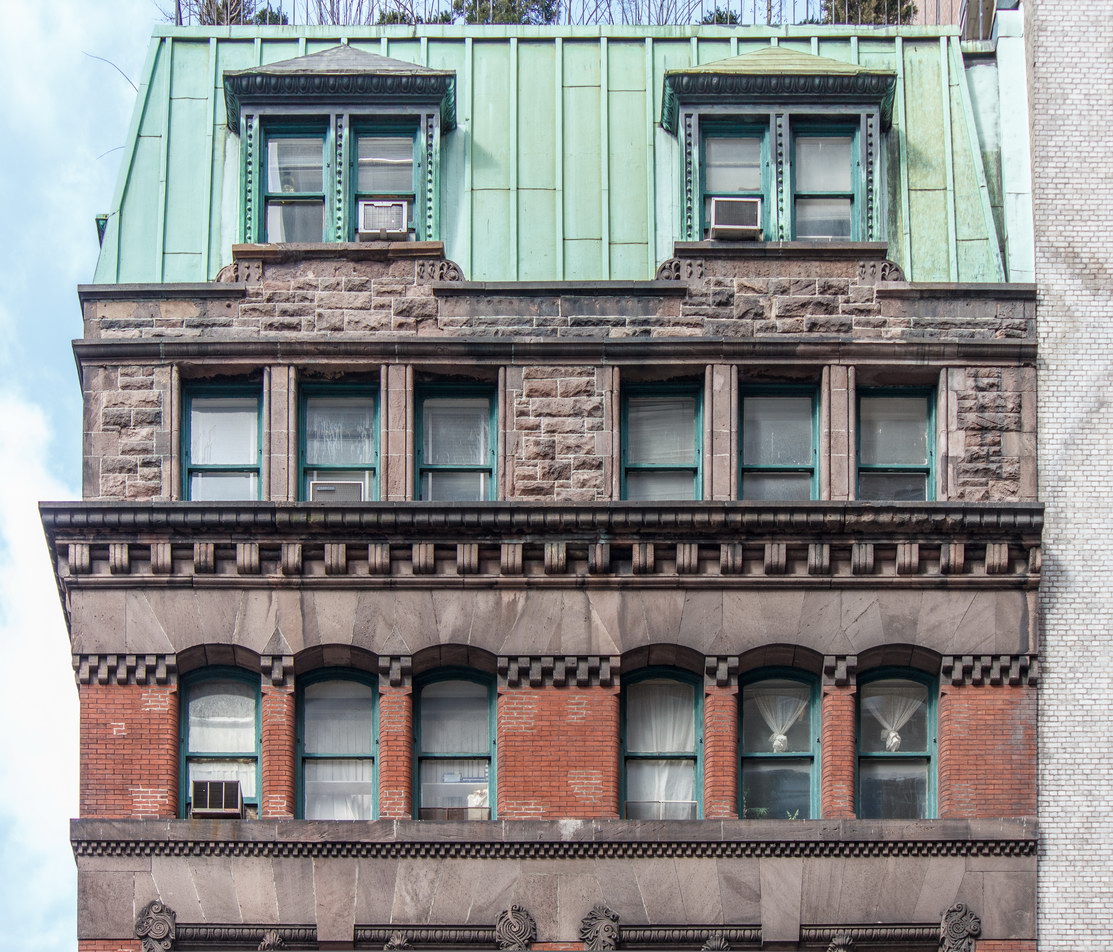
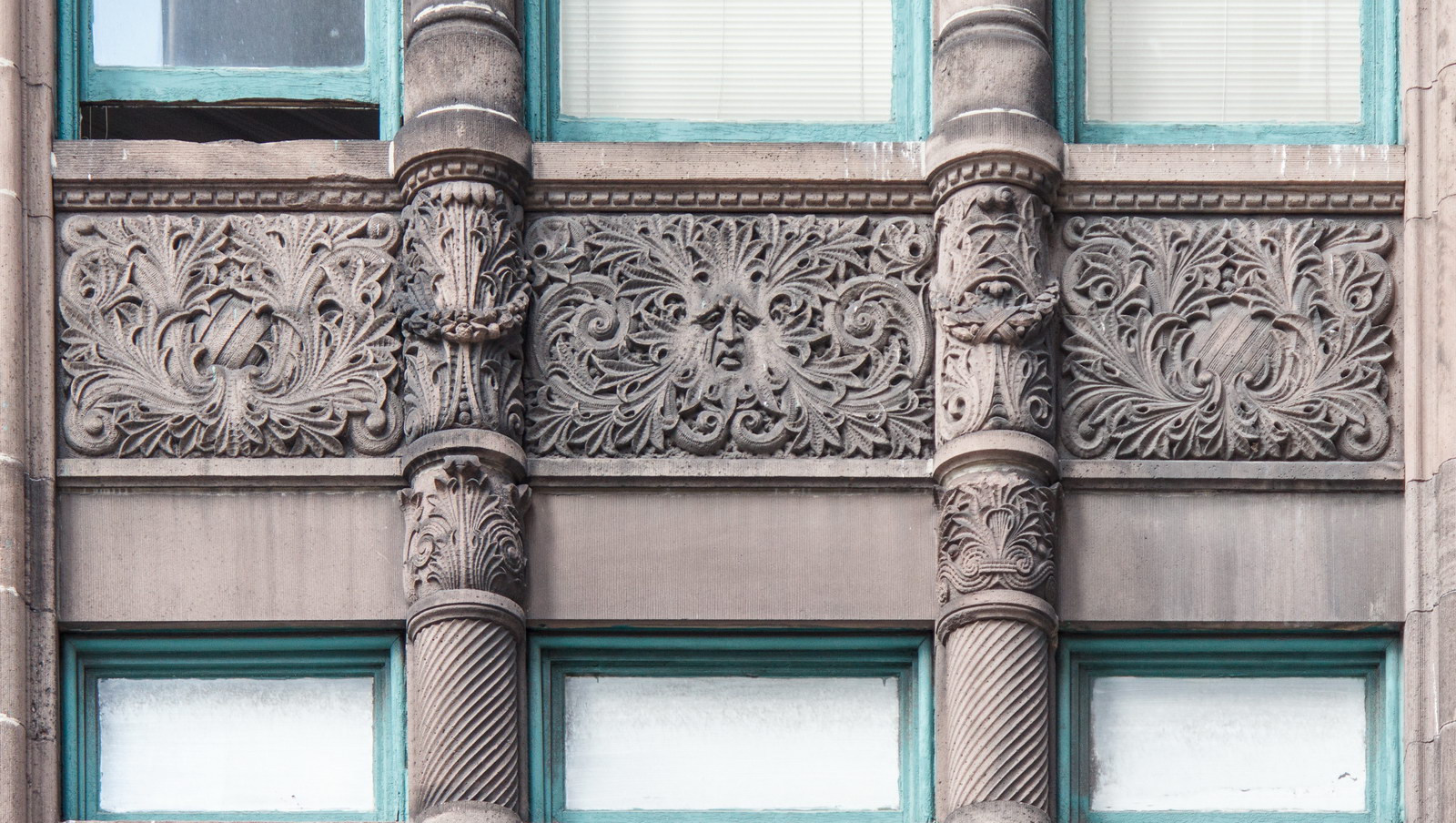
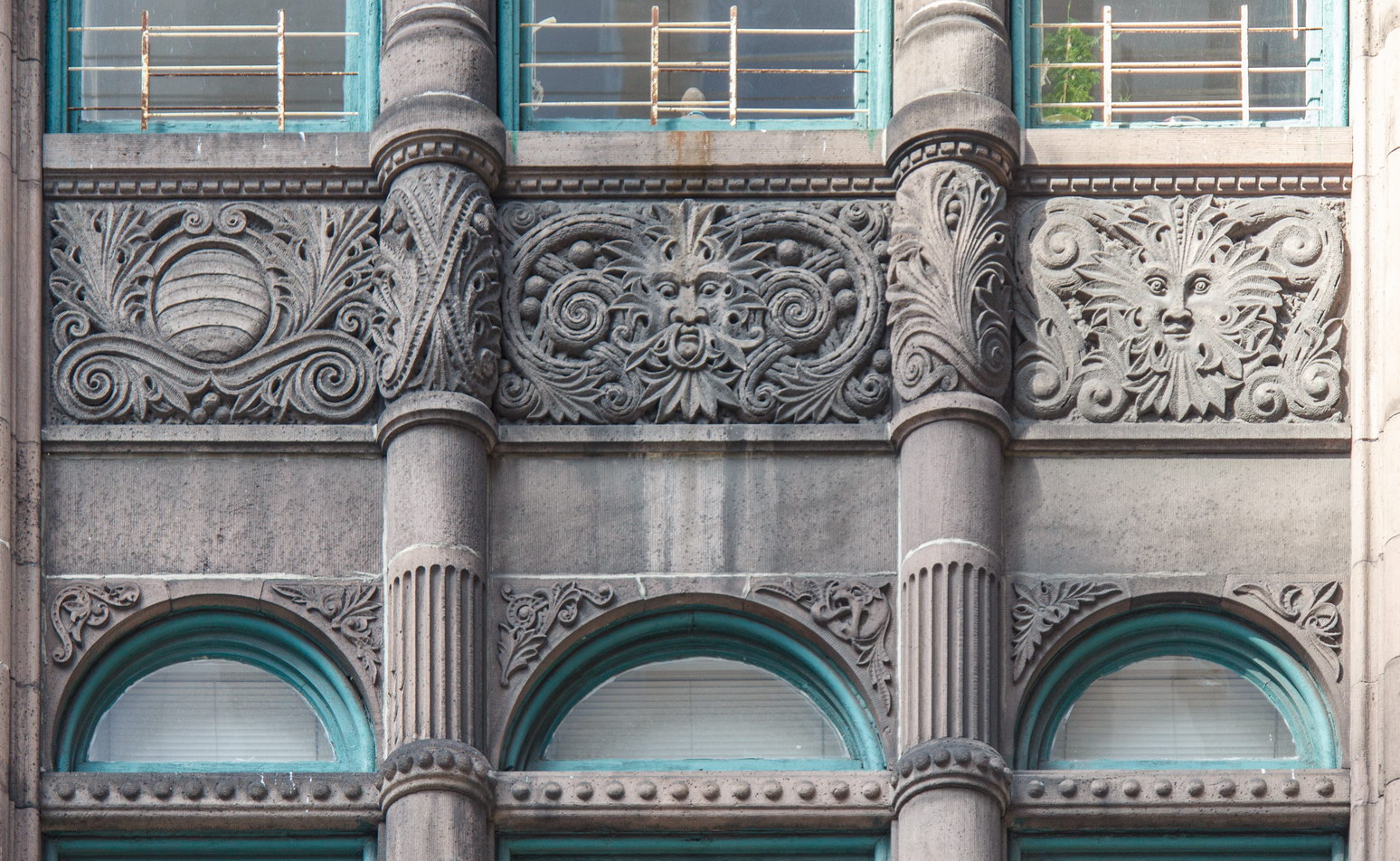
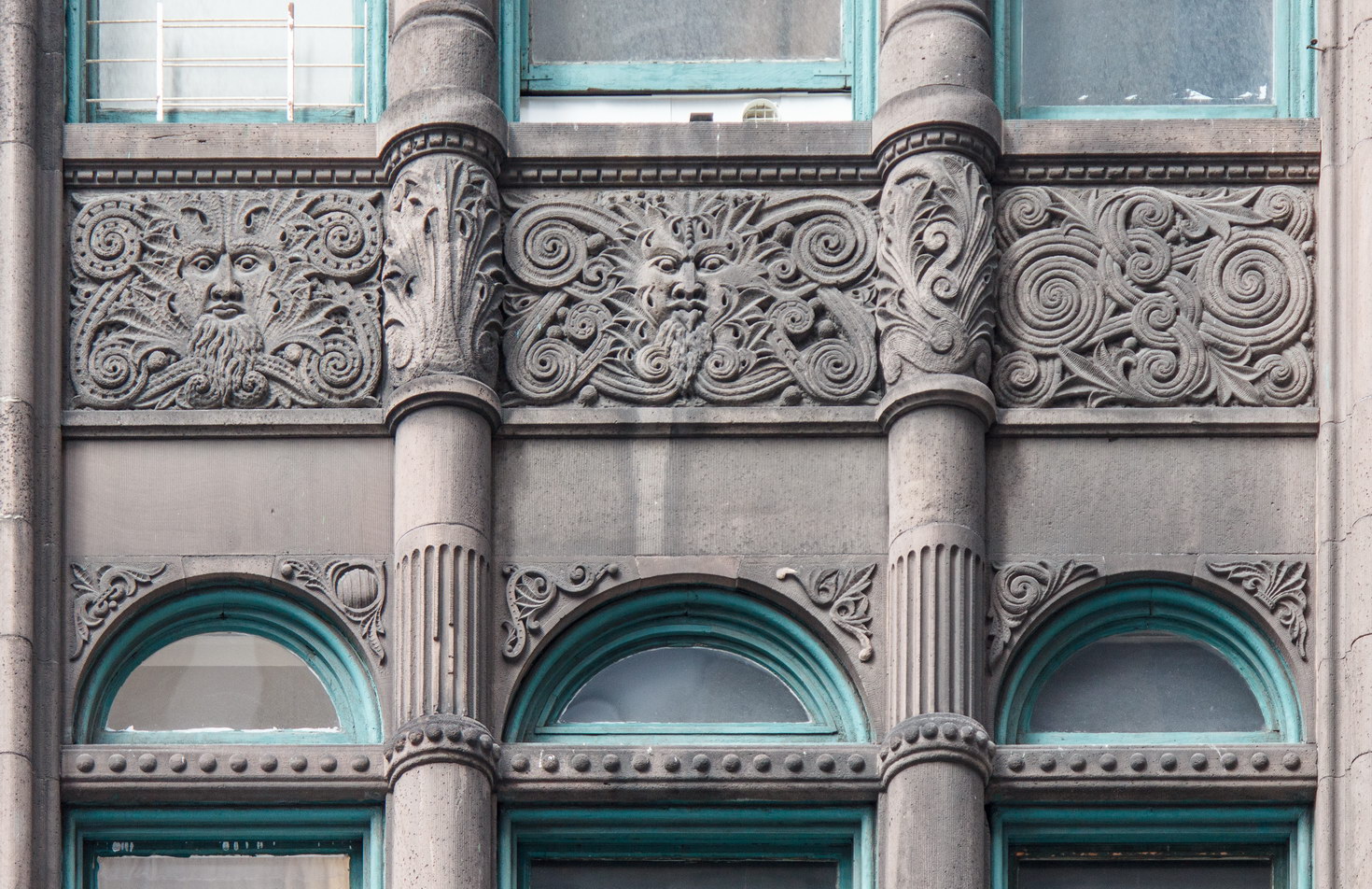
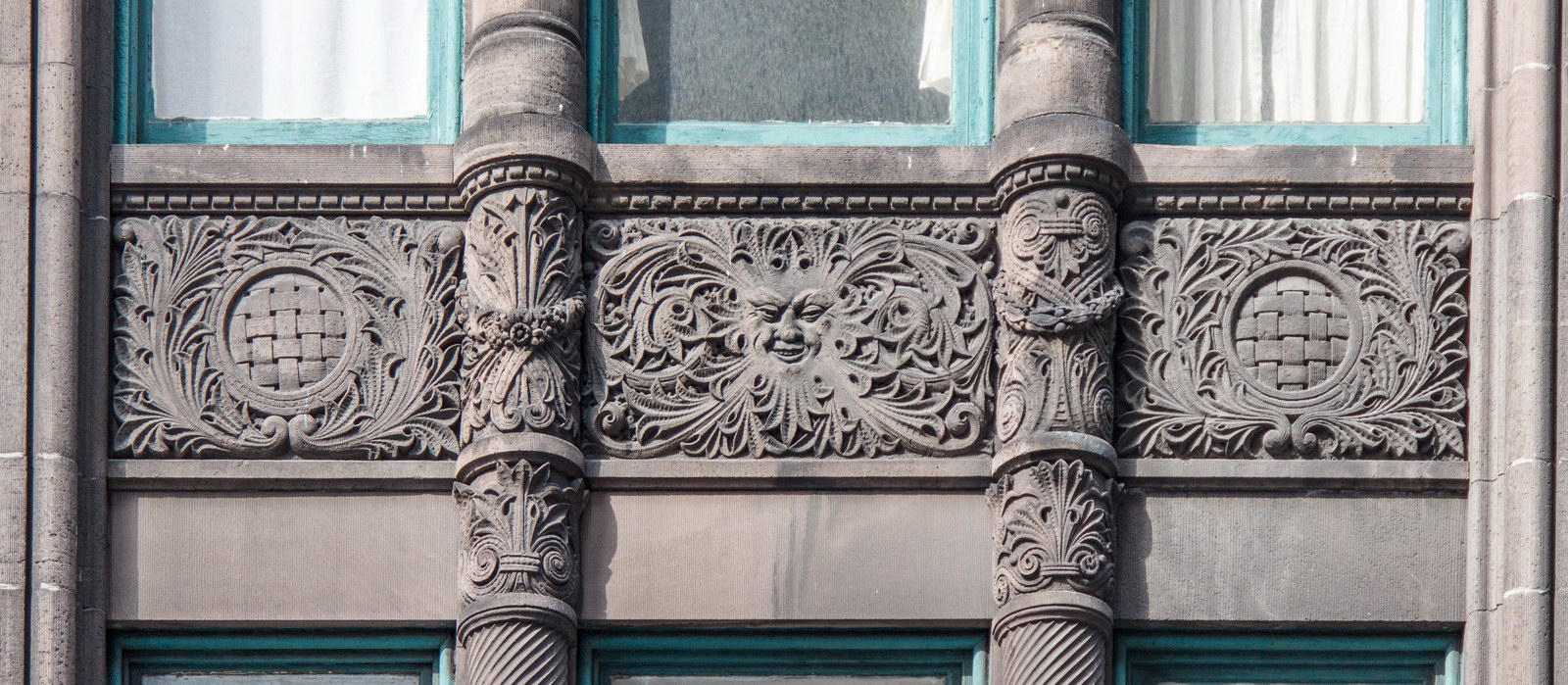
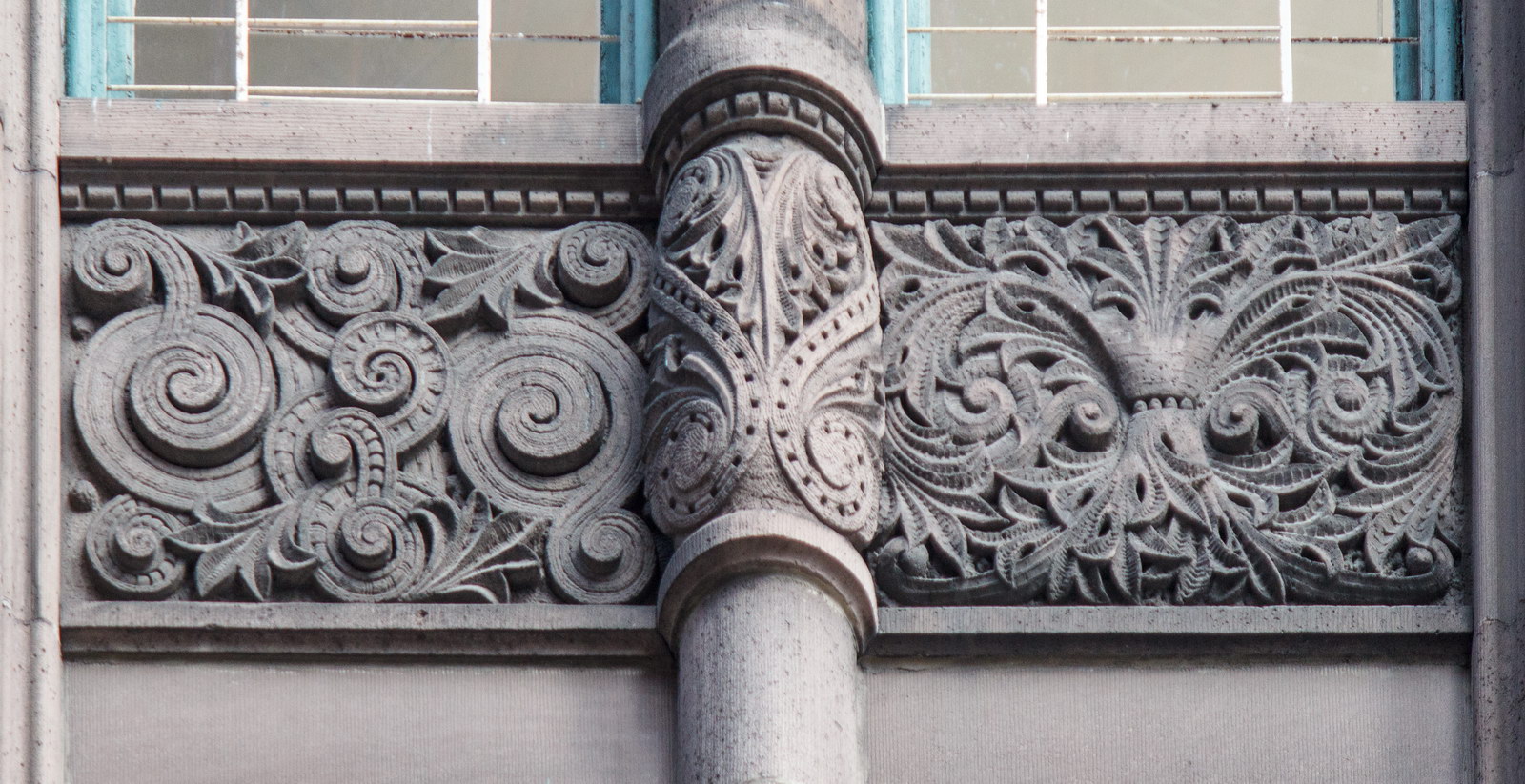
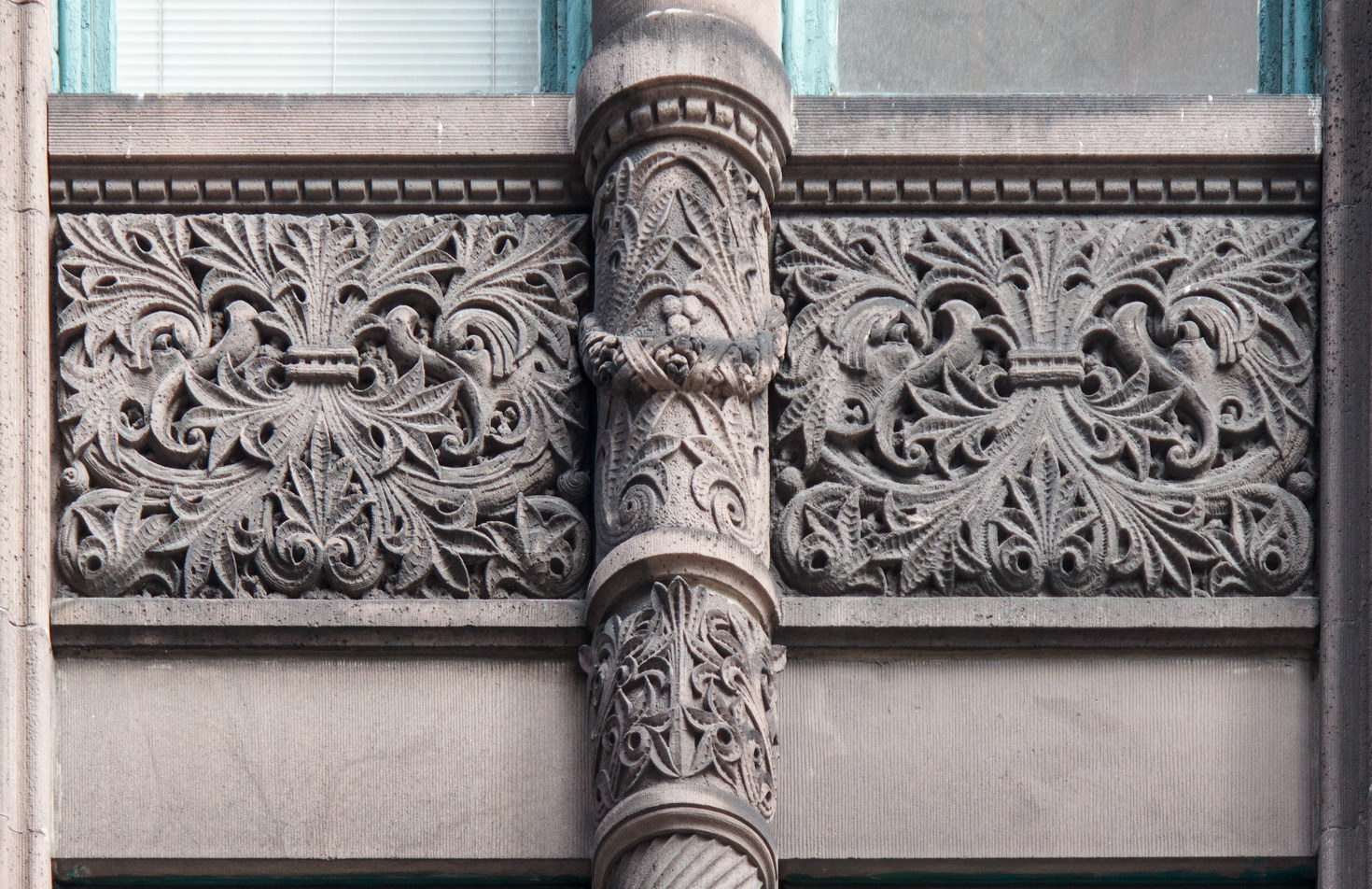
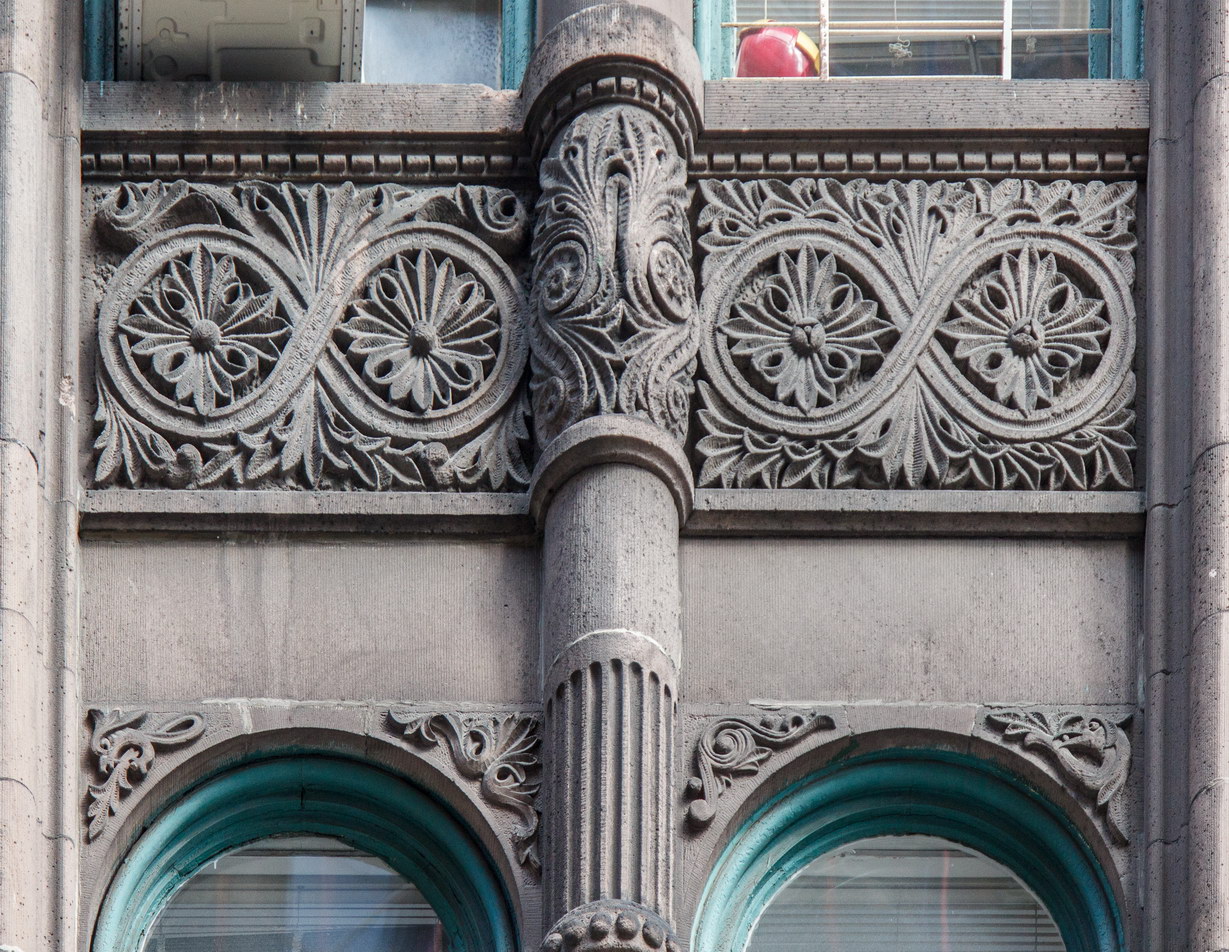
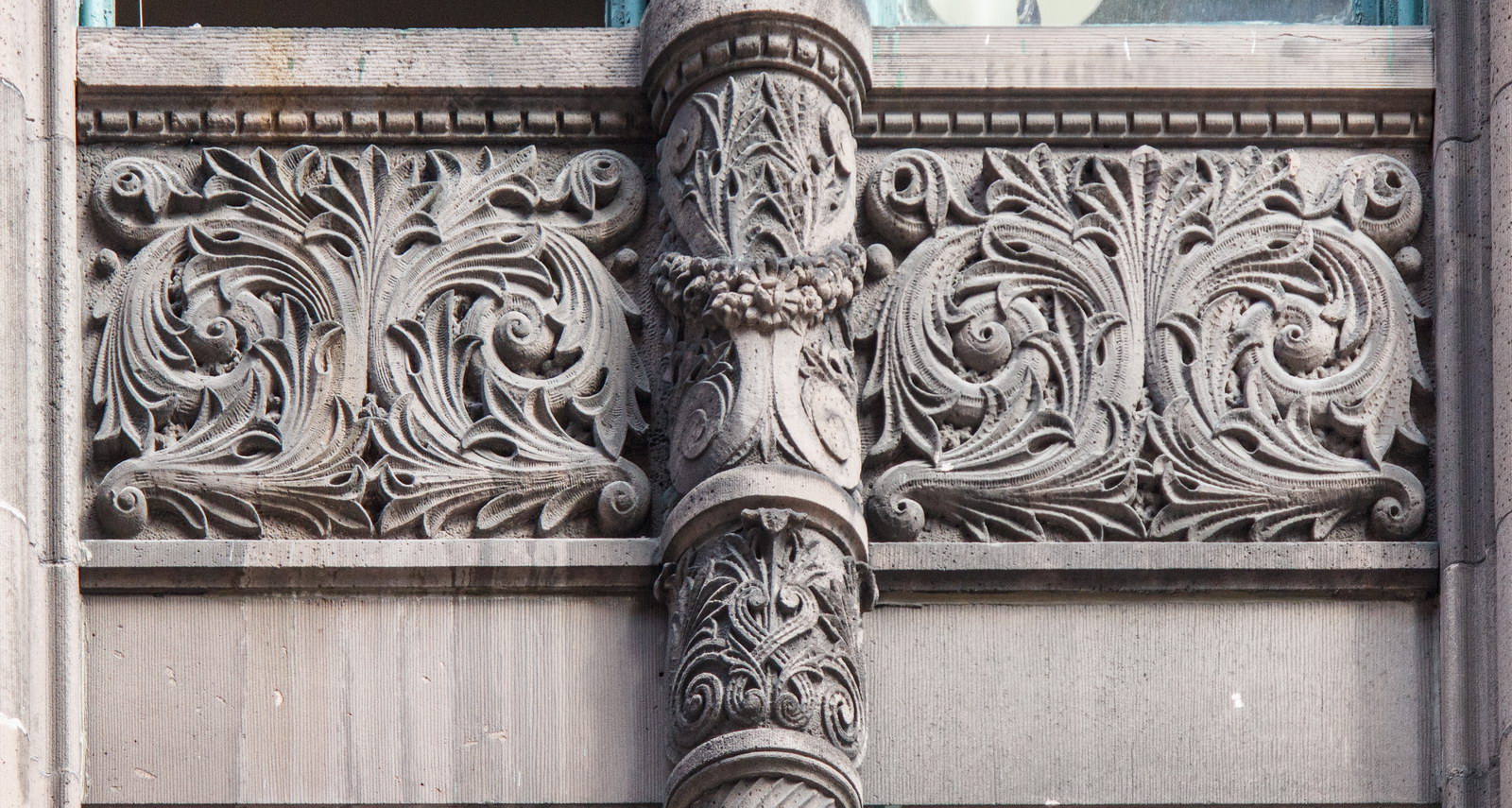
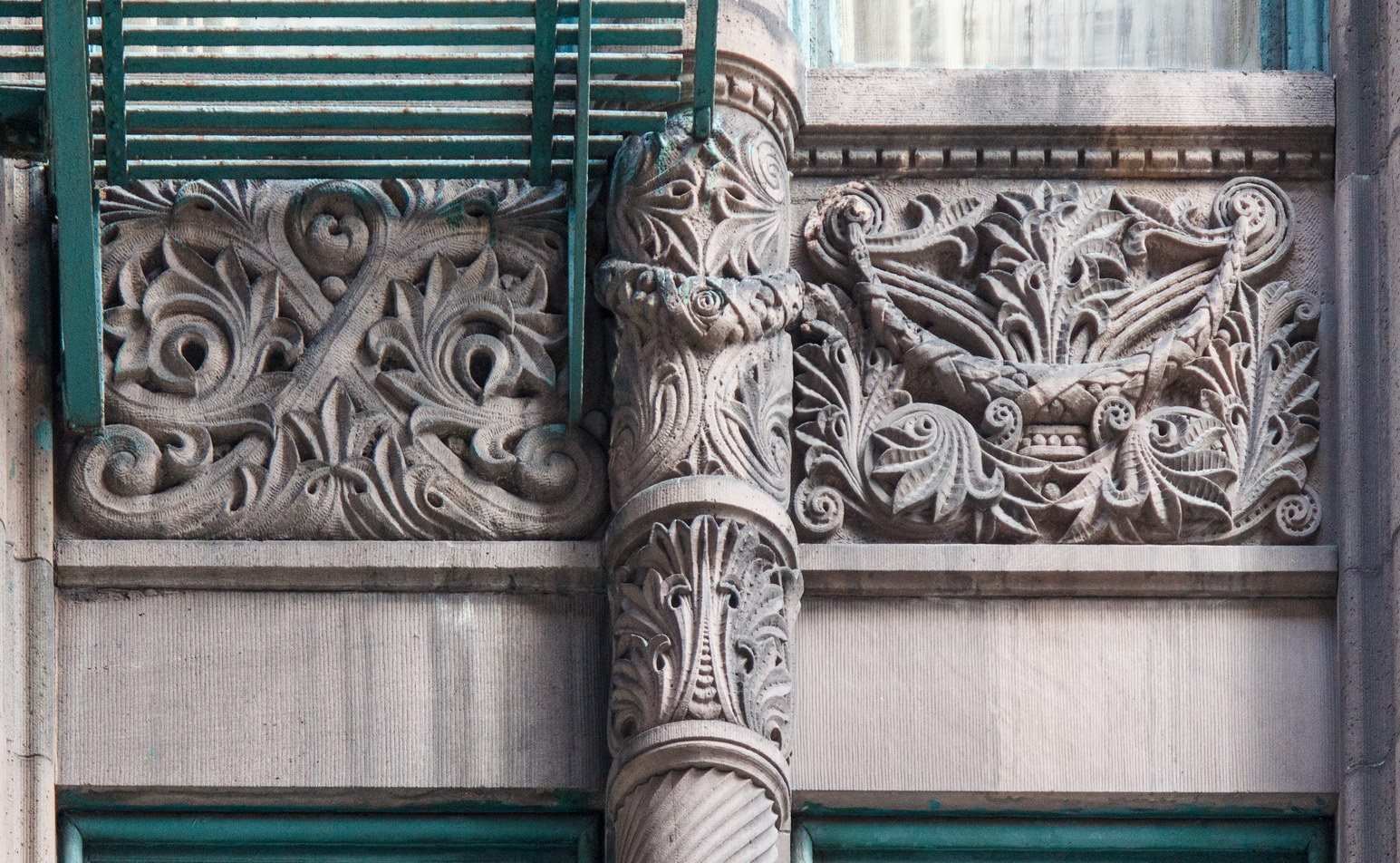
