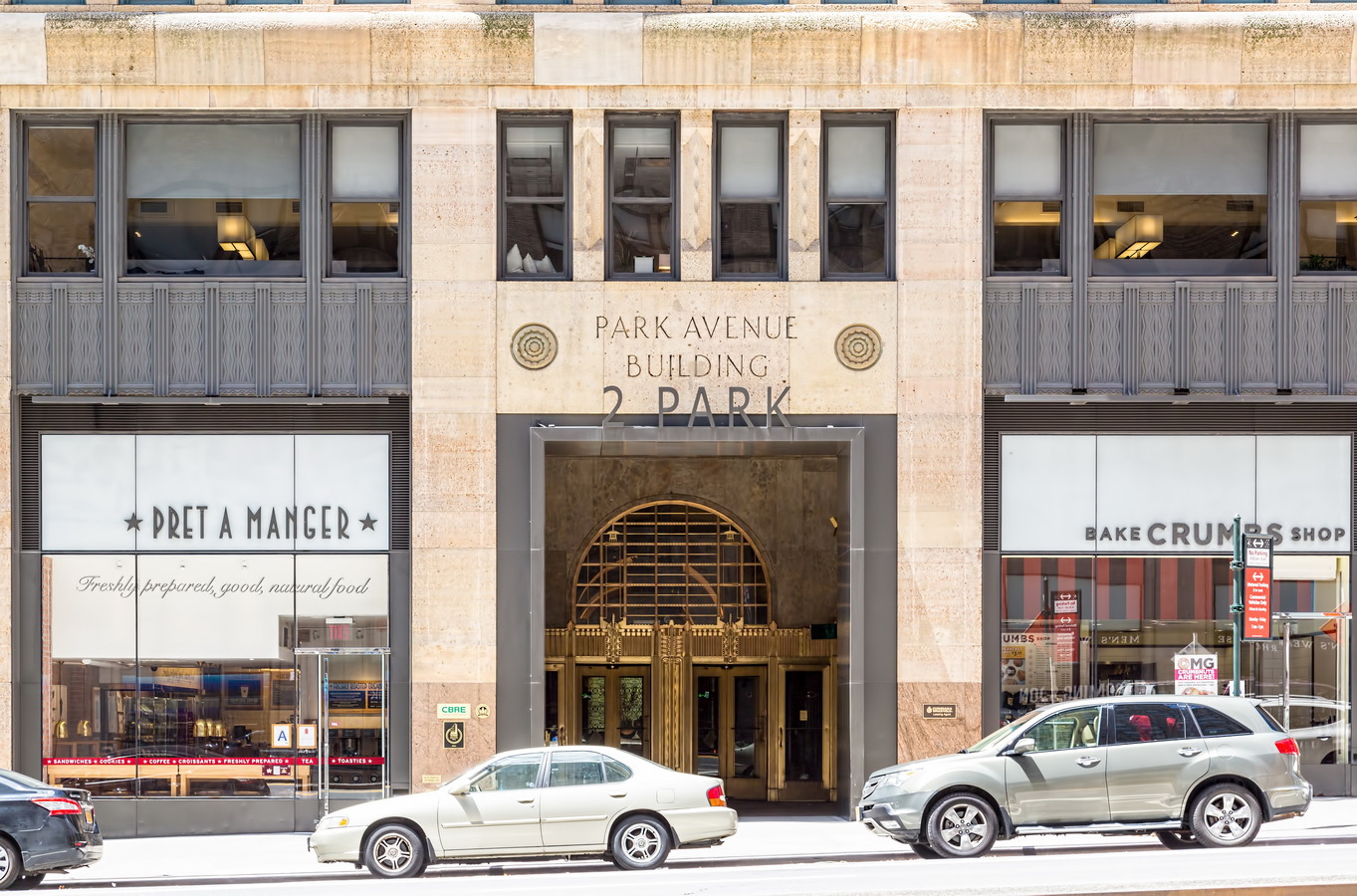
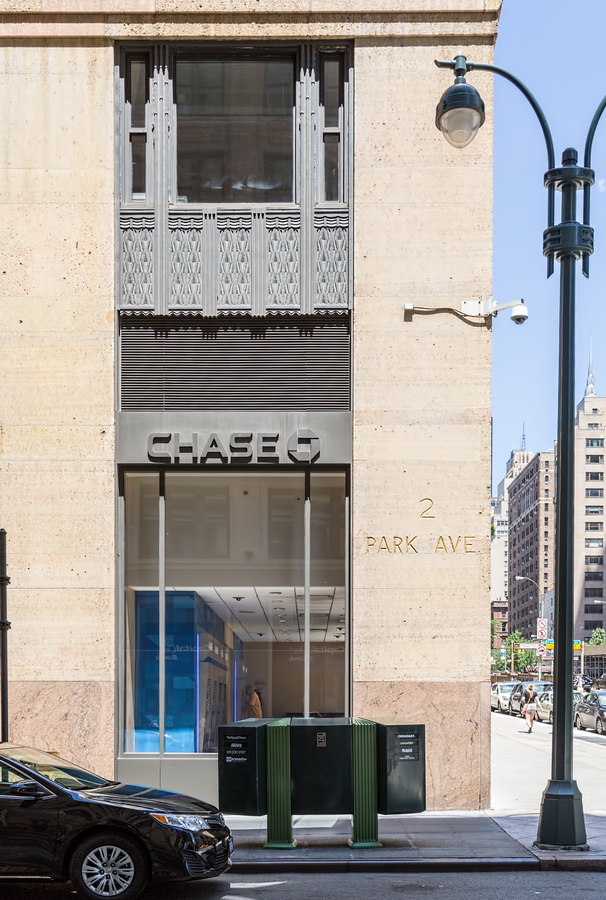
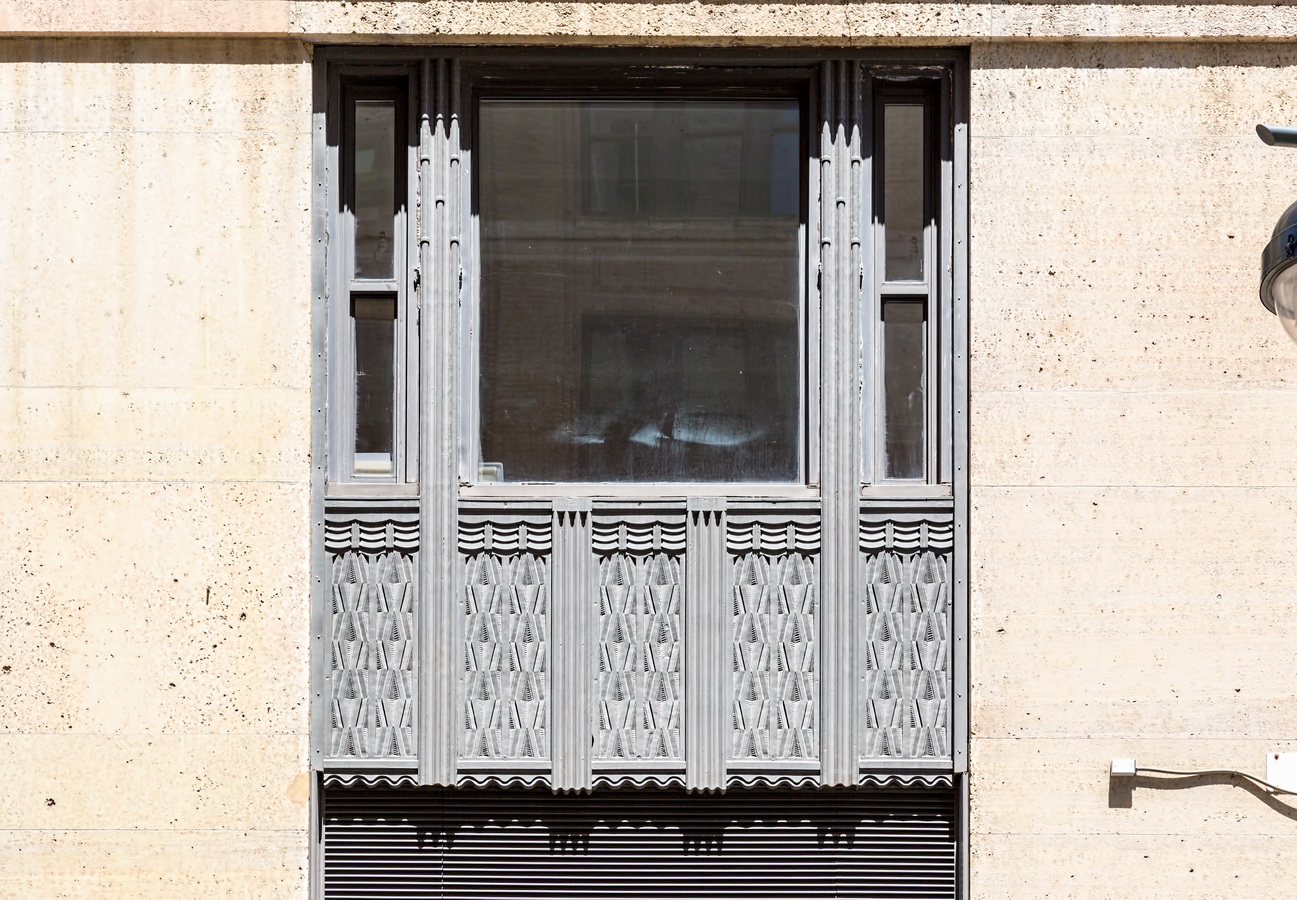
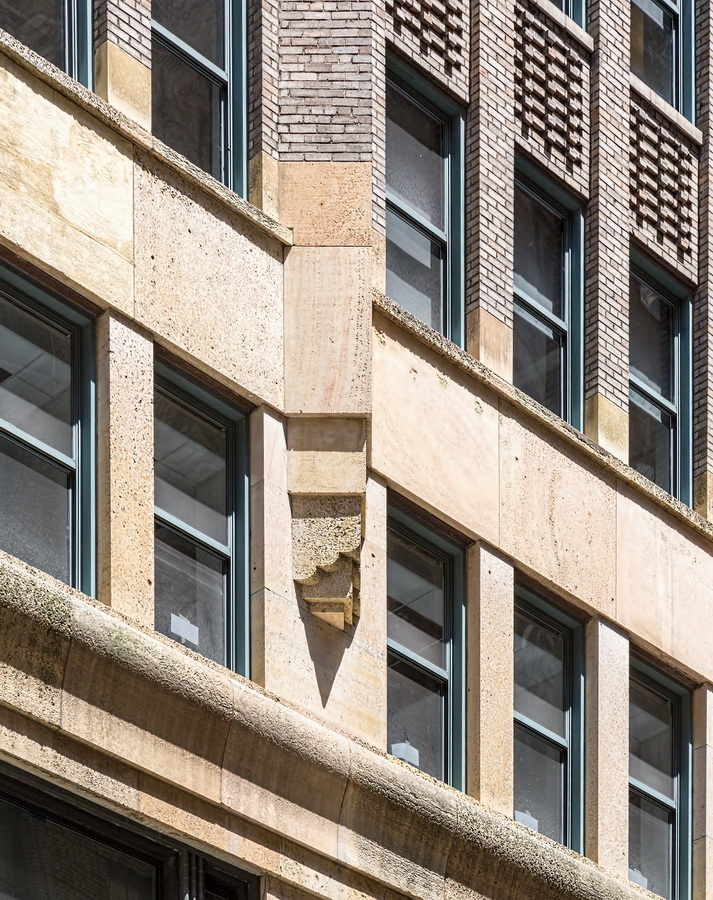
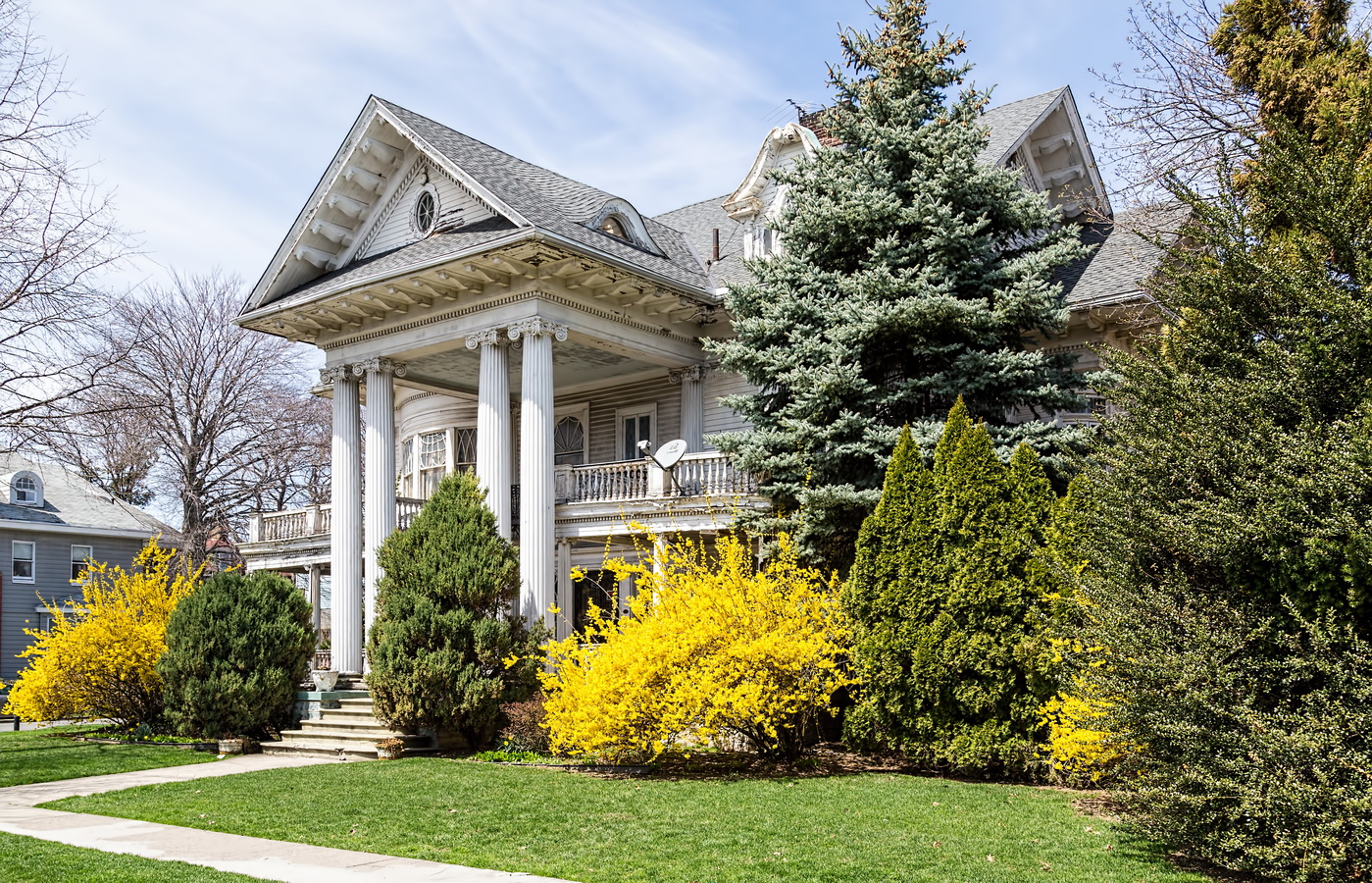
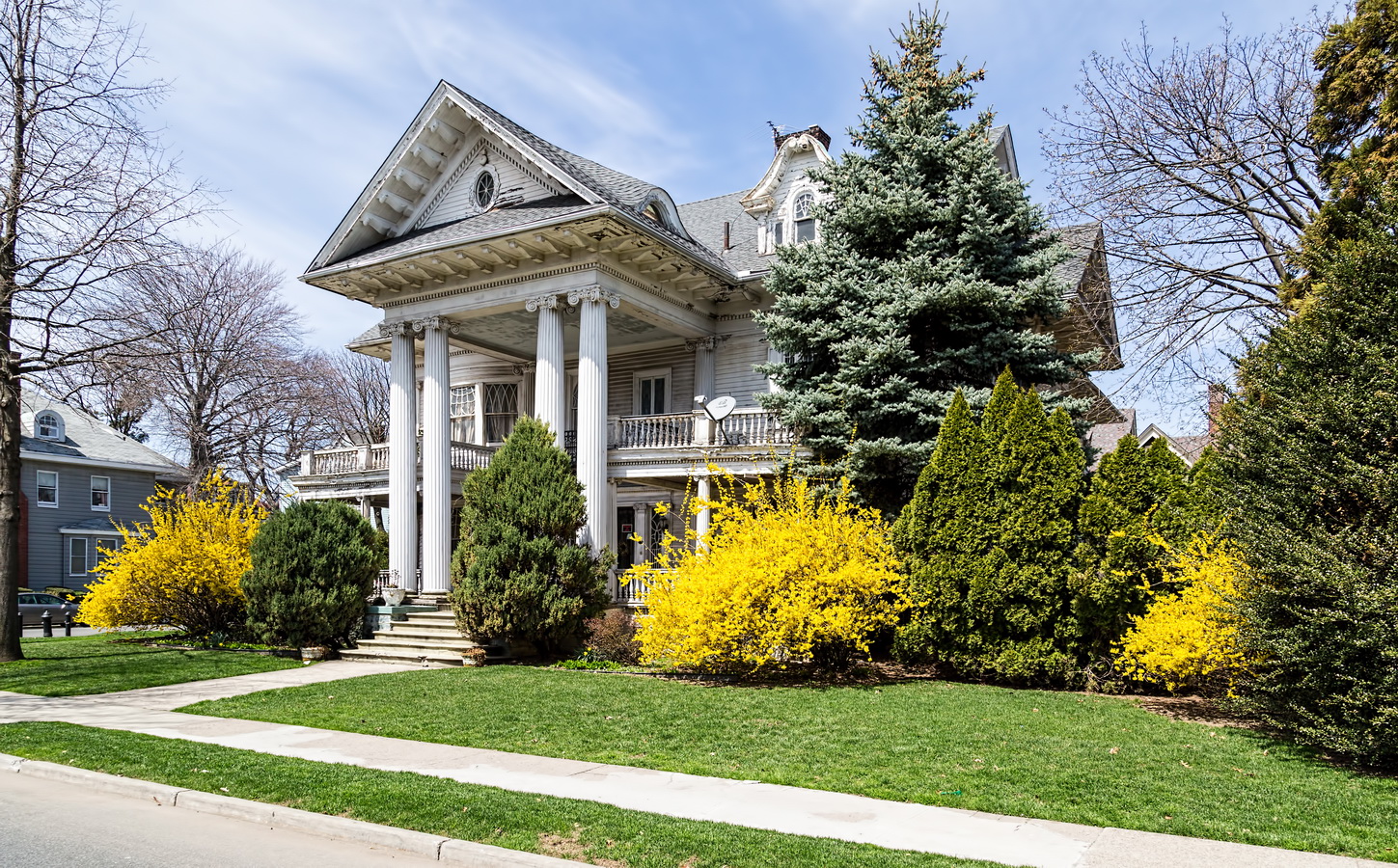