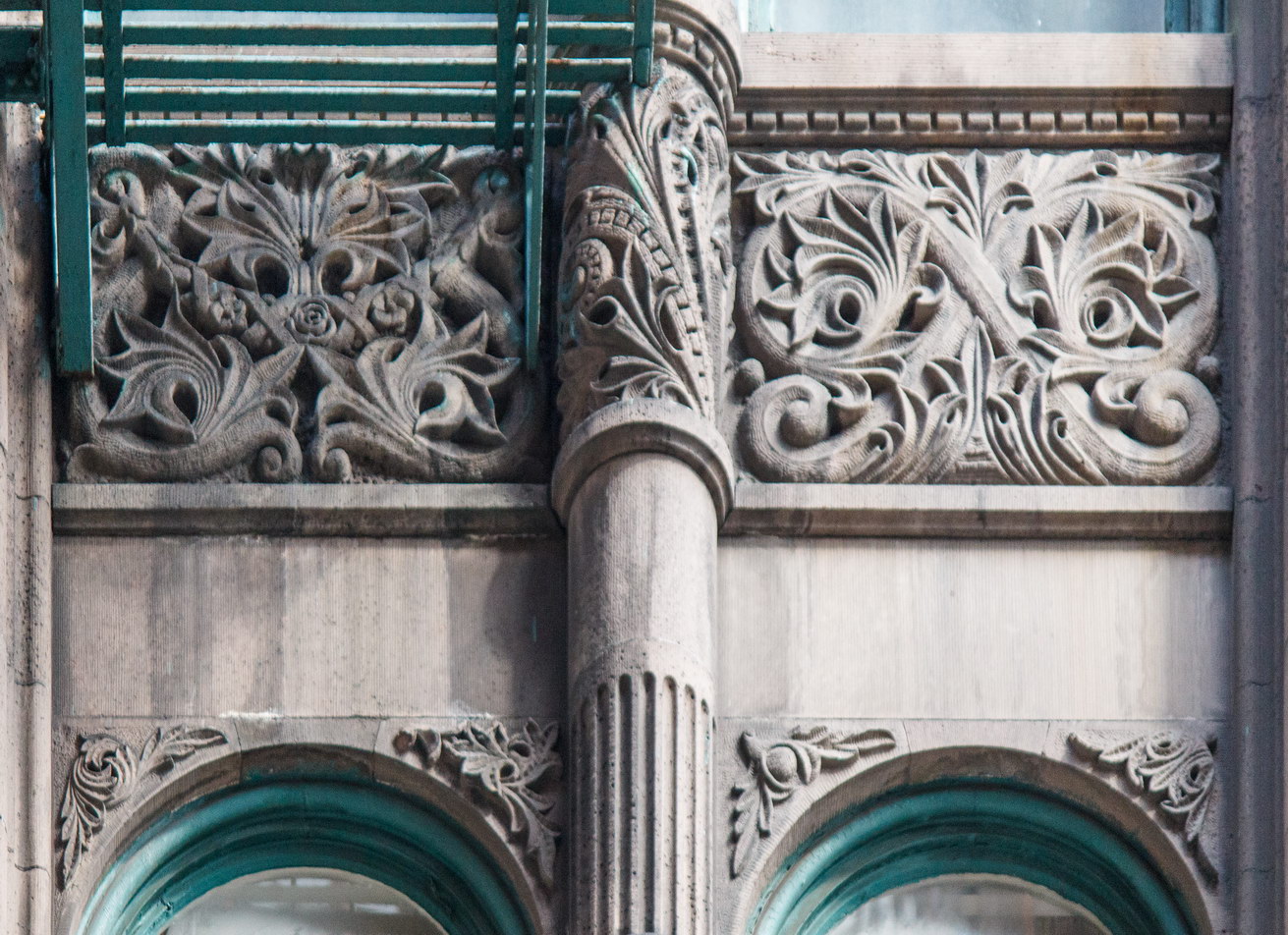
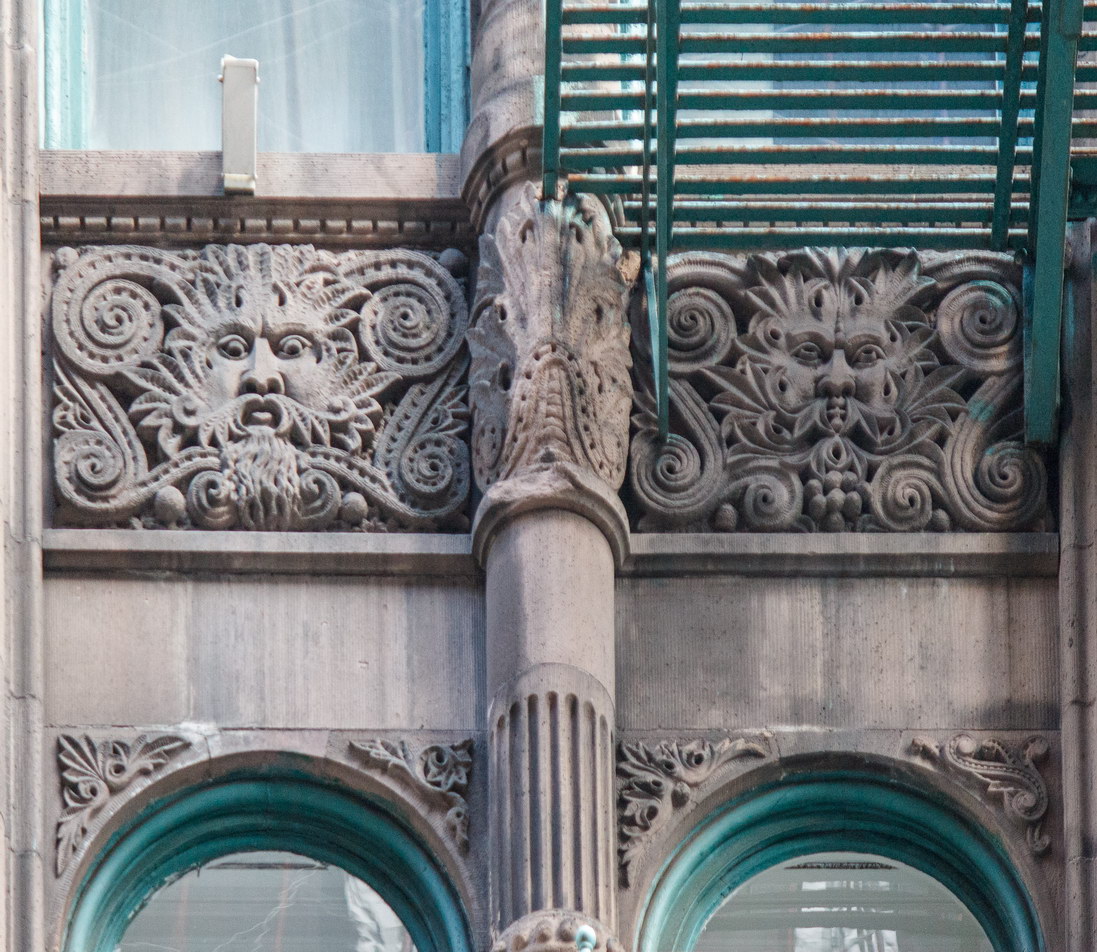
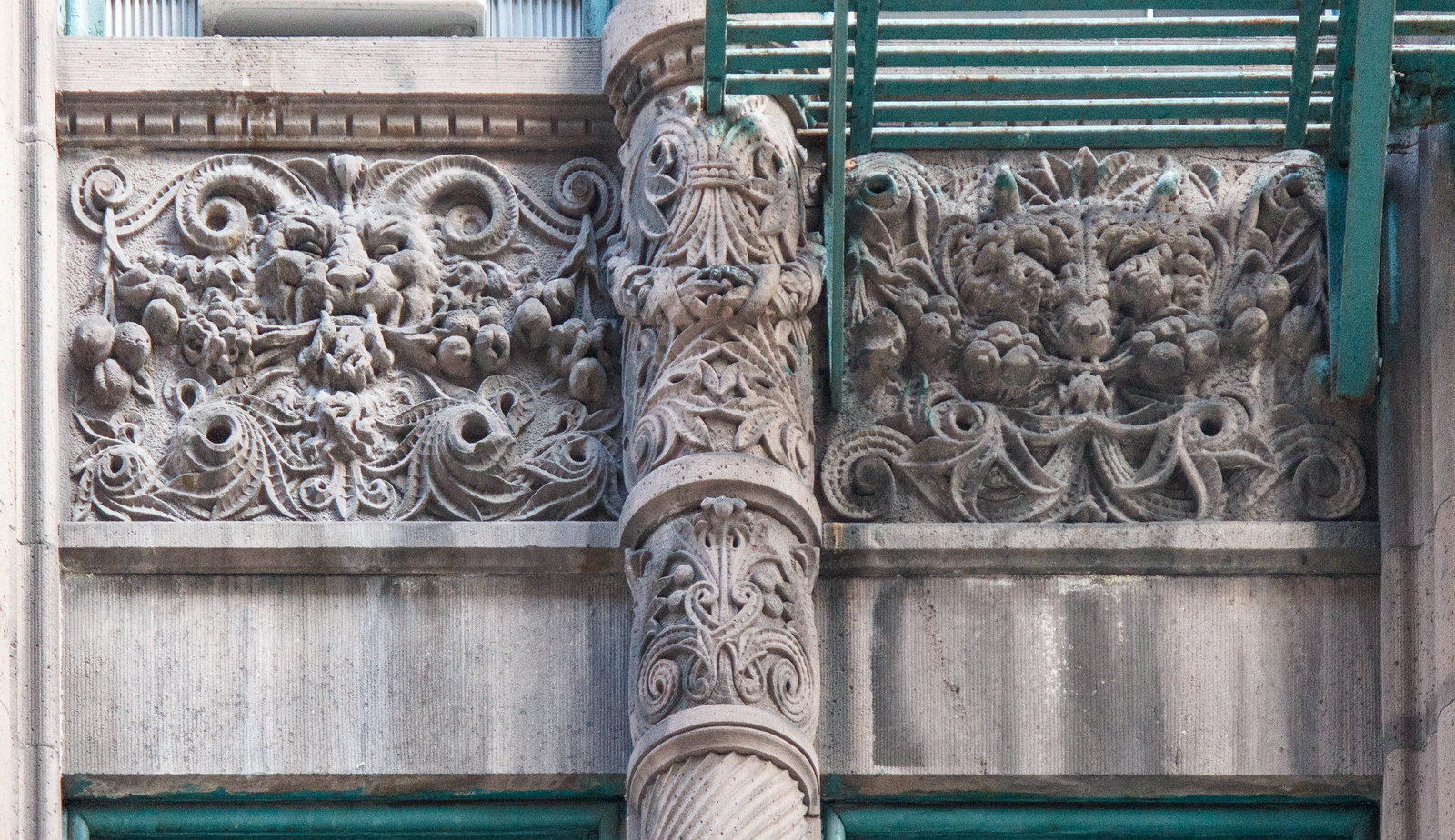
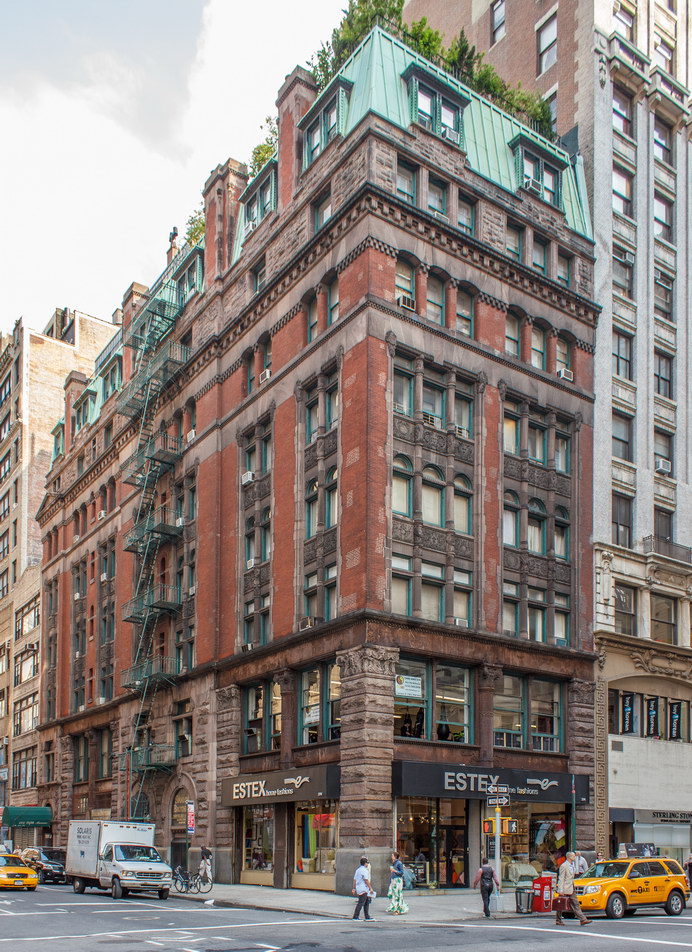
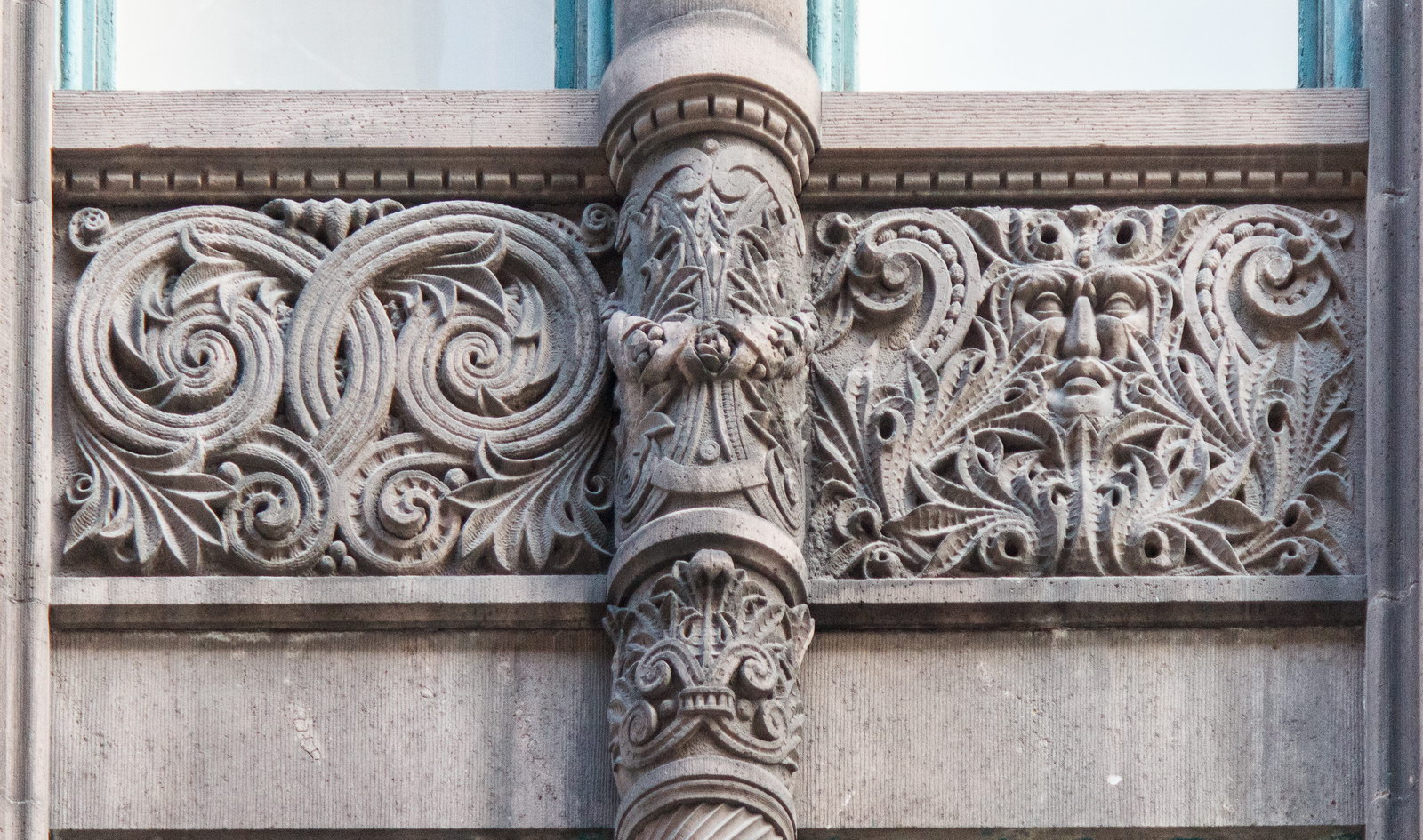
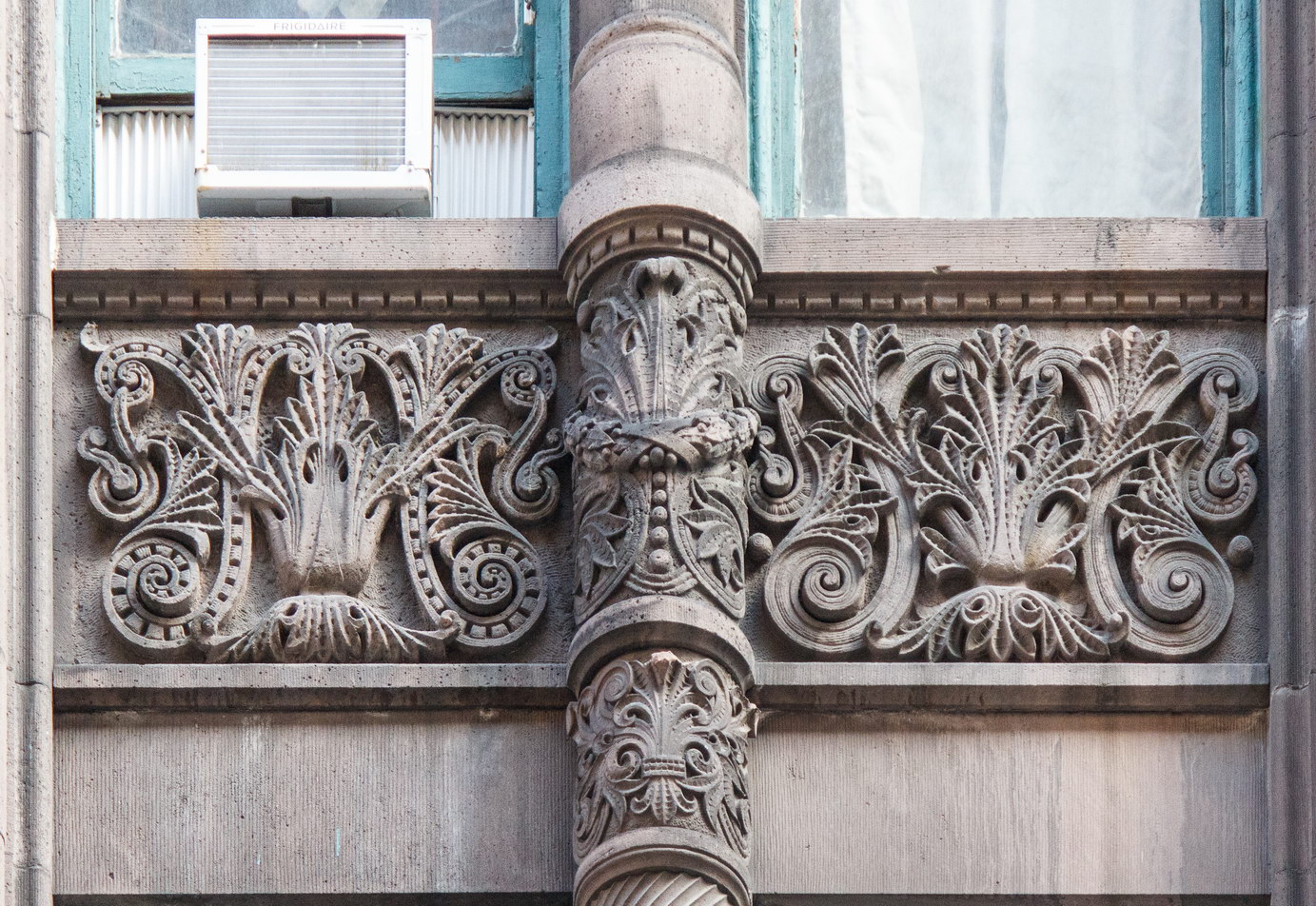
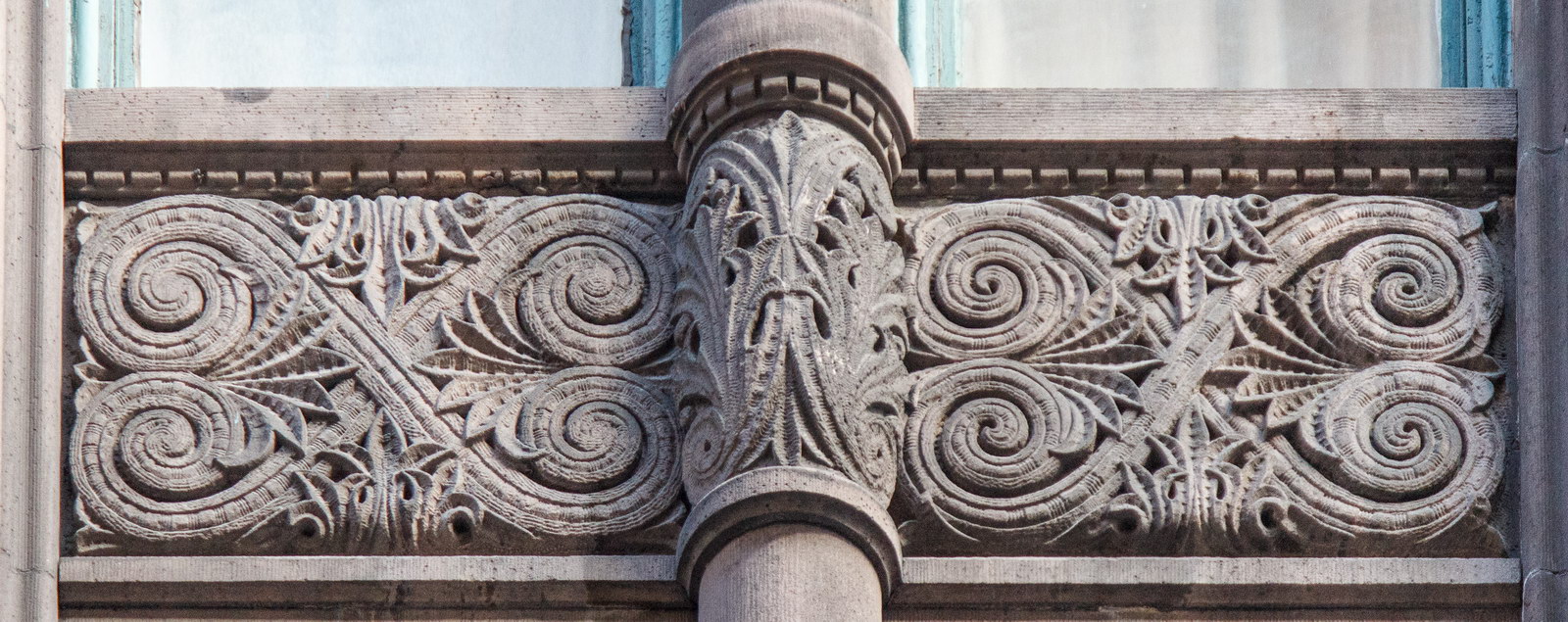
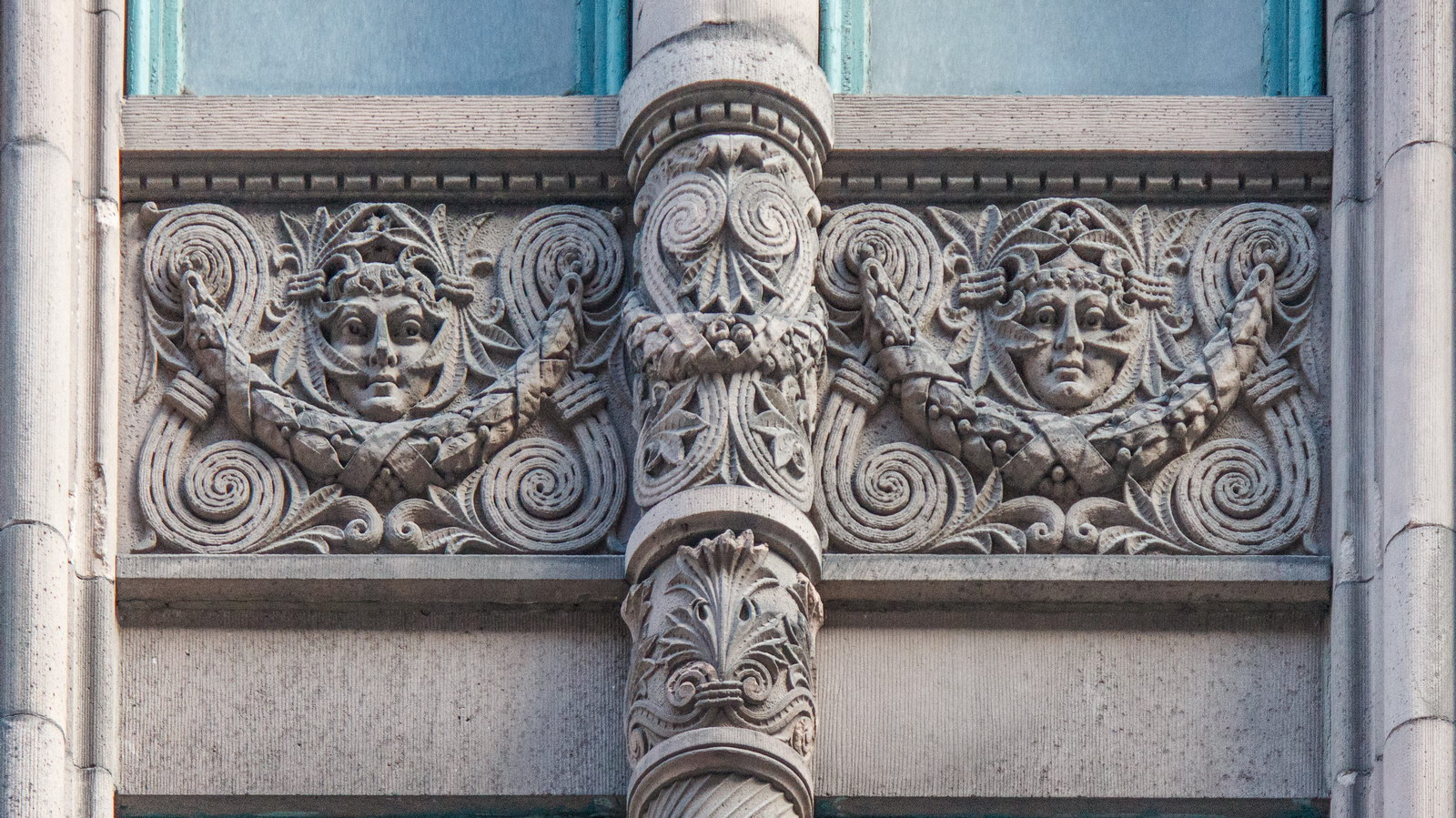
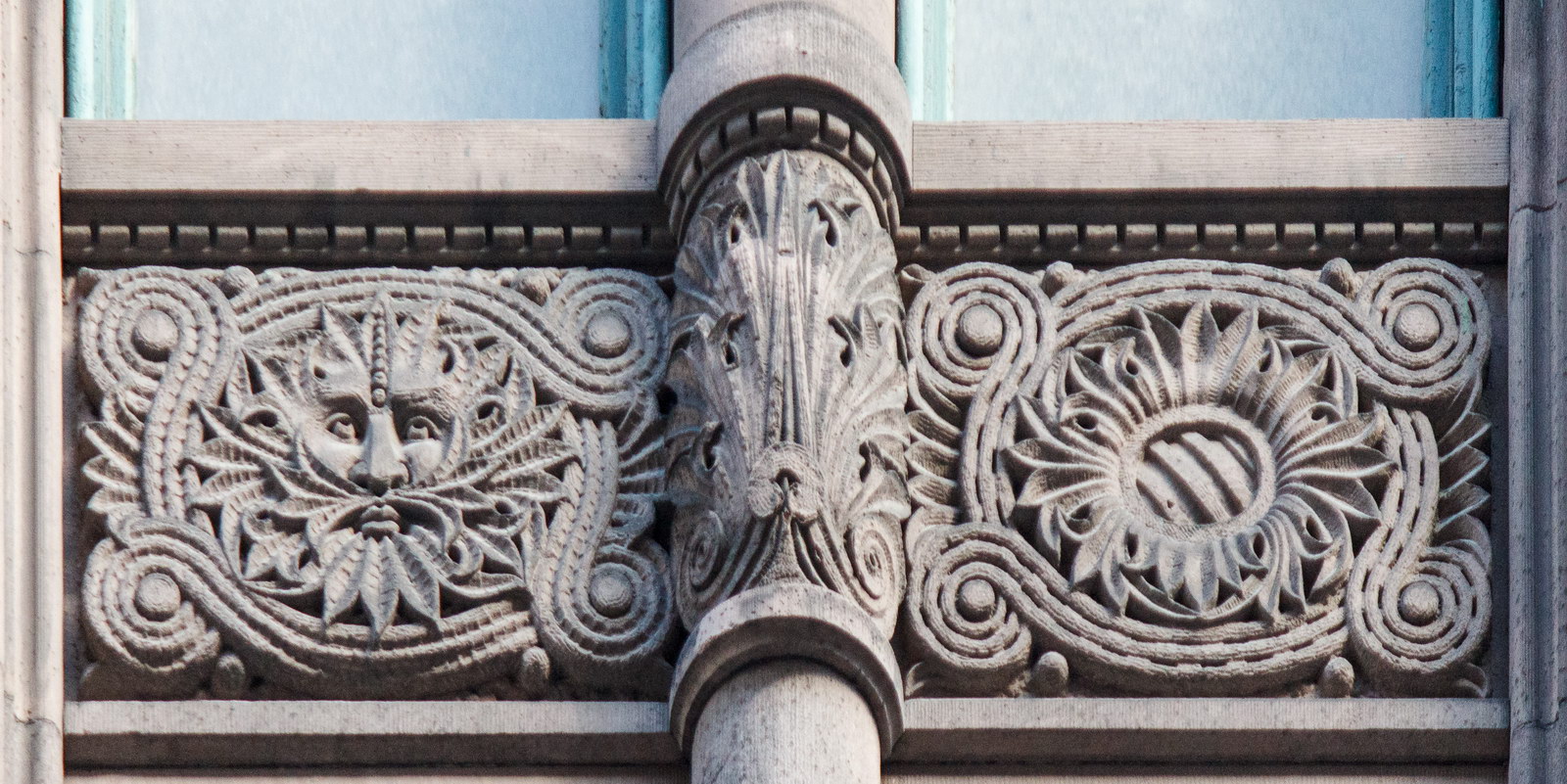
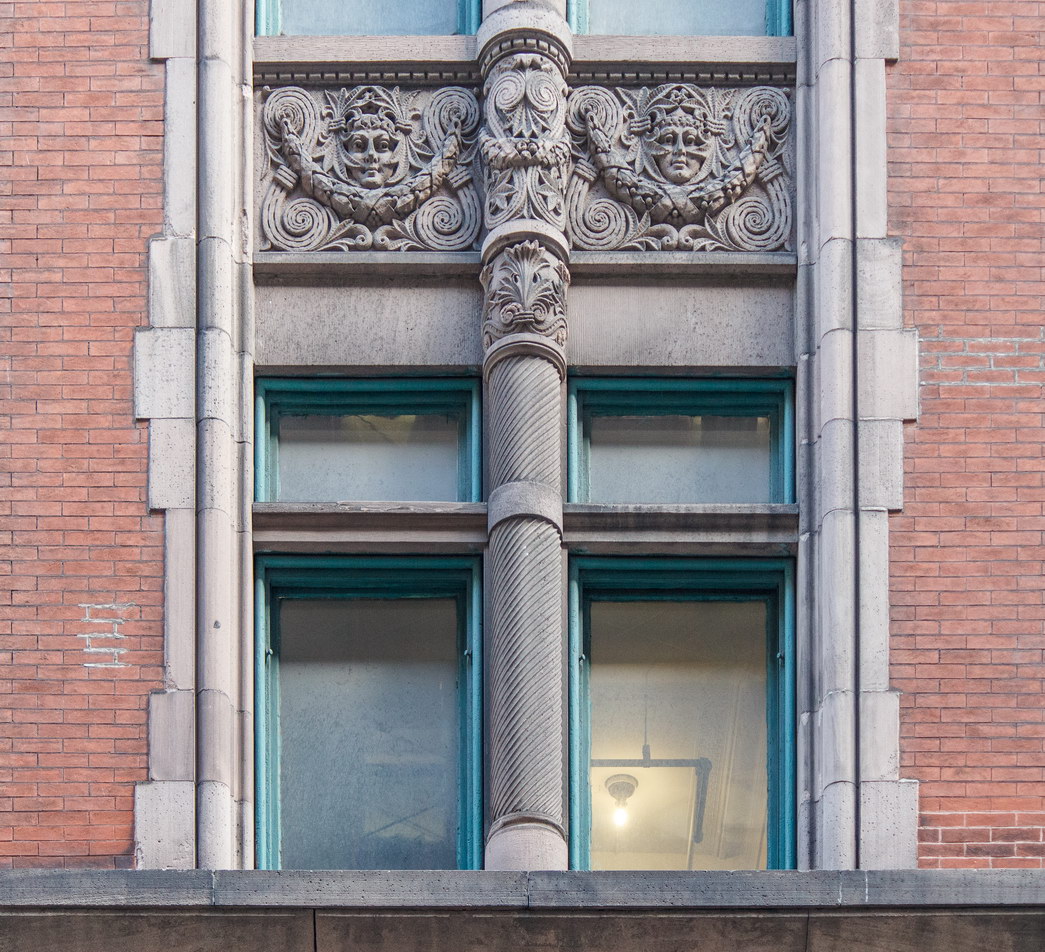
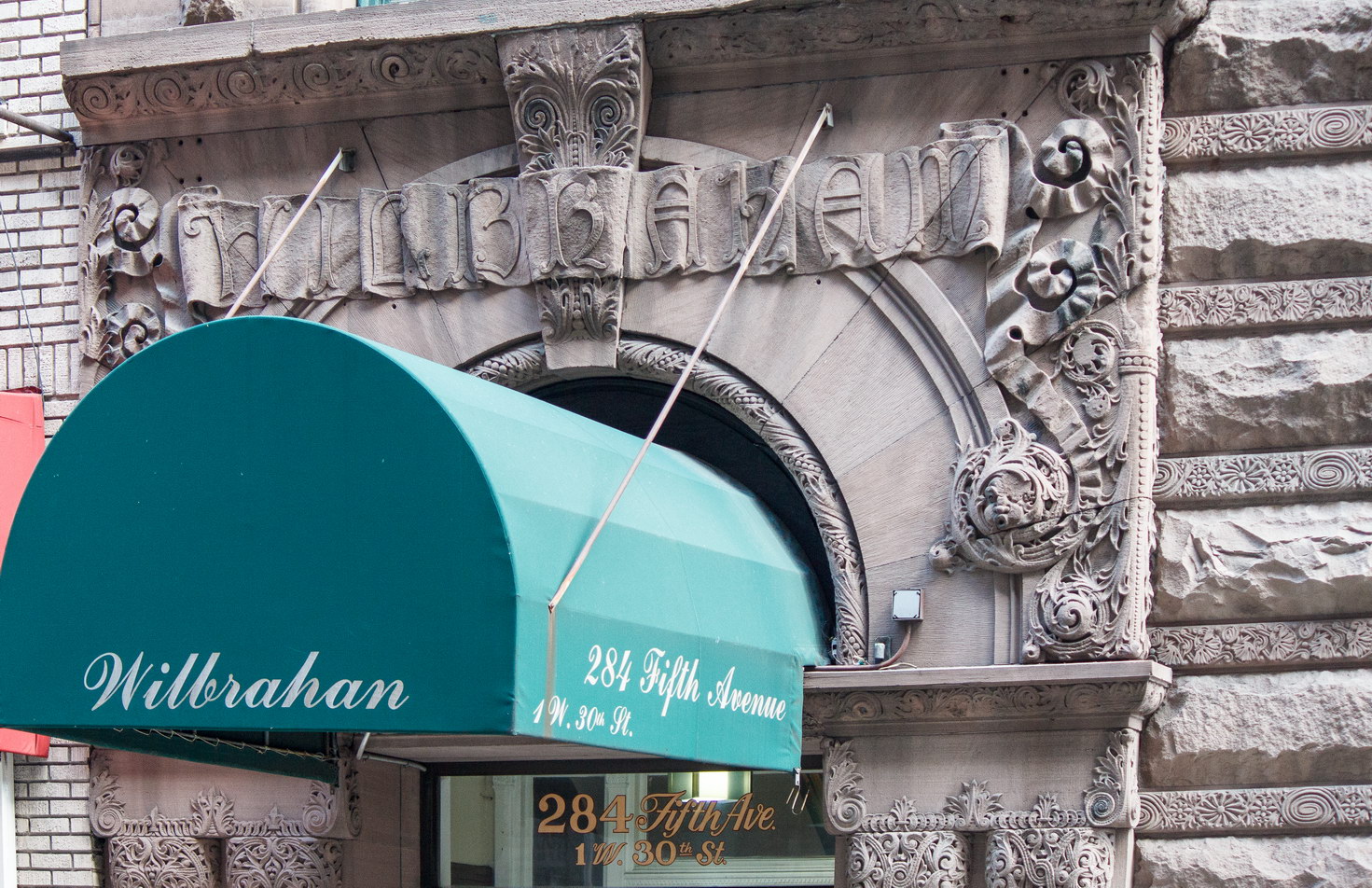
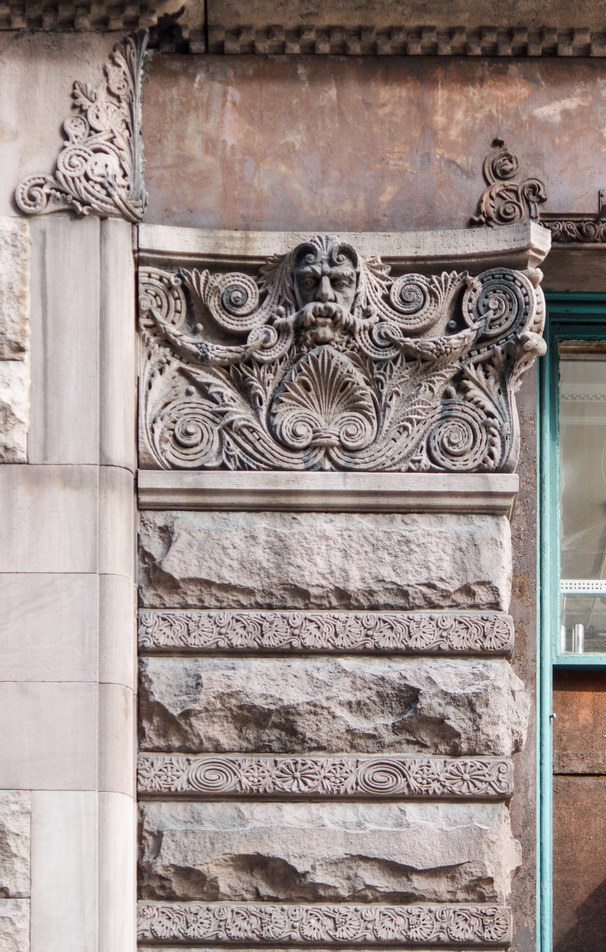
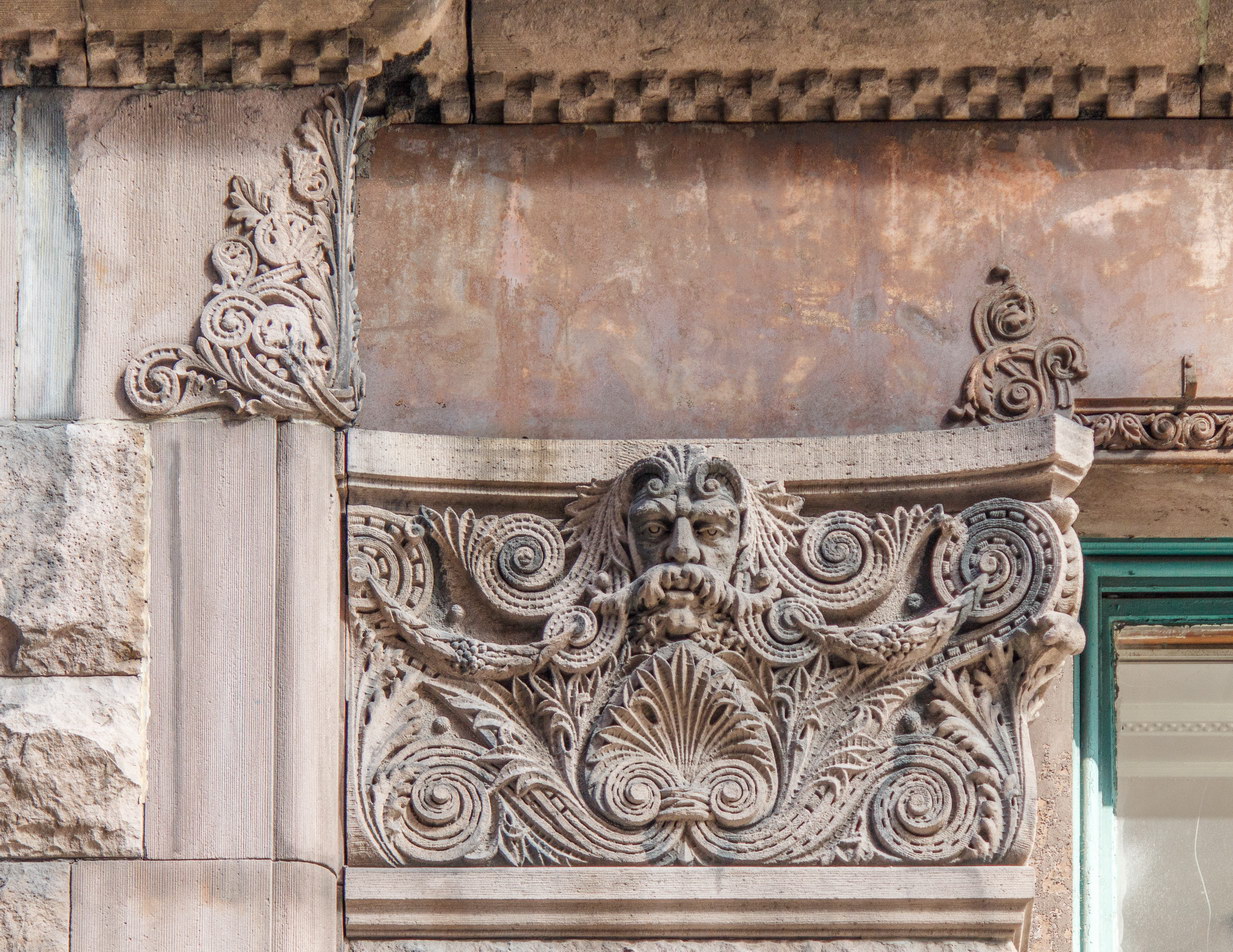
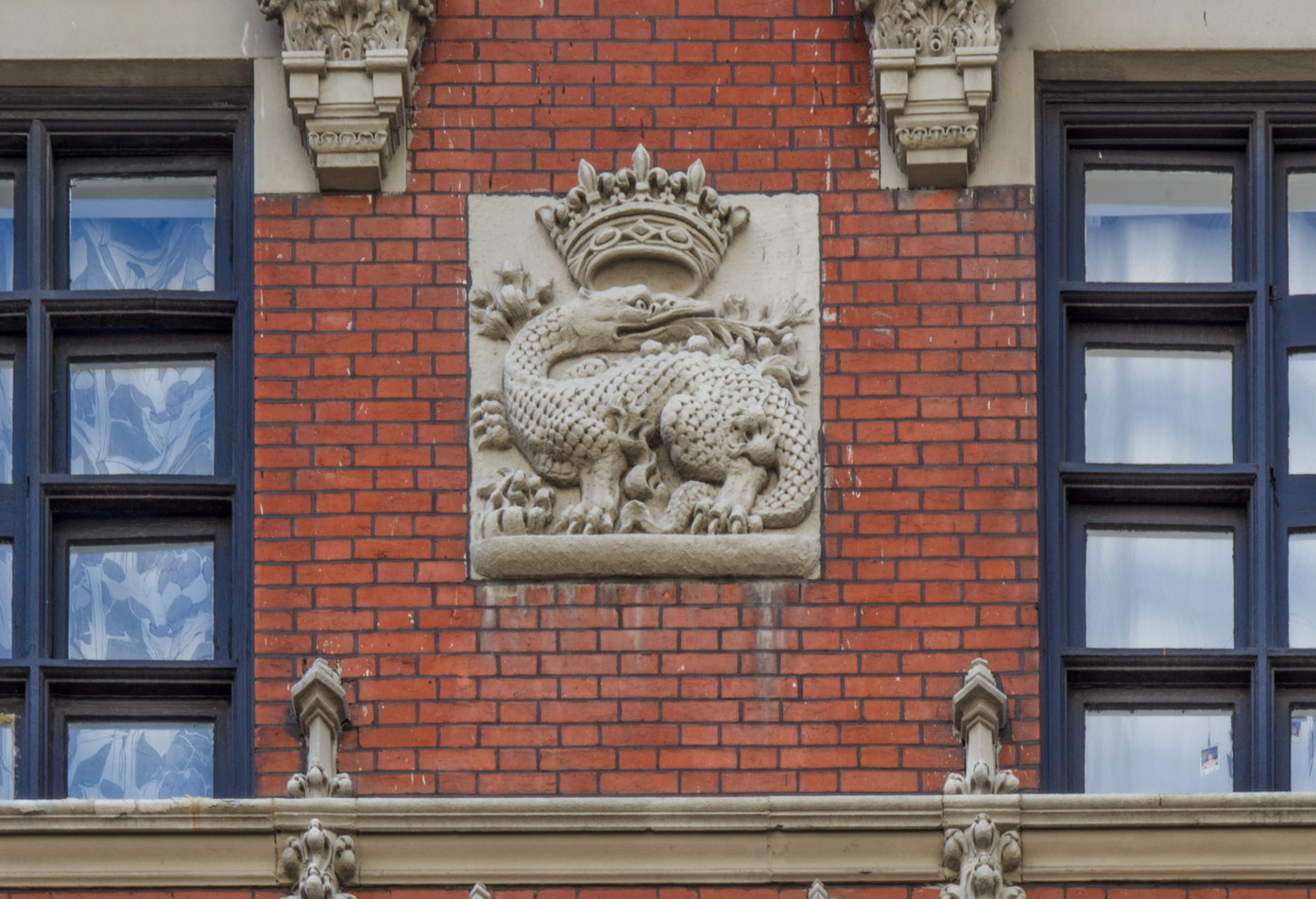
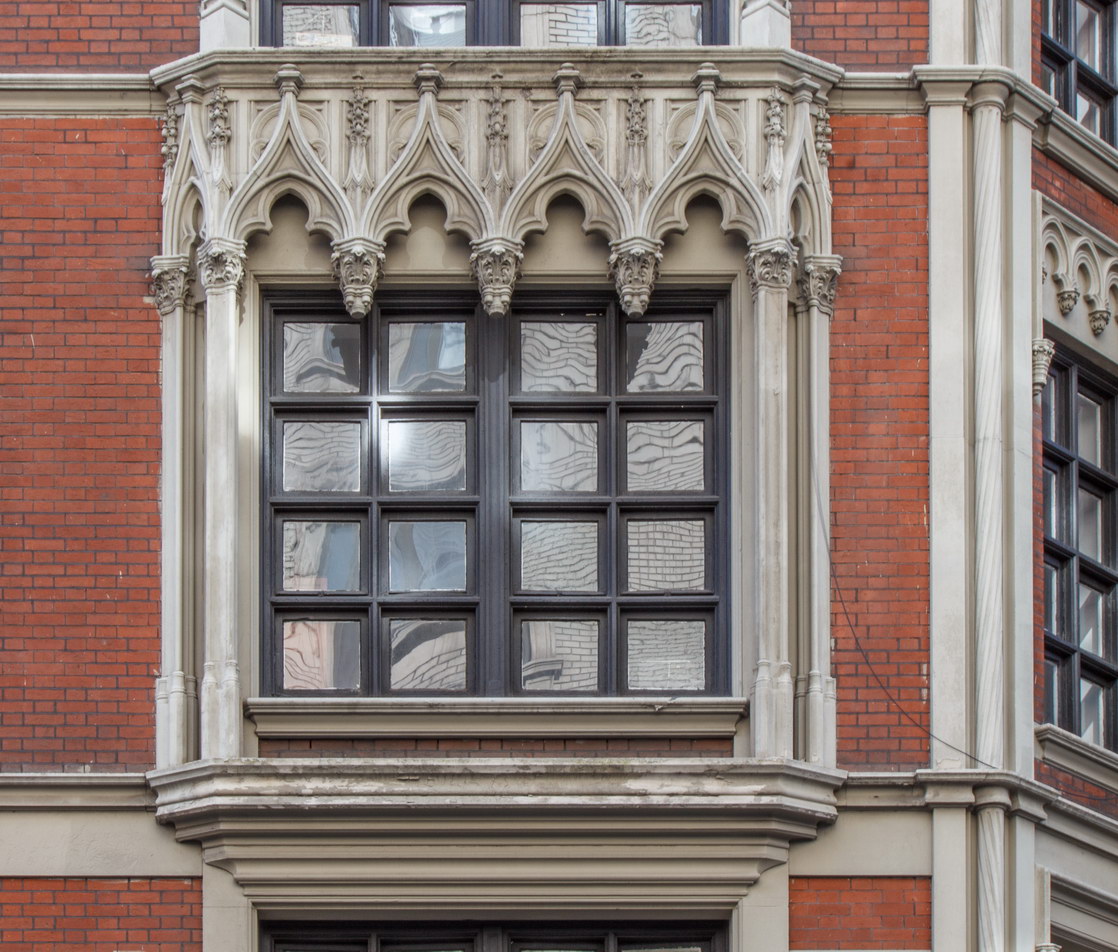
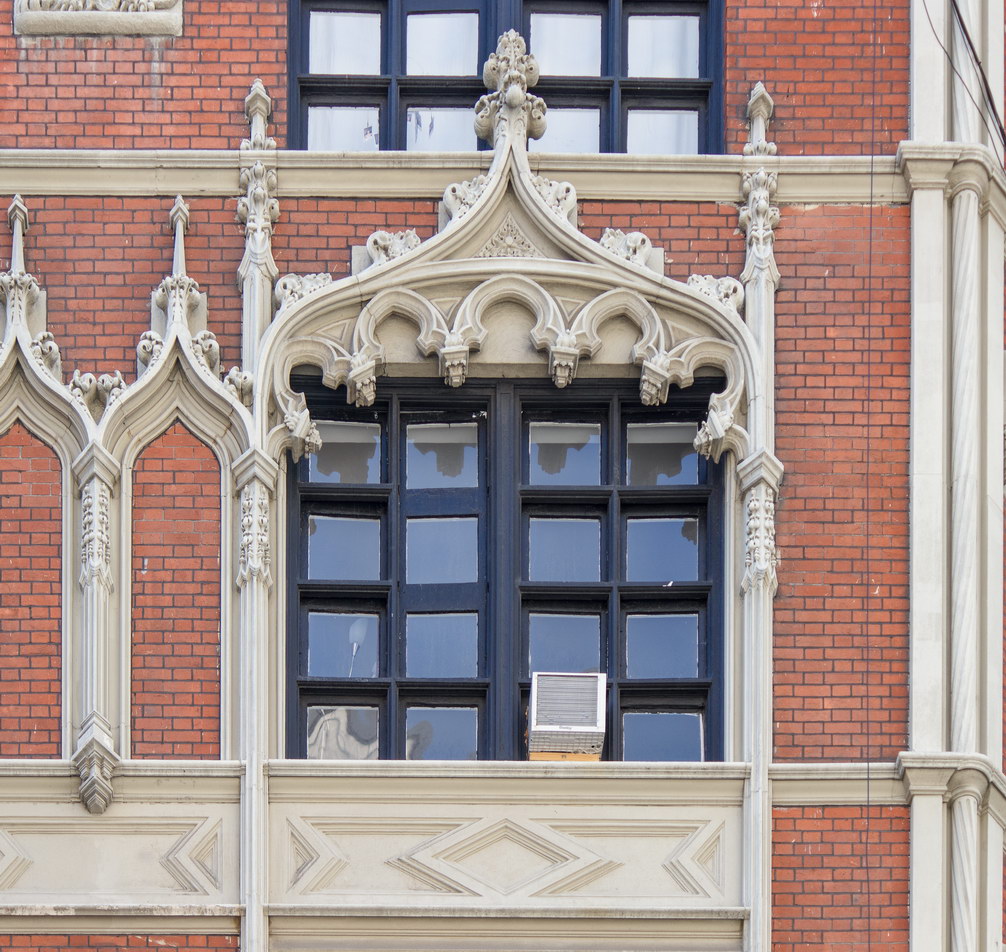
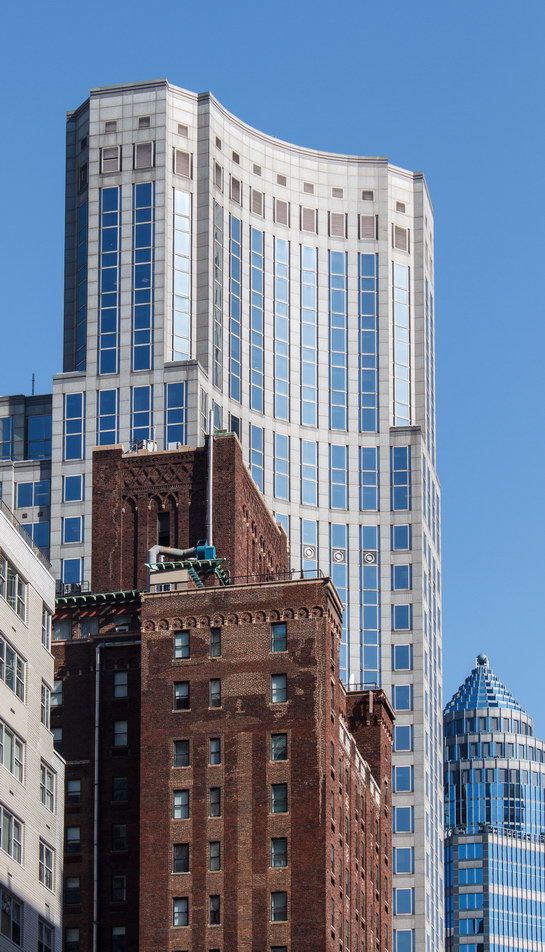
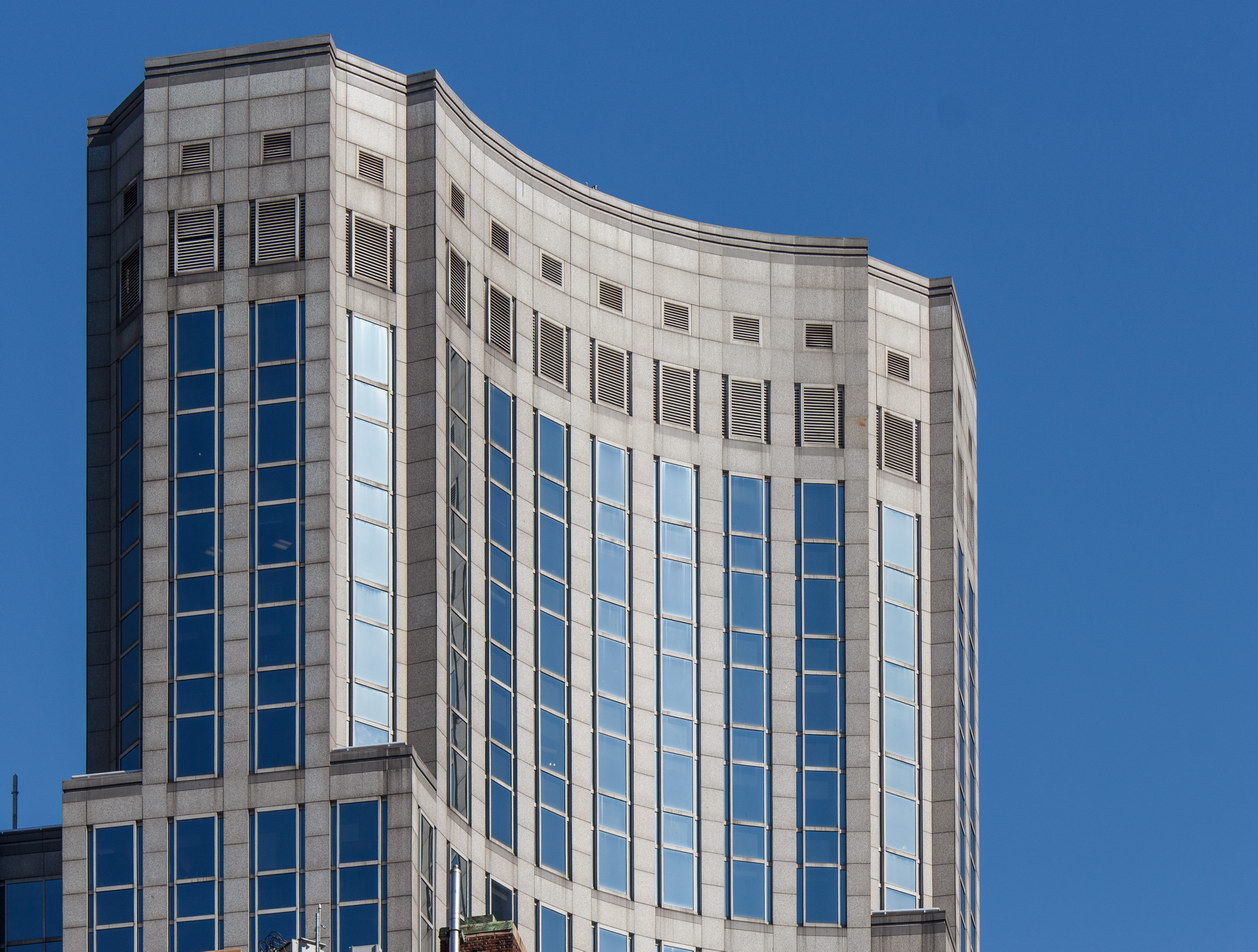
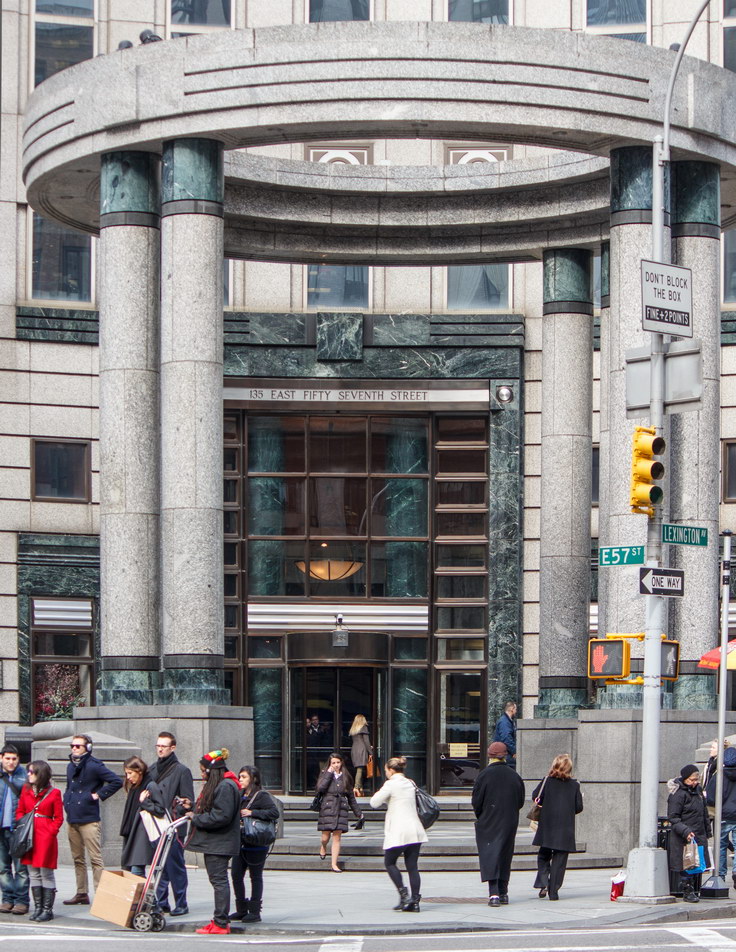
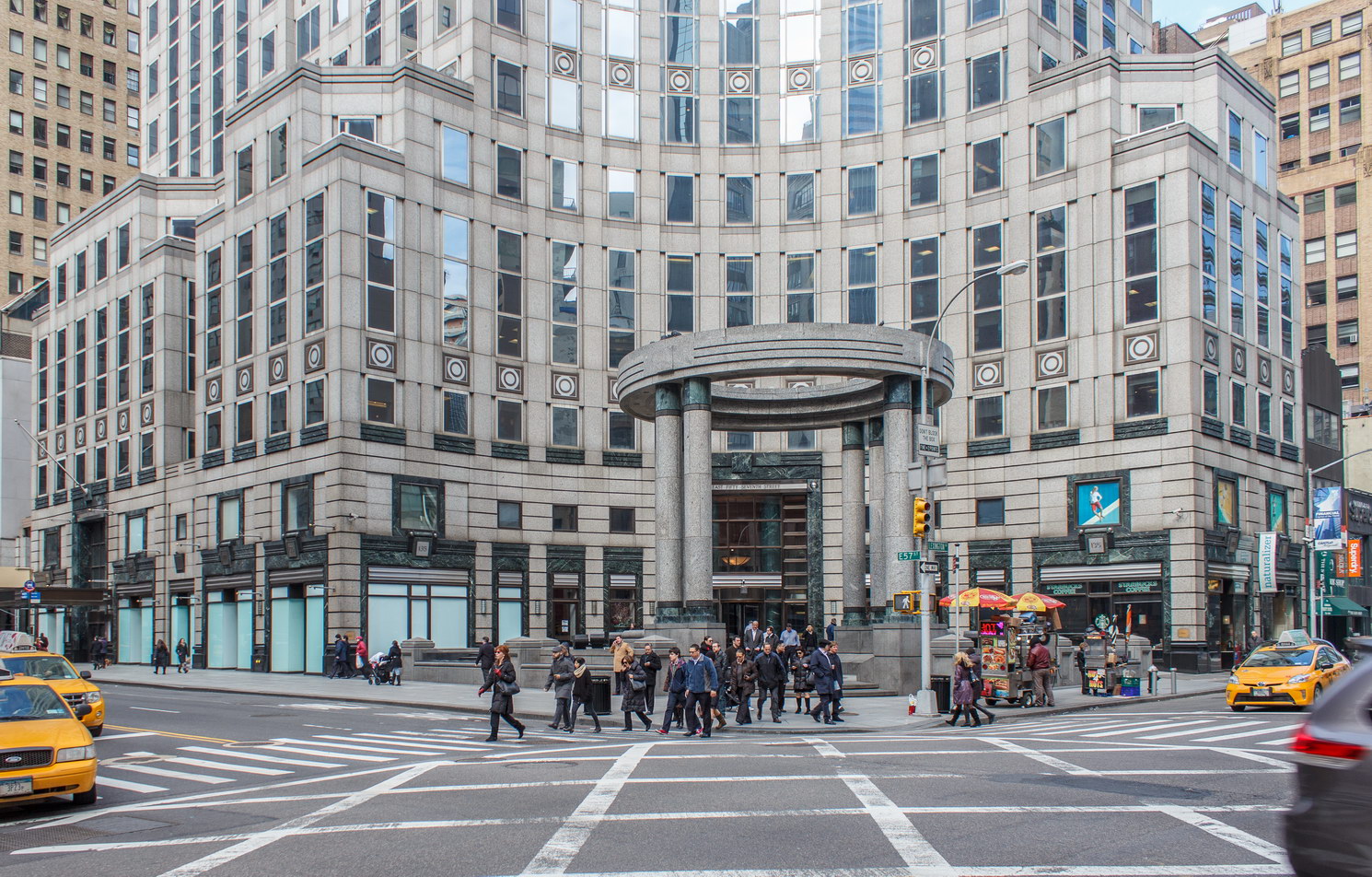
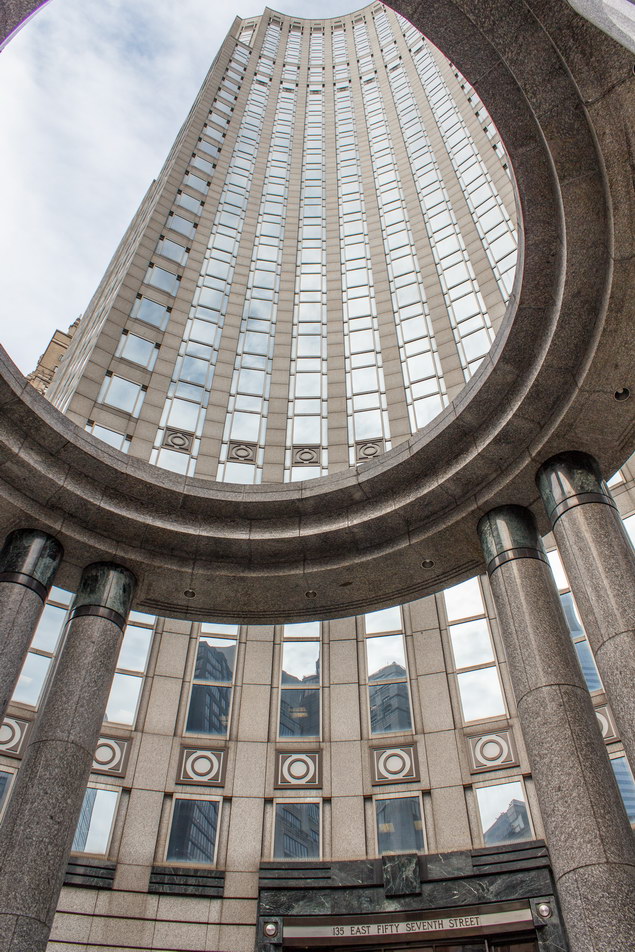