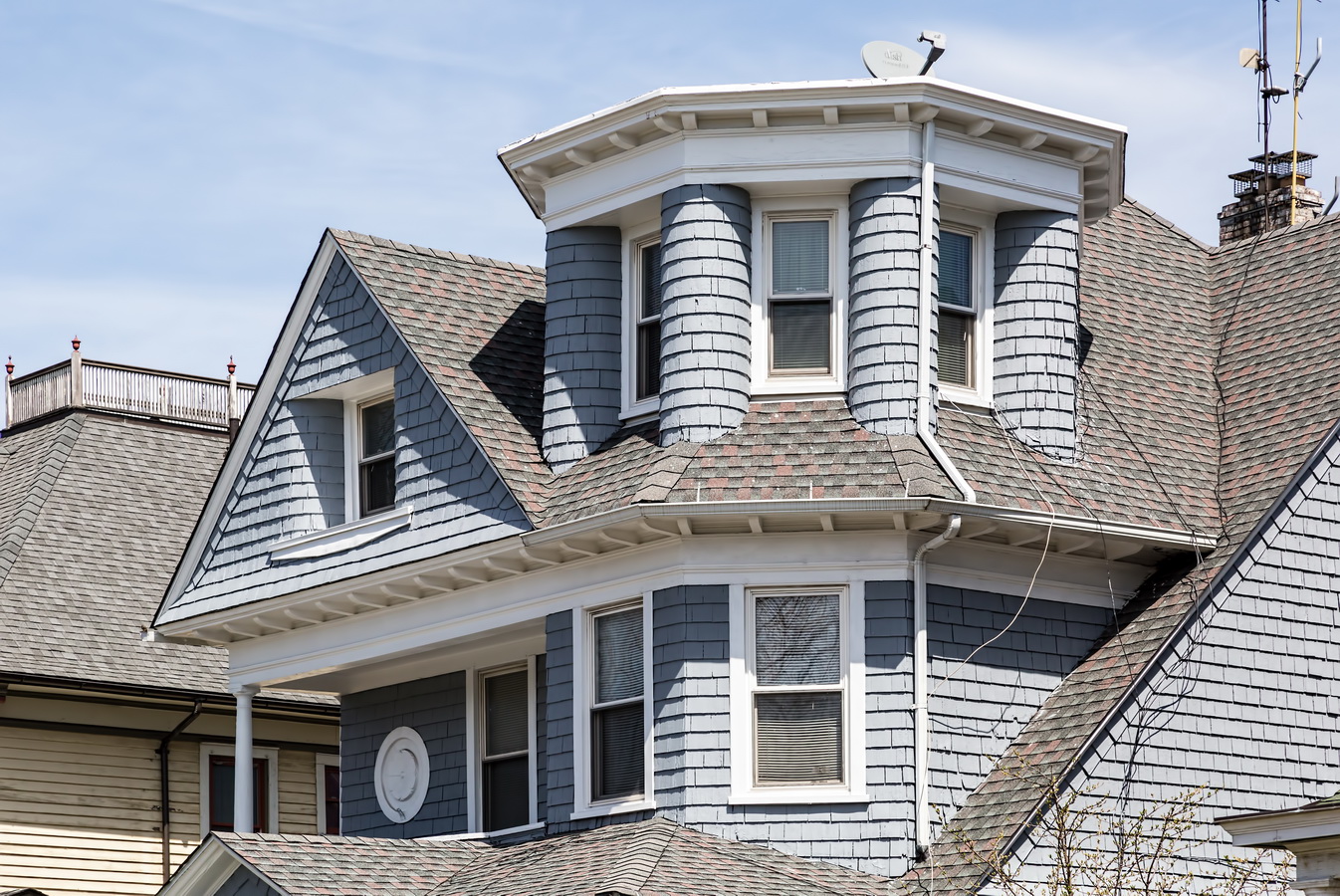
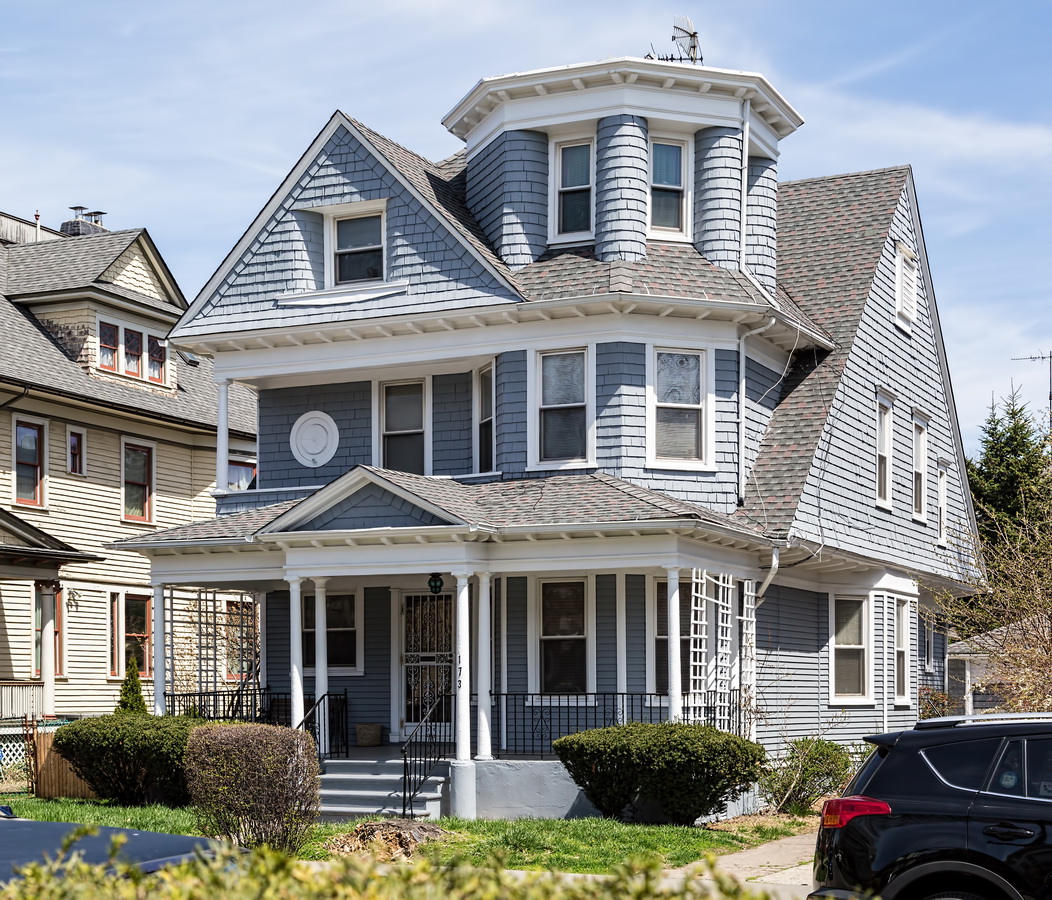
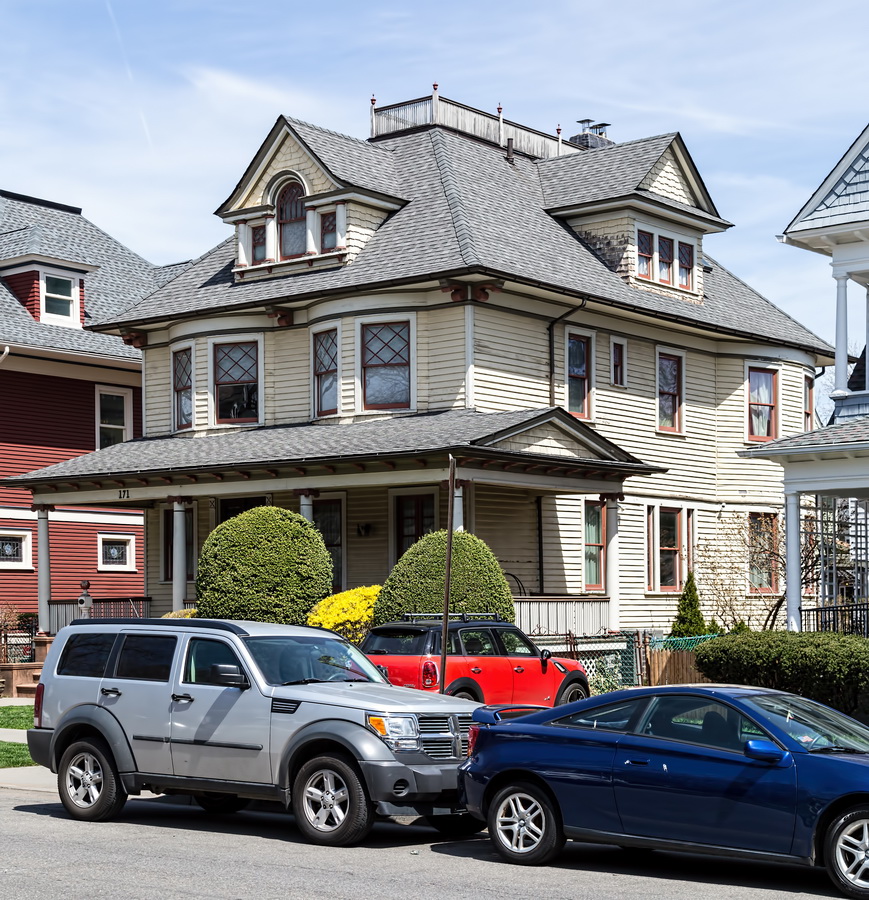
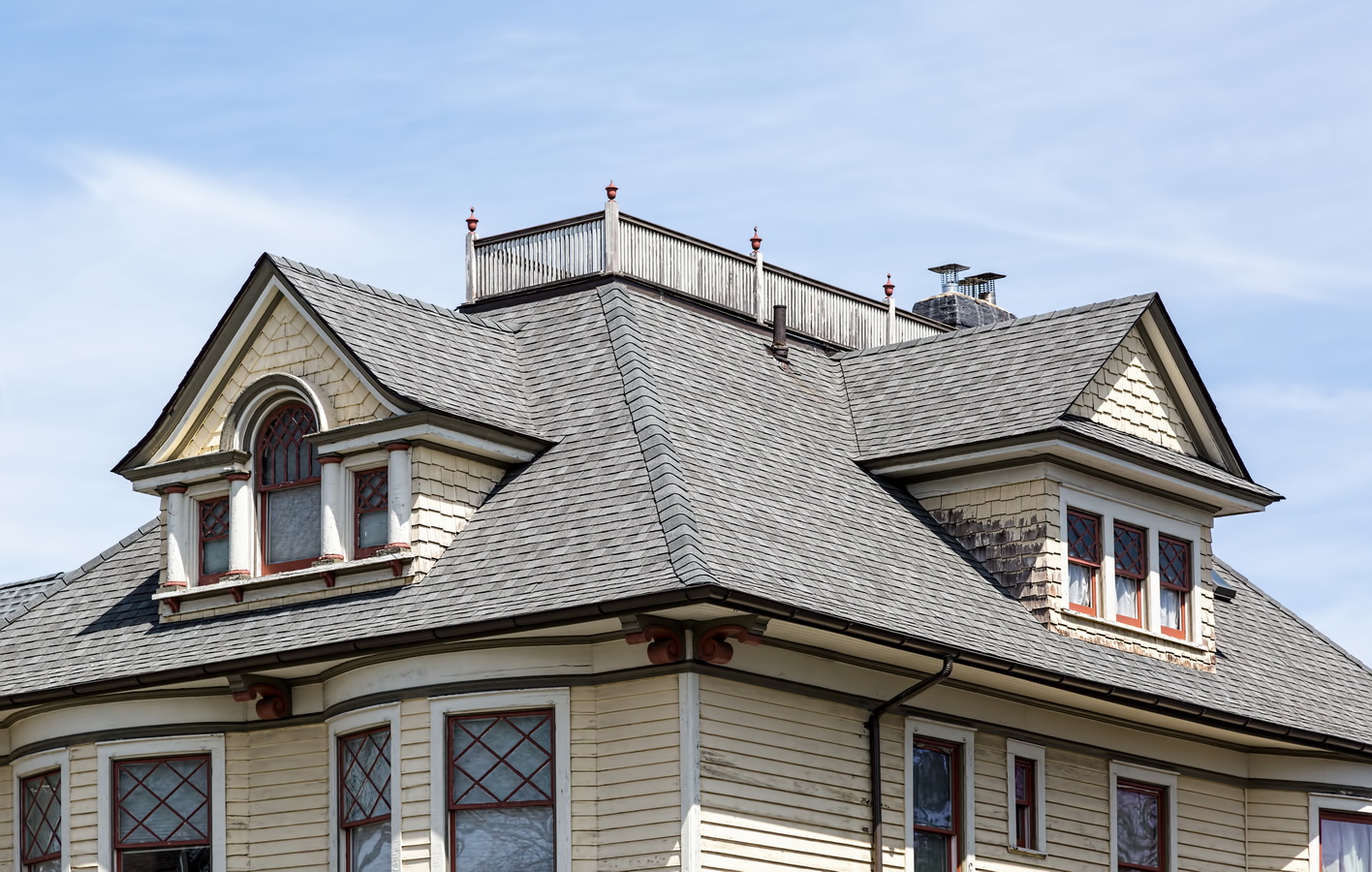
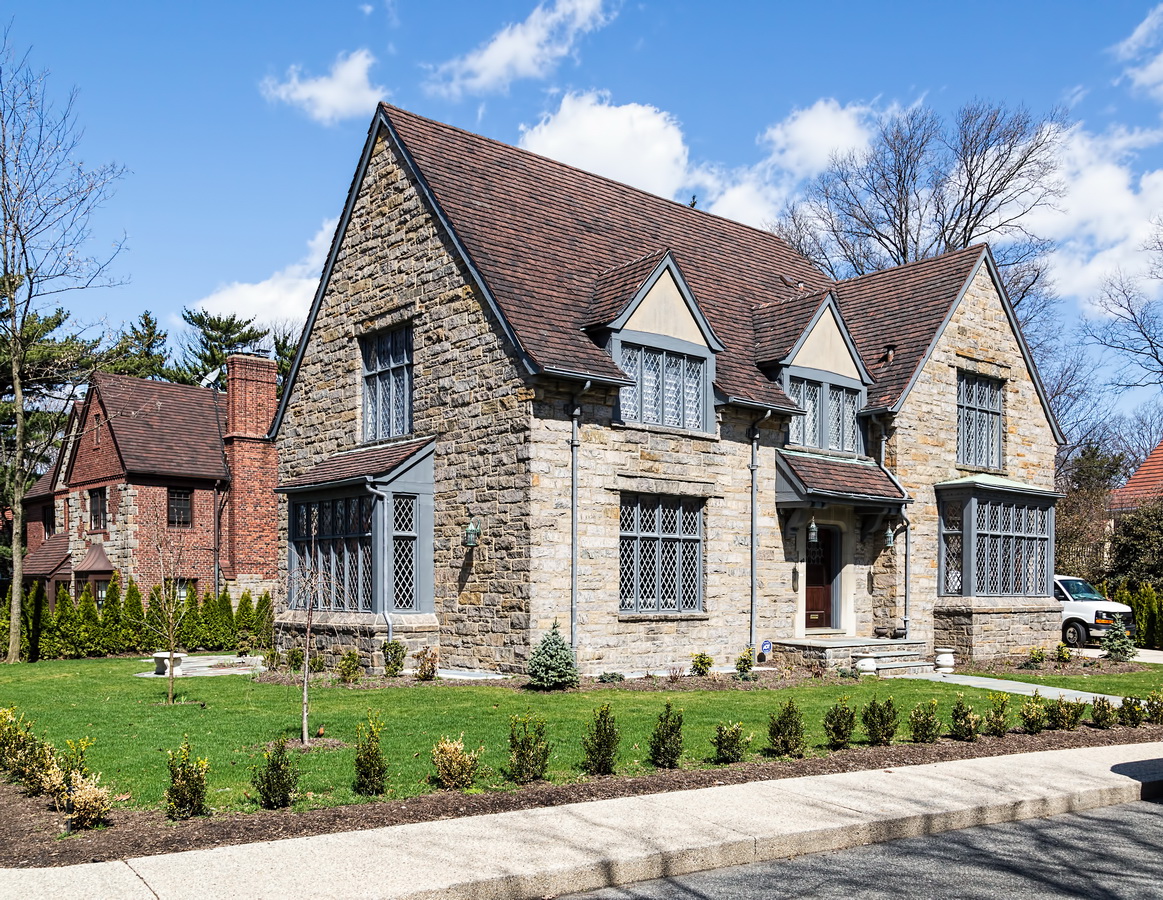
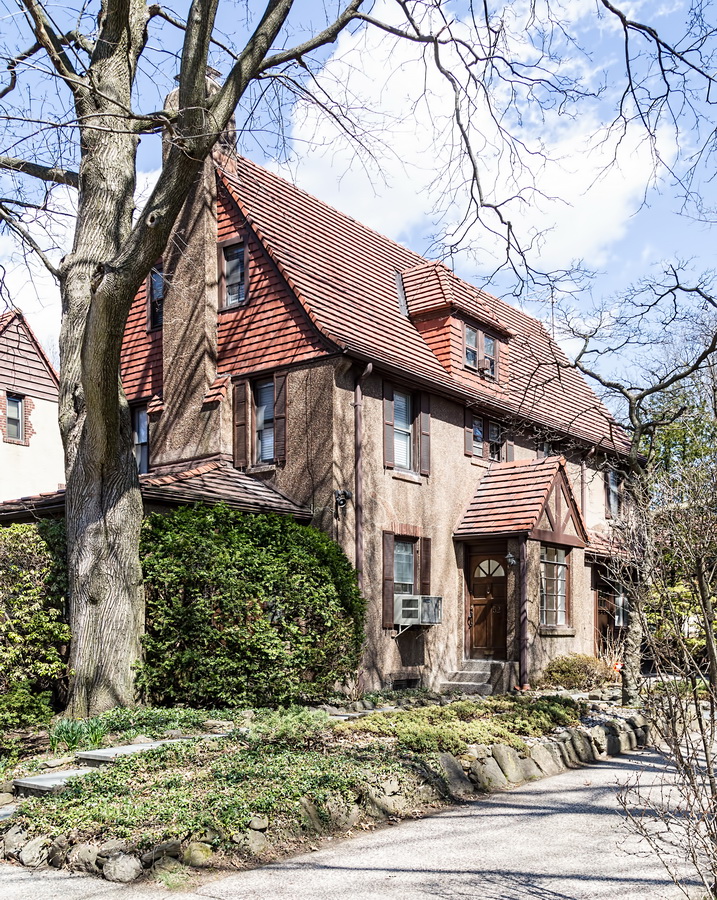