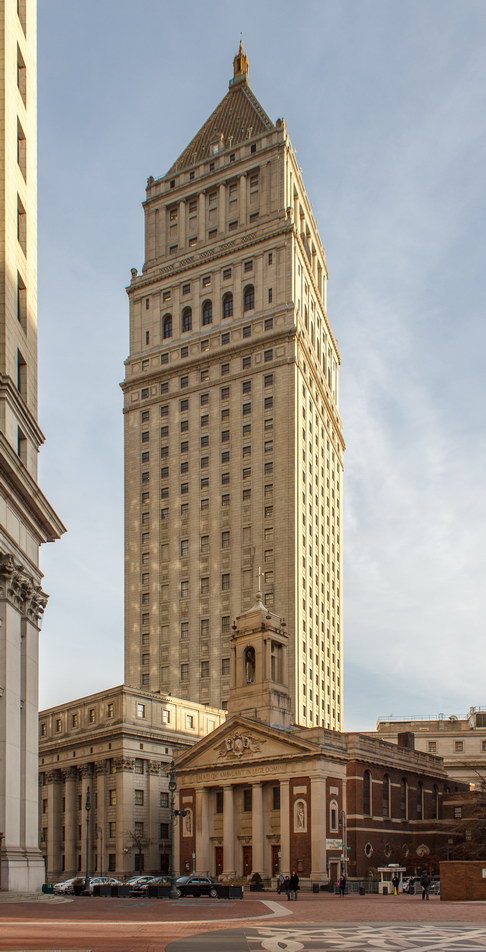
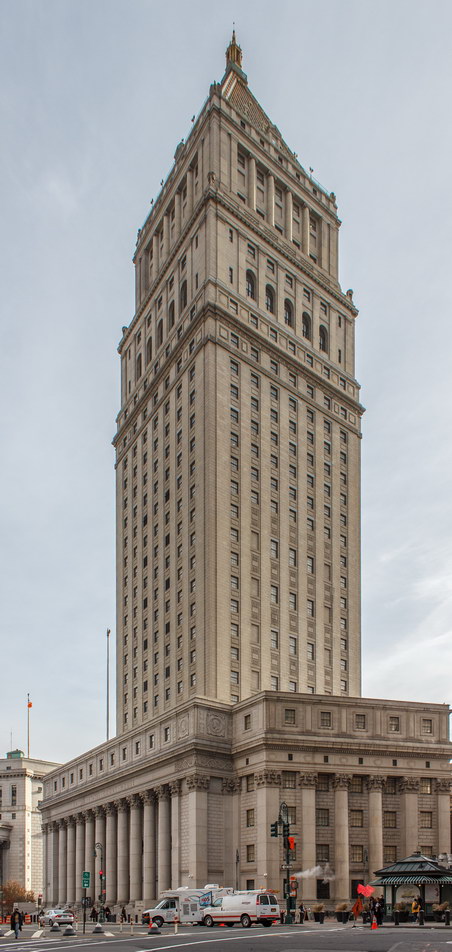
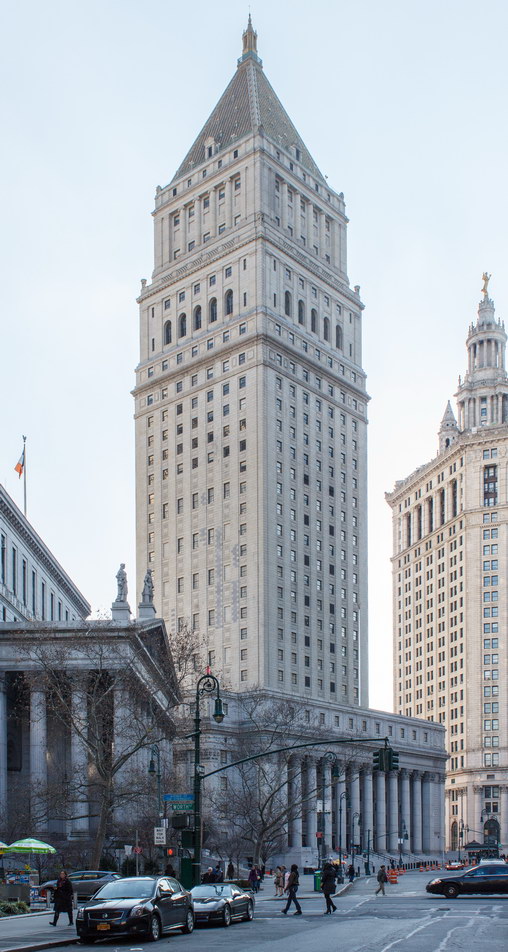
The Thurgood Marshall US Courthouse (originally United States Courthouse, Foley Square) was the last building designed by the famed Cass Gilbert, who died before the project’s completion. His son, Cass Gilbert, Jr., supervised the structure’s completion.
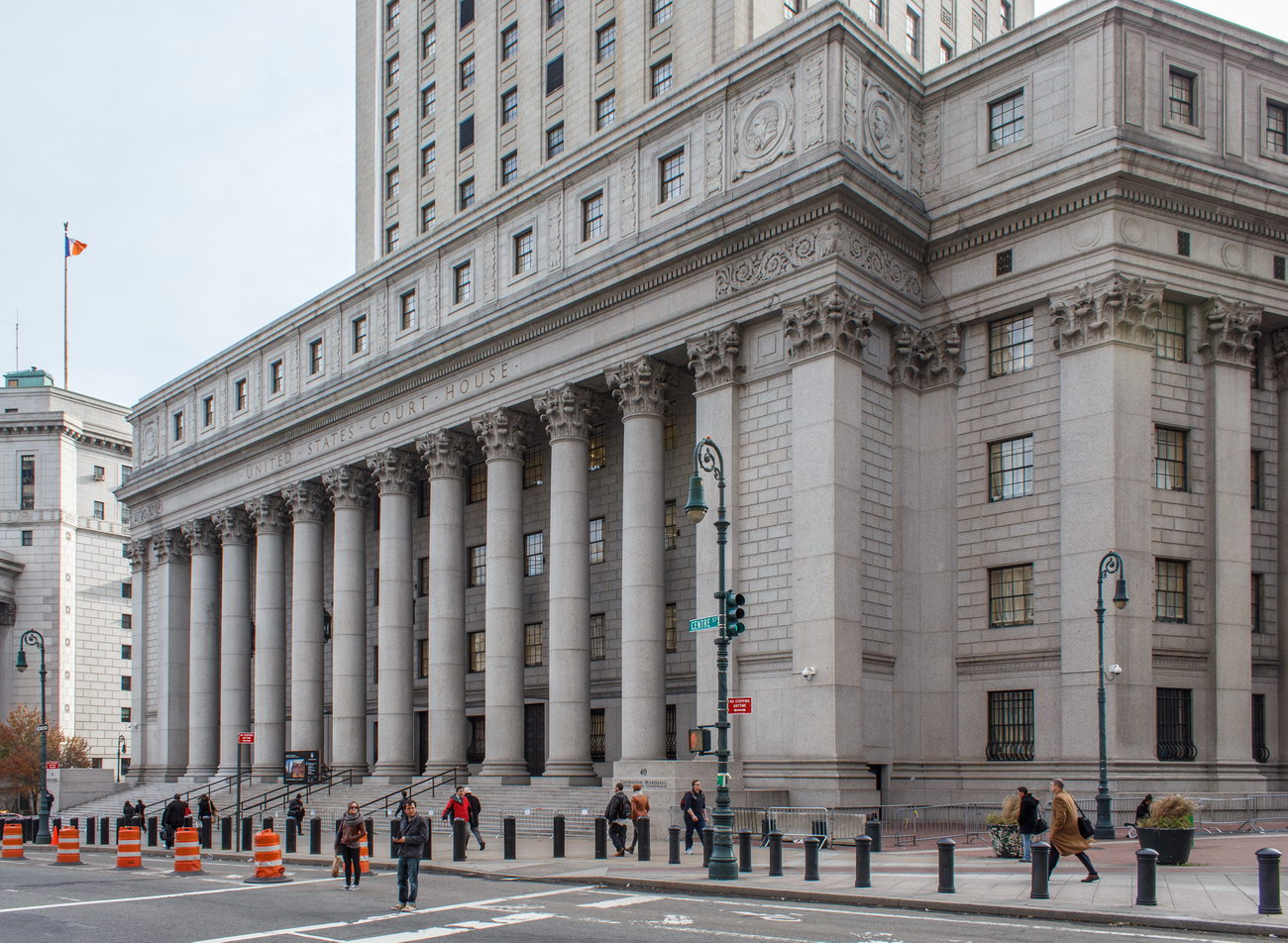
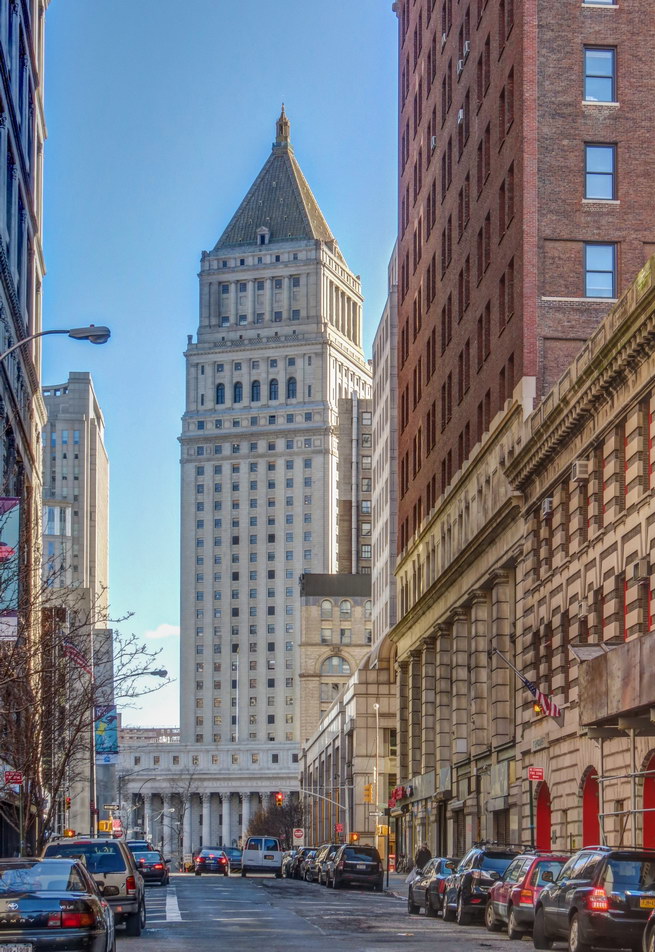