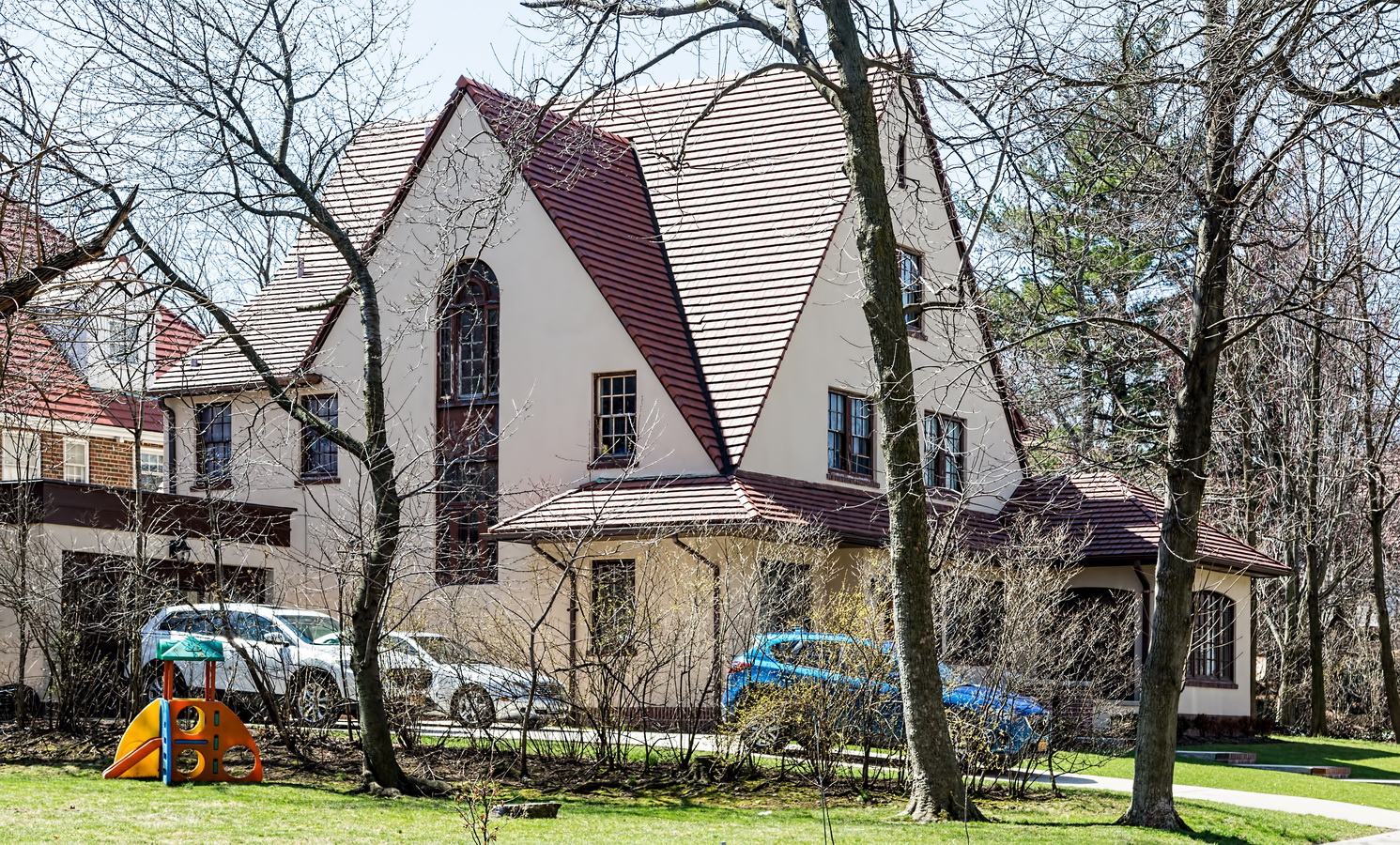
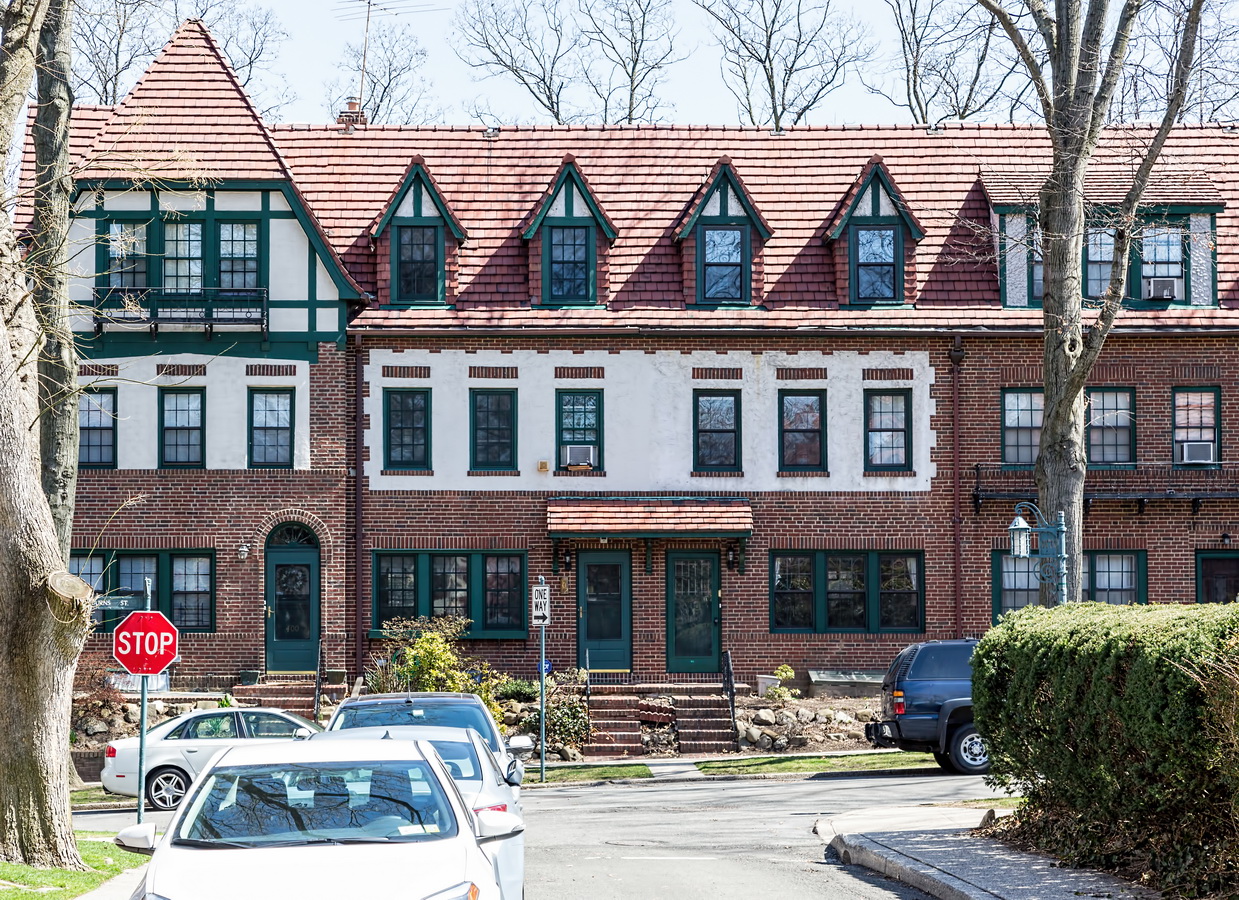
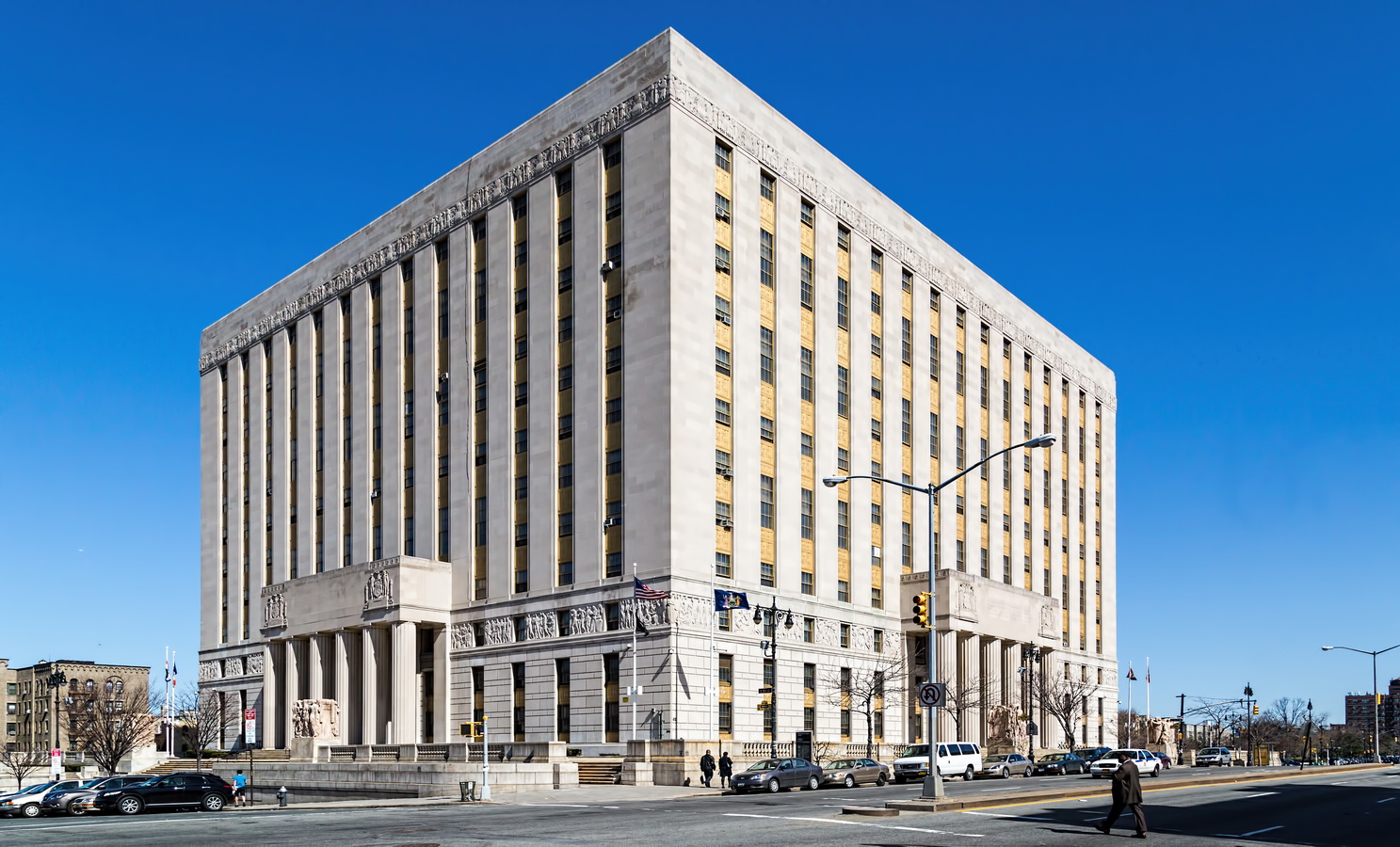
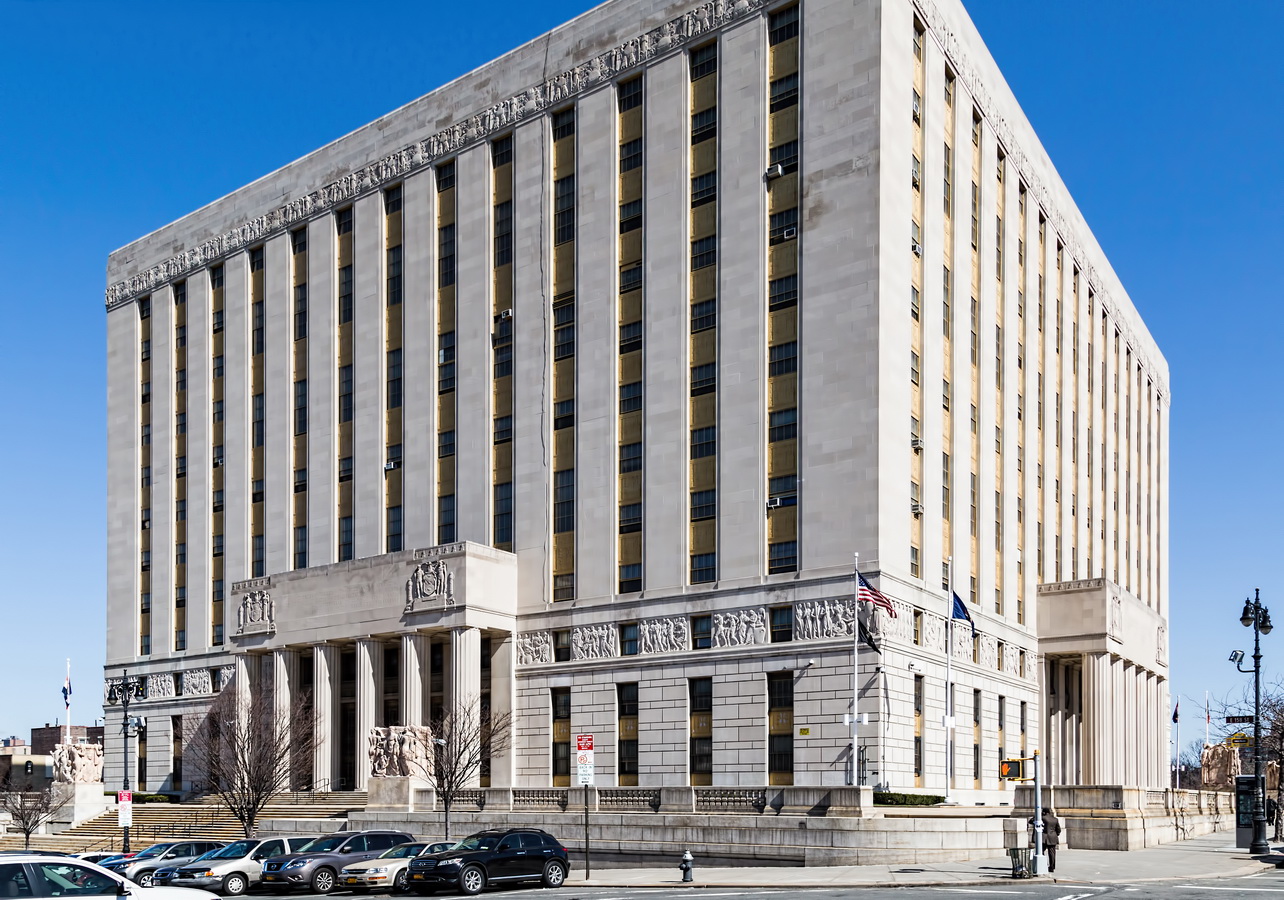
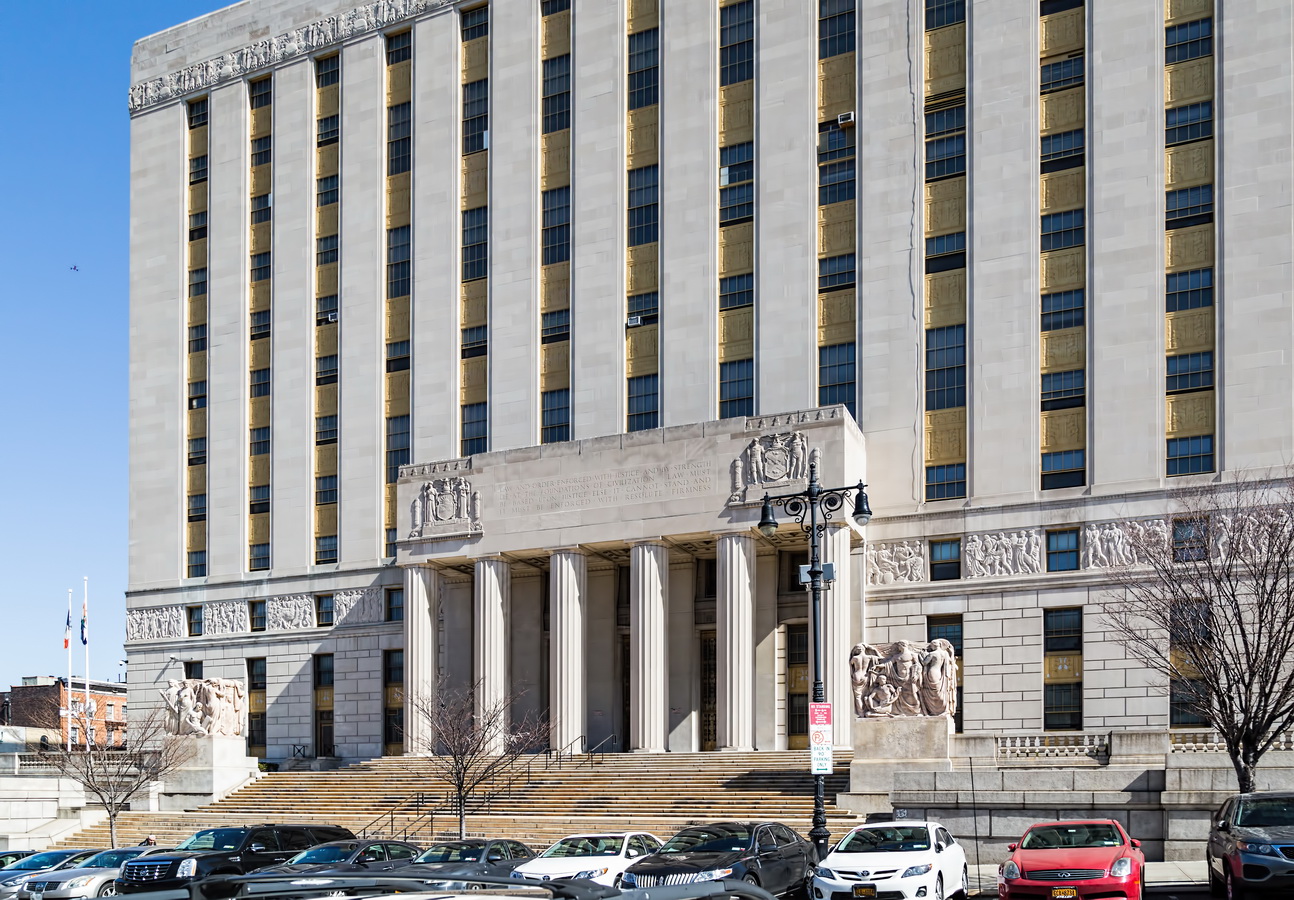
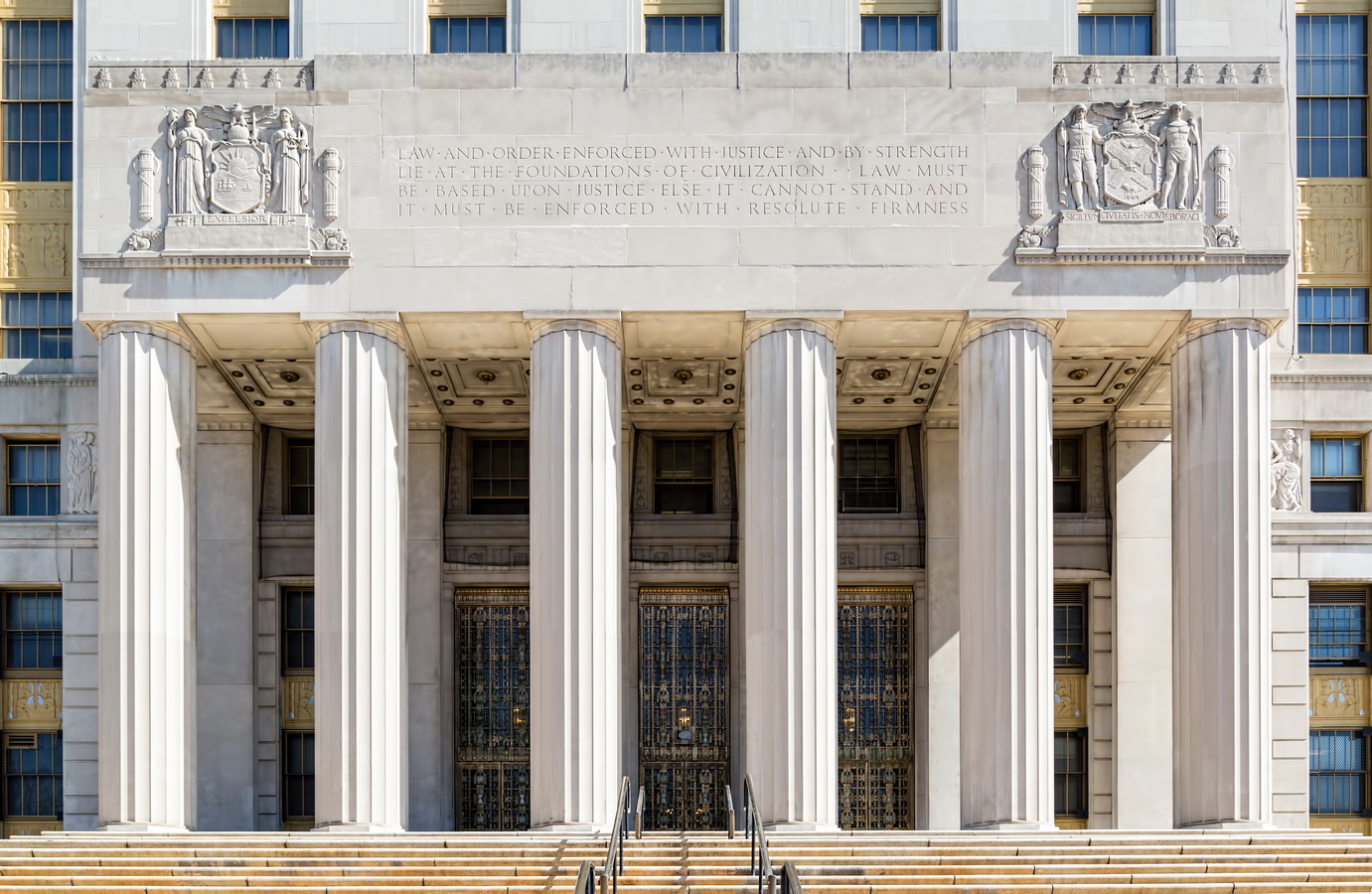
Mapping New York City is a