The 37-story skyscraper design marked a significant departure from other federal government buildings, which until then were all horizontal. The sprawling six-story base, however, blends in with surrounding landmarks.
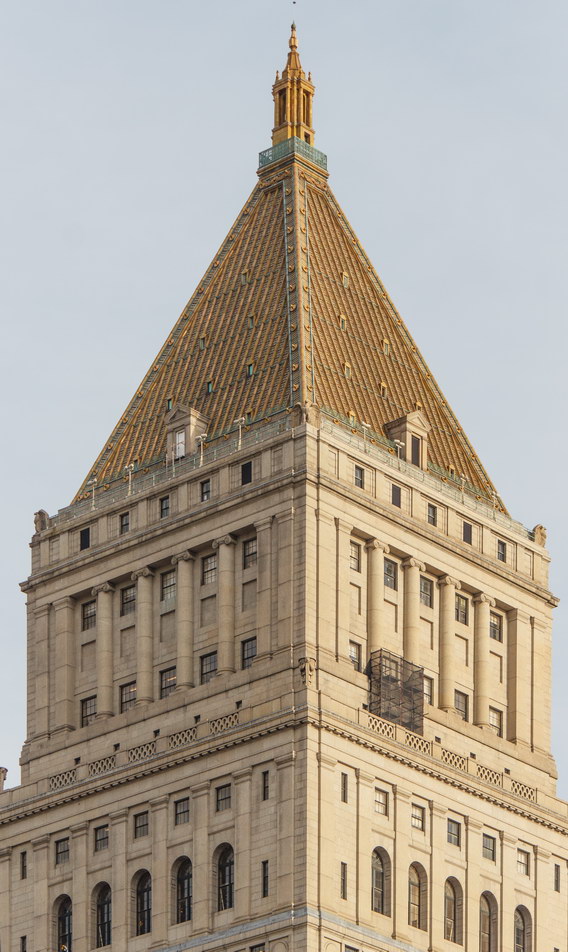
The base and tower are faced in granite from Gilbert’s home state of Minnesota; the pyramidal roof is clad in gilded terra cotta.
The building was renamed Thurgood Marshall United States Courthouse in August 2001, honoring the first African American Supreme Court Justice, who had worked at the courthouse from 1961 to 1965 as a judge of the Second Circuit Court of Appeals.
The building completed a modernization project in 1992; at this writing (December 2012) it is going through a renovation/restoration that was supposed to have been completed in 2009, but seems to be never-ending.
Thurgood Marshall US Courthouse Vital Statistics
- Location: 40 Centre Street at Foley Square
- Year completed: 1936
- Architect: Cass Gilbert
- Floors: 37
- Style: Classic Revival
- New York City Landmark: 1975
- National Register of Historic Places: 1987
Thurgood Marshall US Courthouse Suggested Reading
- Wikipedia entry
- NYC Landmarks Preservation Commission designation report
- General Services Administration property listing
- Cass Gilbert Society feature
- NY Sun renovation article
- Emporis database
- SkyscraperPage.com listing


![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5401 11/20/2012 9:19:34 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5401 11/20/2012 9:19:34 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5401_resize.jpg)

![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5432 11/20/2012 9:40:29 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5432 11/20/2012 9:40:29 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5432_resize.jpg)


![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5510 11/20/2012 10:30:01 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5510 11/20/2012 10:30:01 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5510_resize.jpg)
![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5522 11/20/2012 10:37:45 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5522 11/20/2012 10:37:45 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5522_resize.jpg)
![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5533 11/20/2012 10:44:25 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5533 11/20/2012 10:44:25 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5533_resize.jpg)
![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5538 11/20/2012 10:47:35 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5538 11/20/2012 10:47:35 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5538_resize.jpg)
![[Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5547 11/20/2012 10:51:17 AM [Thurgood Marshall Courthouse] IMG_5547 11/20/2012 10:51:17 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/thurgood-marshall-us-courthouse/i_5547_resize.jpg)



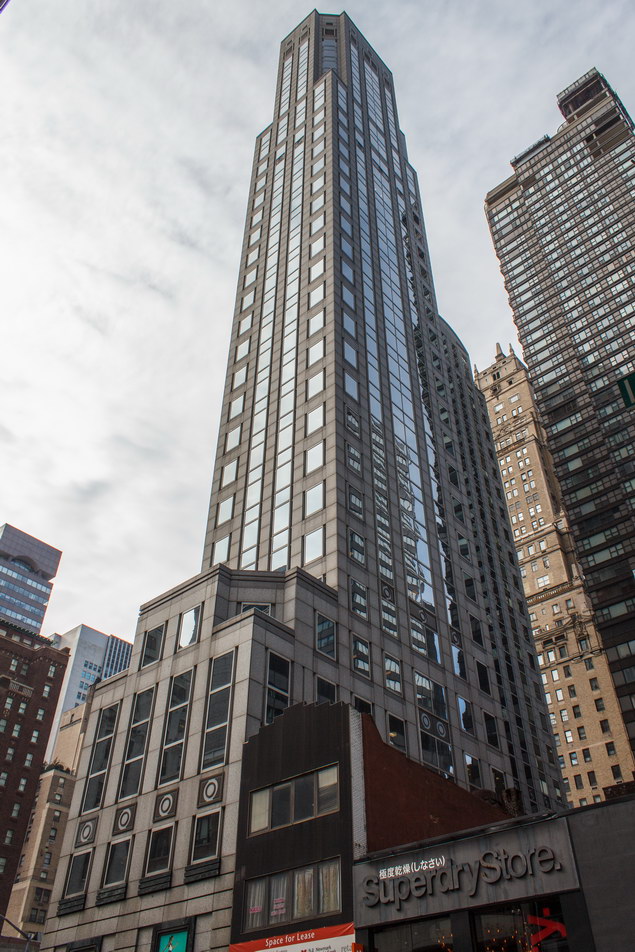
![[90 West Street Building] IMG_6480 12/28/2012 10:33:26 AM [90 West Street Building] IMG_6480 12/28/2012 10:33:26 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/90-west-street/IMG_6480_resize.jpg)
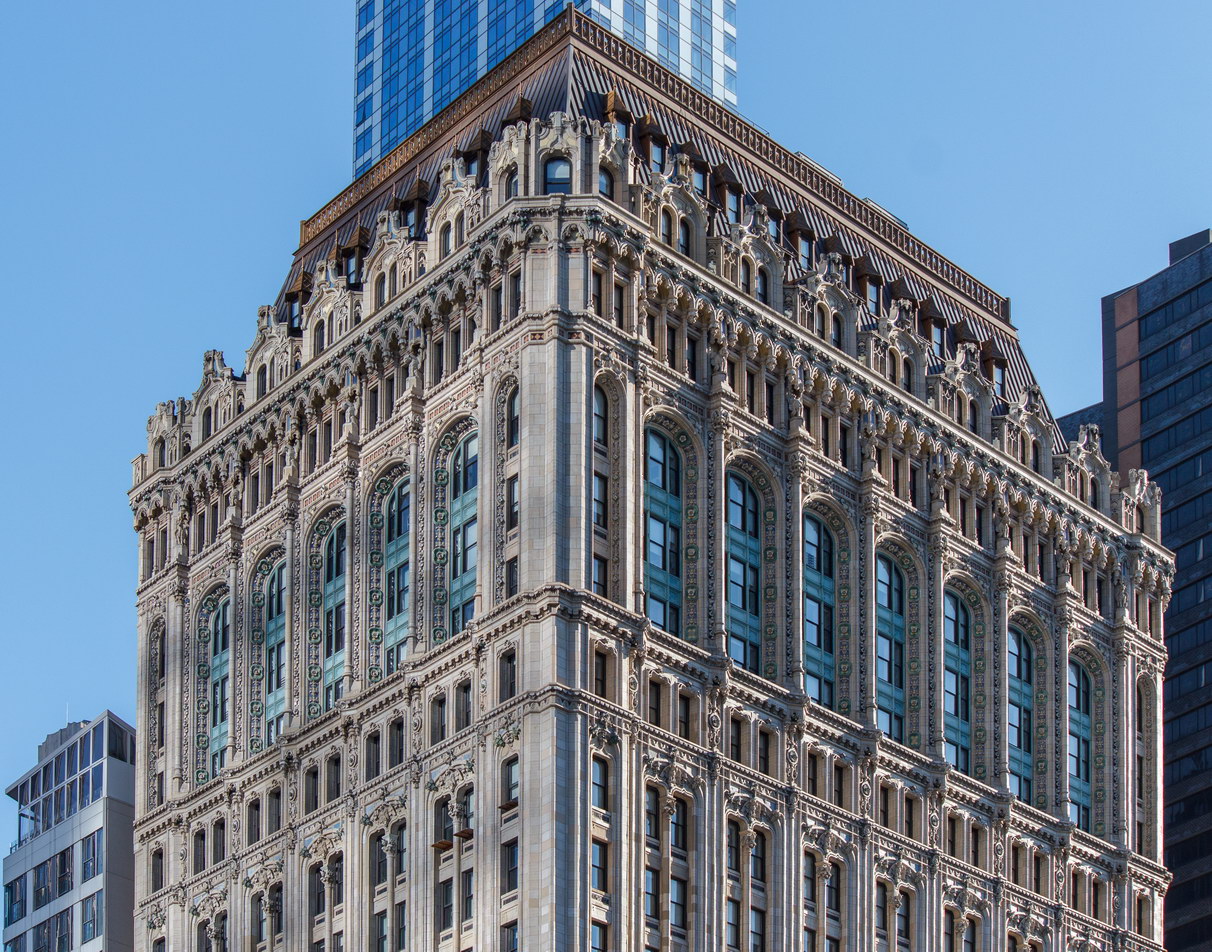
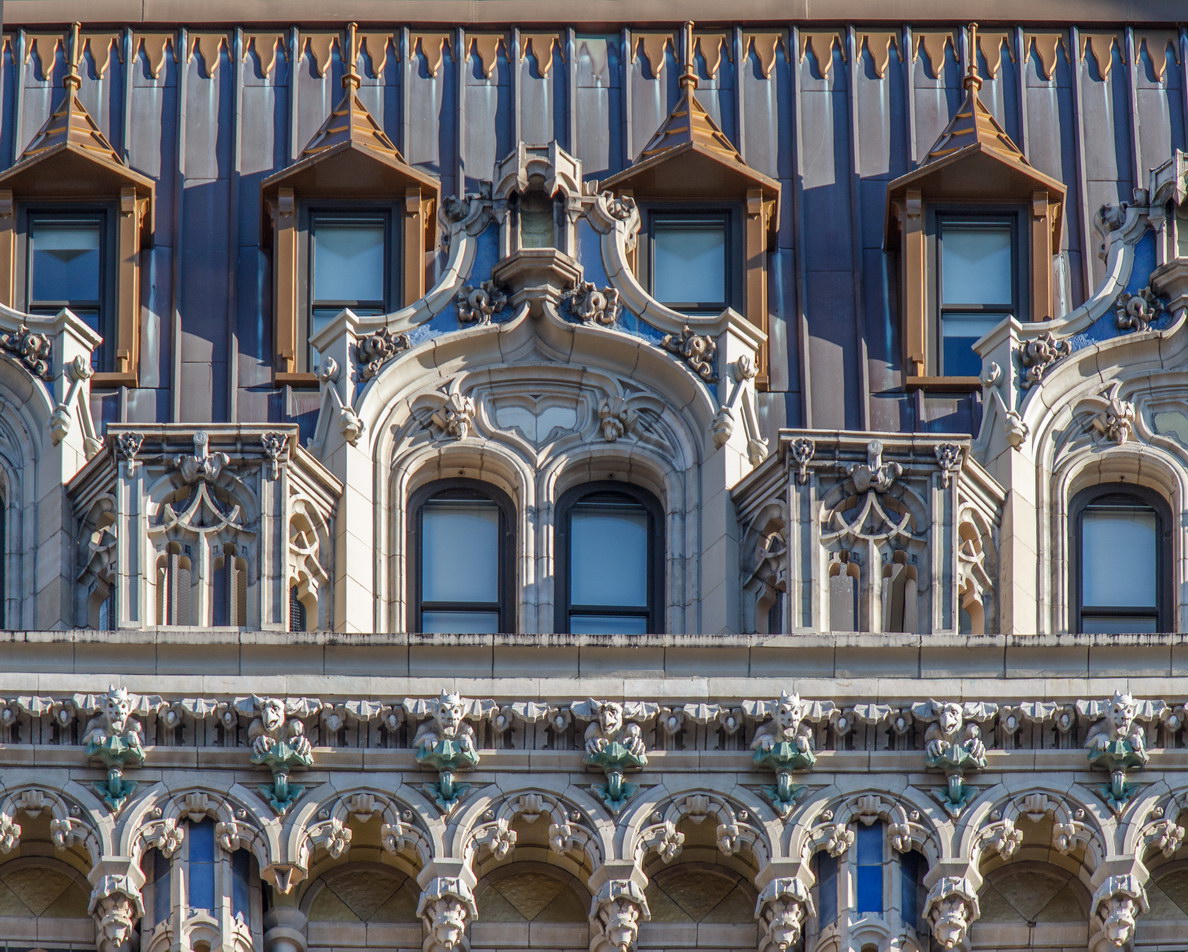
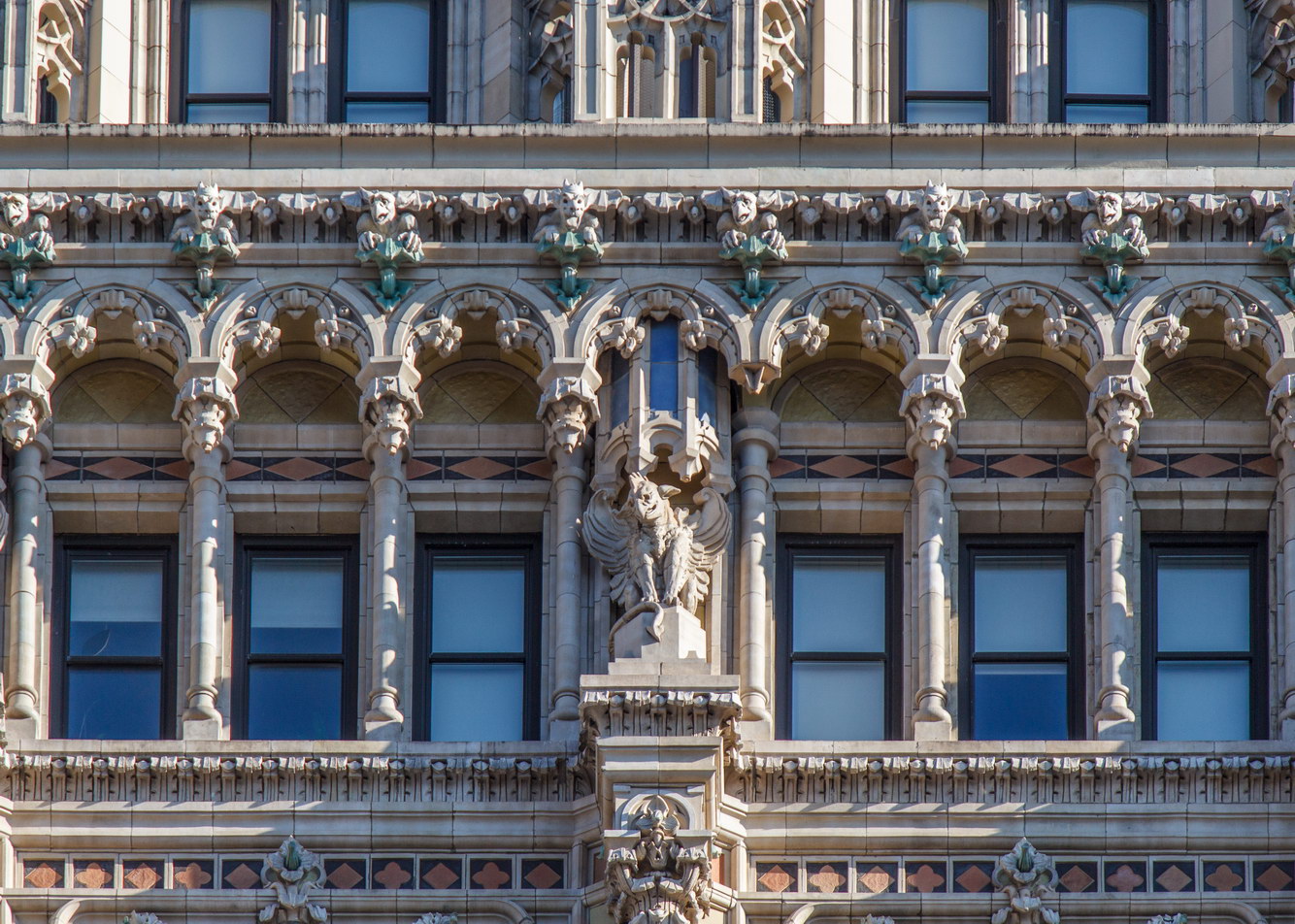
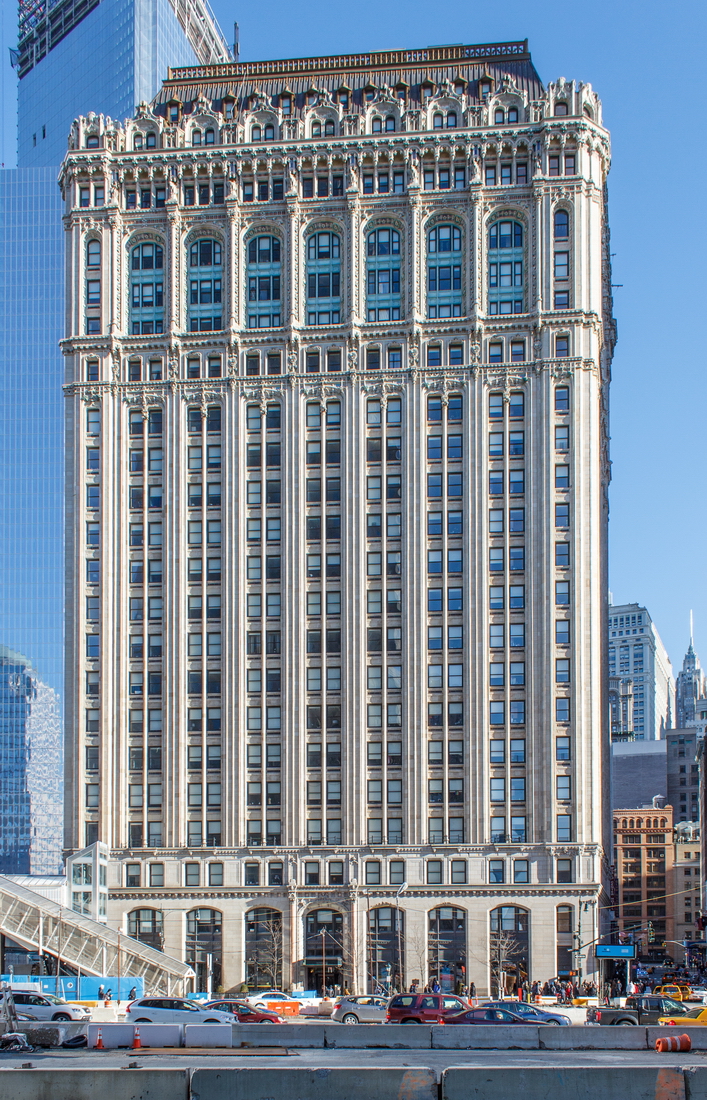
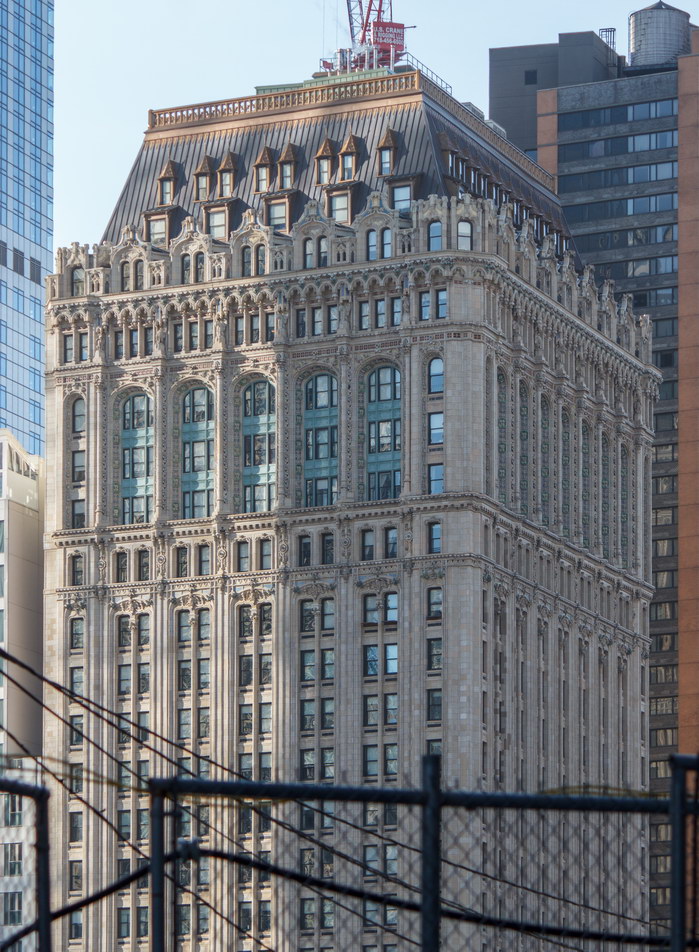
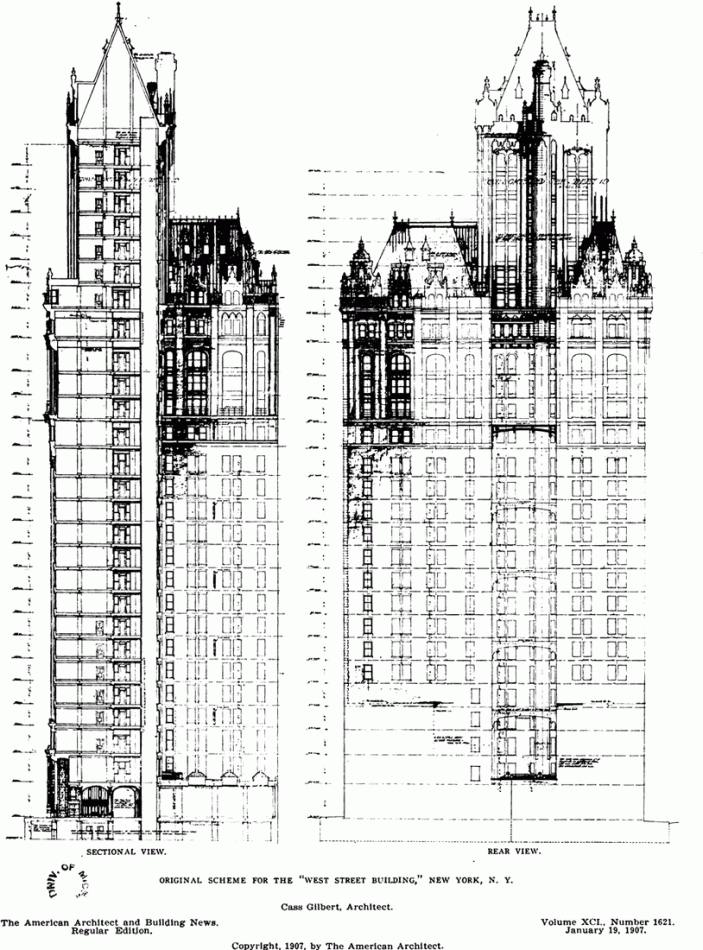







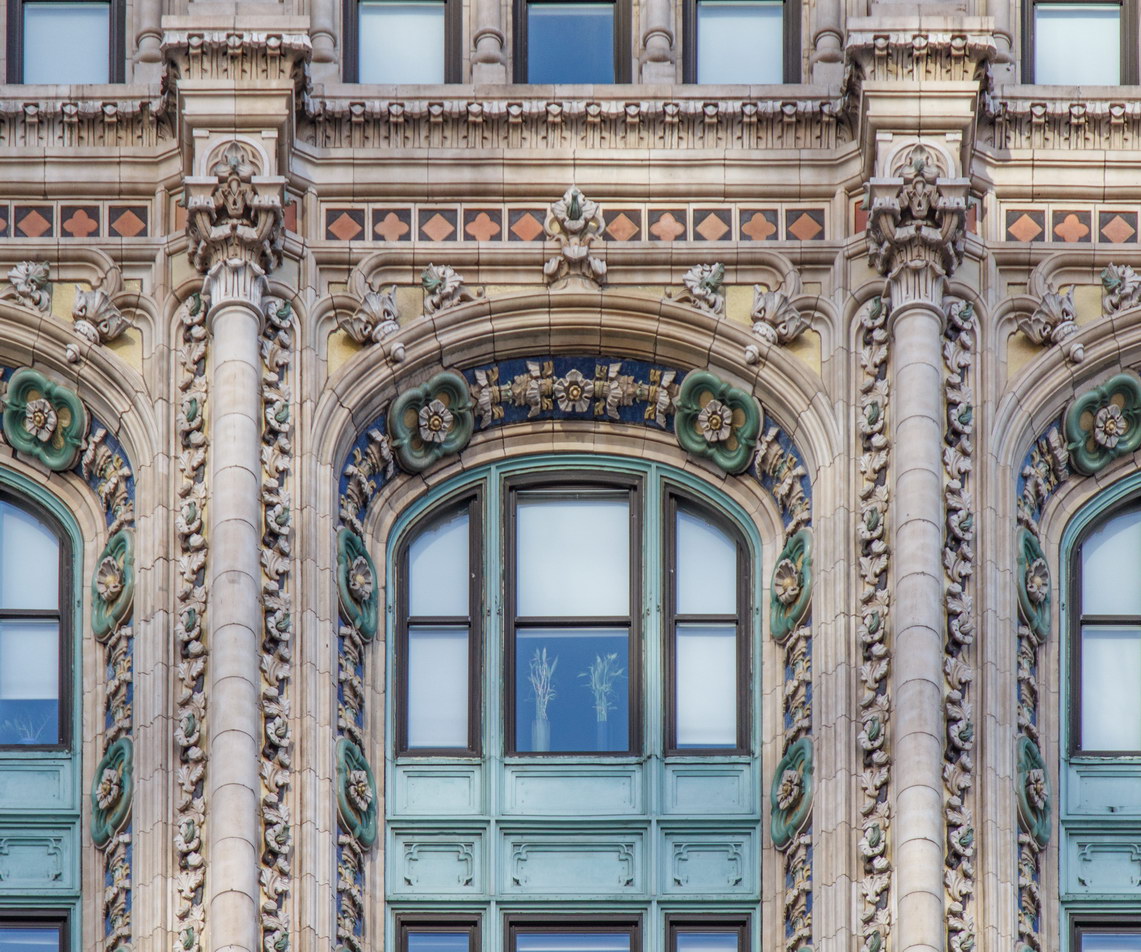
![[90 West Street Building] IMG_3966 10/18/2012 3:16:22 PM [90 West Street Building] IMG_3966 10/18/2012 3:16:22 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/90-west-street/IMG_3966_resize.jpg)
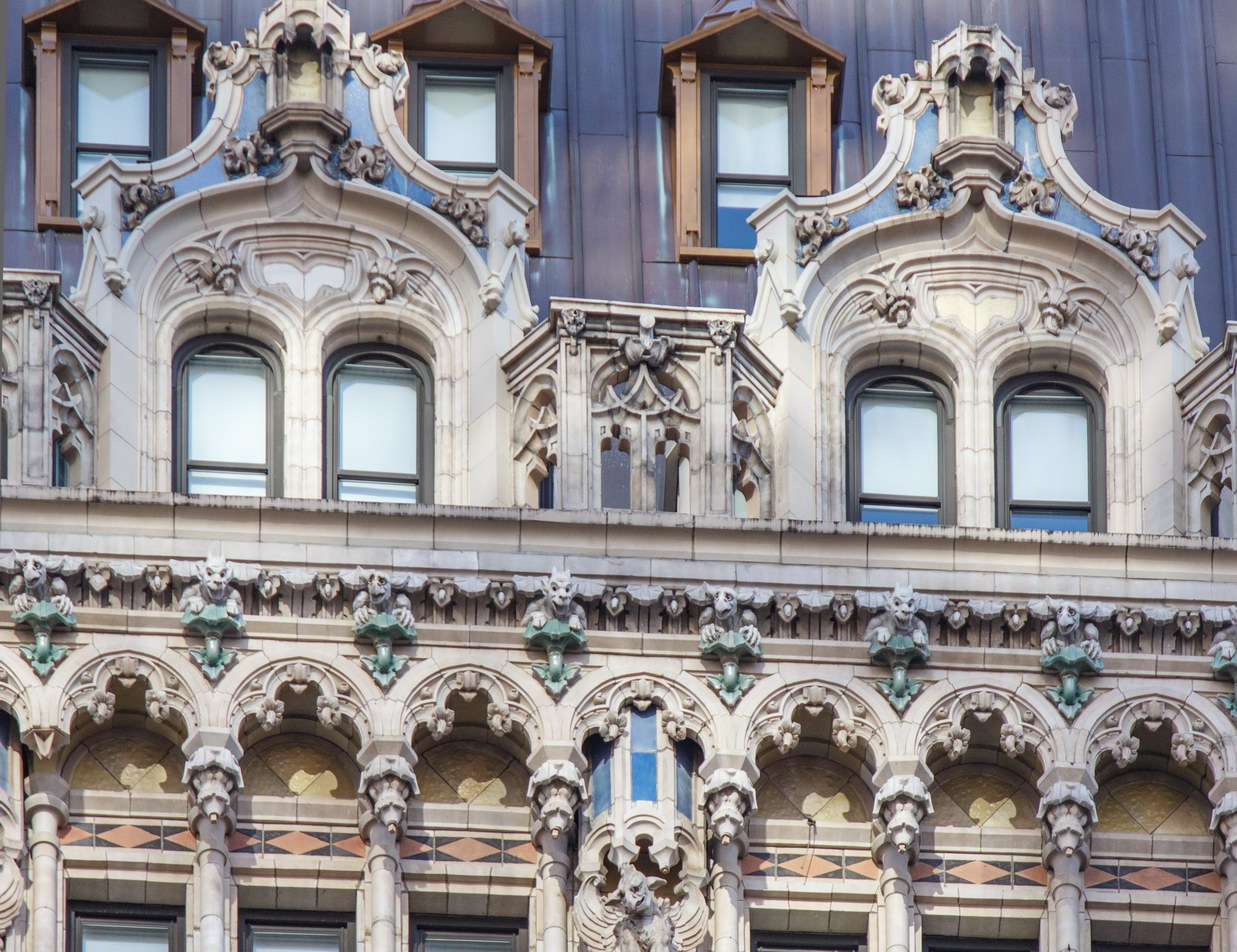
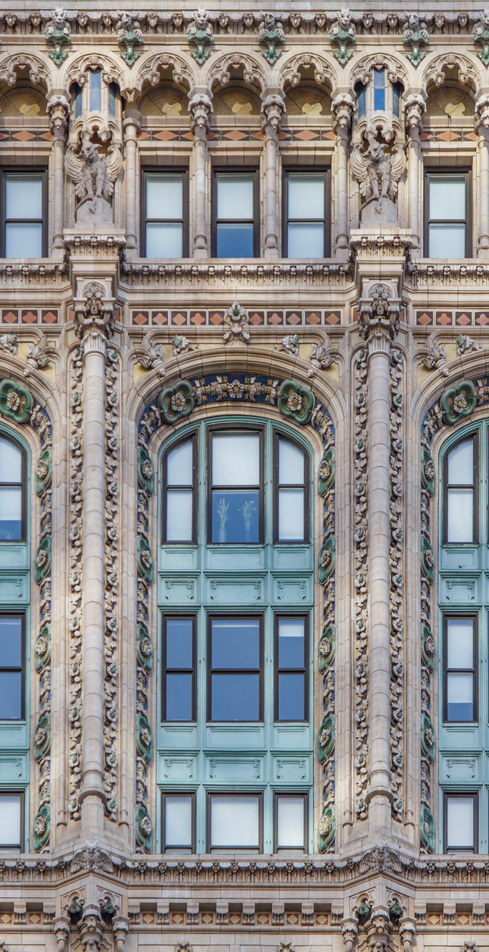
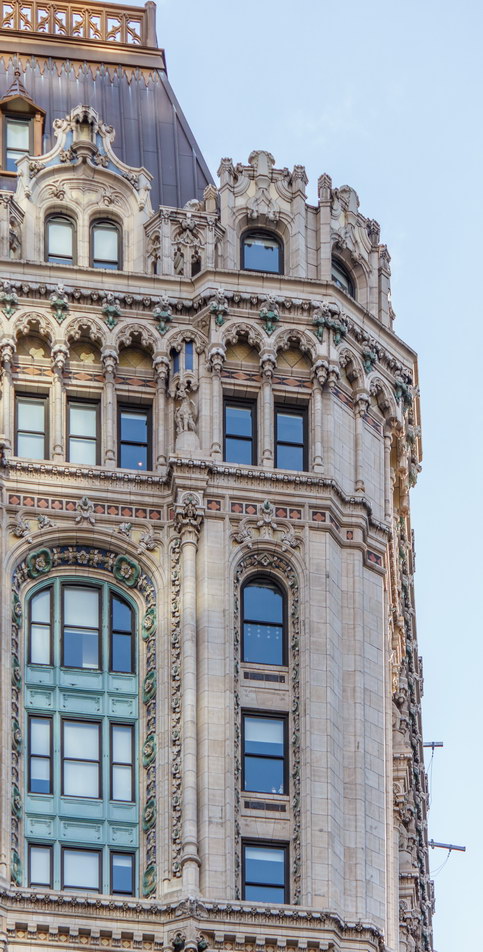




![[90 West Street Building] IMG_6467 12/28/2012 10:29:08 AM [90 West Street Building] IMG_6467 12/28/2012 10:29:08 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/90-west-street/IMG_6467_resize.jpg)
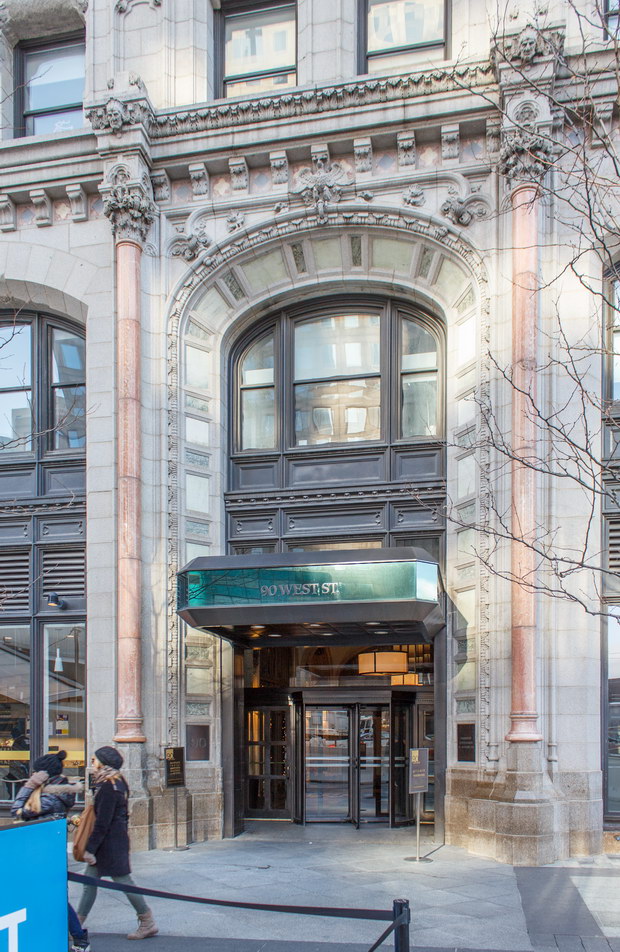
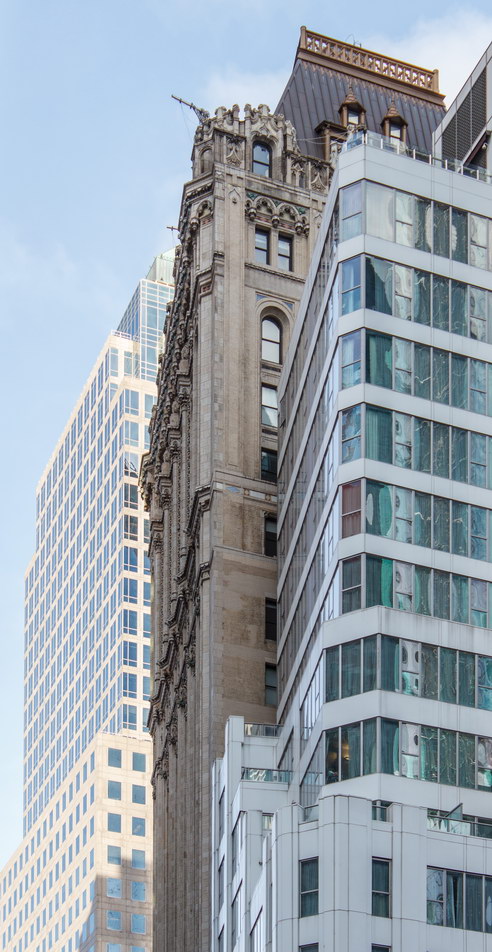
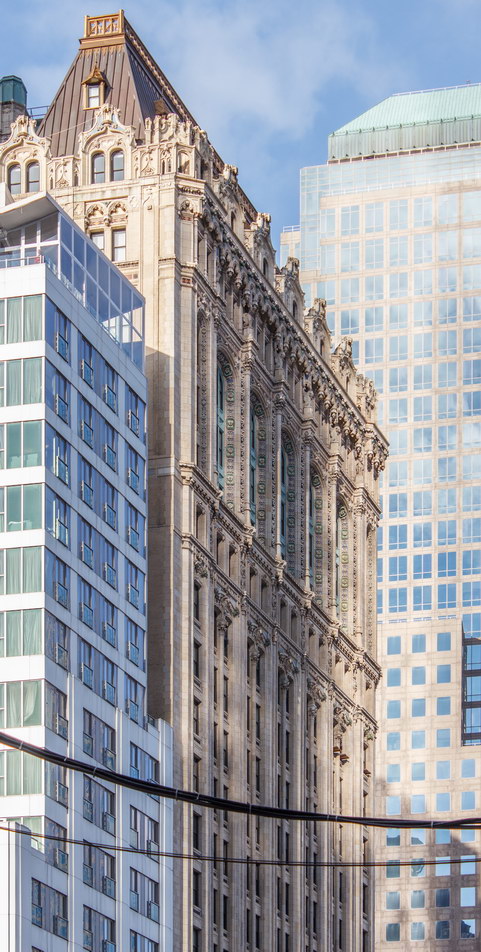




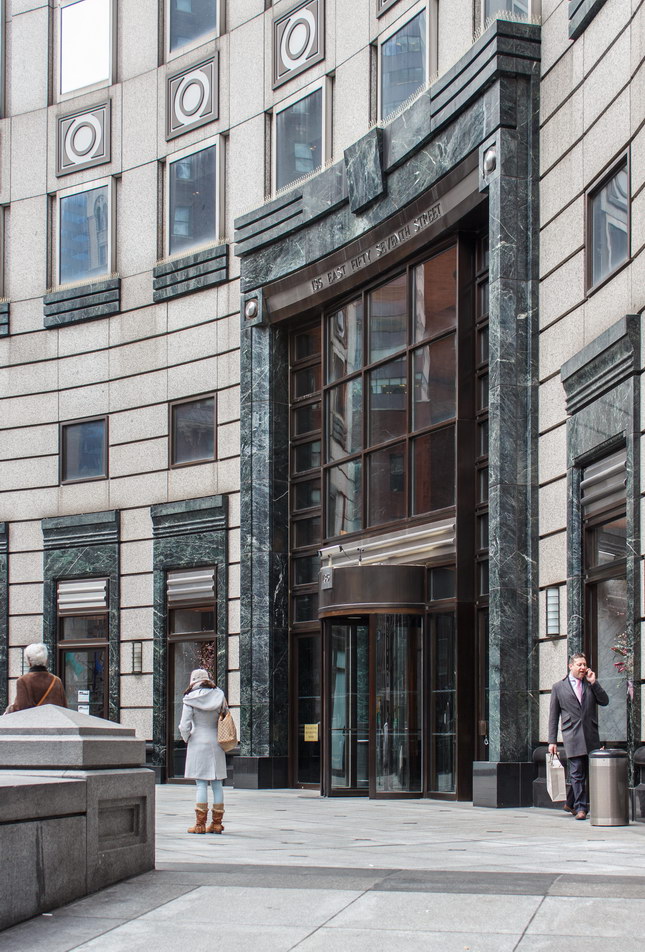
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6545 1/10/2013 3:34:47 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6545 1/10/2013 3:34:47 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6545_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6549 1/10/2013 3:37:39 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6549 1/10/2013 3:37:39 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6549_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6550 1/10/2013 3:39:03 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6550 1/10/2013 3:39:03 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6550_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6551 1/10/2013 3:39:33 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6551 1/10/2013 3:39:33 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6551_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6553 1/10/2013 3:41:24 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6553 1/10/2013 3:41:24 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6553_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6559 1/10/2013 3:45:53 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6559 1/10/2013 3:45:53 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6559_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6562 1/10/2013 3:47:08 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6562 1/10/2013 3:47:08 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6562_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6565 1/10/2013 3:47:45 PM [Herald Towers] IMG_6565 1/10/2013 3:47:45 PM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6565_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6614 7/12/2012 7:40:06 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6614 7/12/2012 7:40:06 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6614_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6630 7/12/2012 7:48:43 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6630 7/12/2012 7:48:43 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6630_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6632 7/12/2012 7:48:55 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6632 7/12/2012 7:48:55 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6632_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6635 7/12/2012 7:49:15 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6635 7/12/2012 7:49:15 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6635_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6642 7/12/2012 7:53:59 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6642 7/12/2012 7:53:59 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6642_resize.jpg)
![[Herald Towers] IMG_6645 7/12/2012 7:54:50 AM [Herald Towers] IMG_6645 7/12/2012 7:54:50 AM](https://www.newyorkitecture.com/wp-content/gallery/herald-towers/IMG_6645_resize.jpg)



























































