full-time endeavor of hundreds, if not thousands, of amateur and professional digital cartographers. Thanks to the paid and unpaid users, it’s getting easier and easier to find anything or any place in the Big Apple.
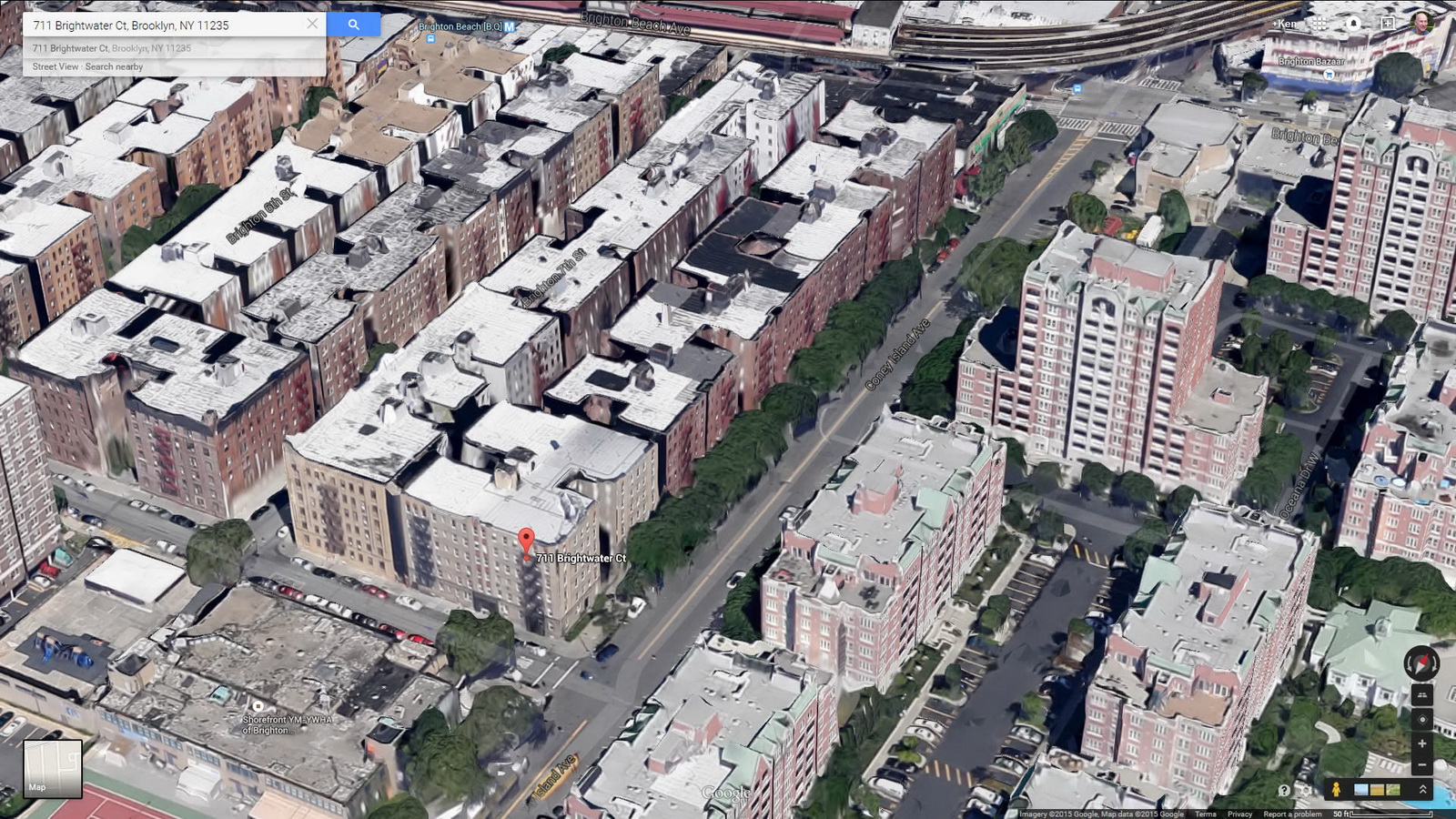
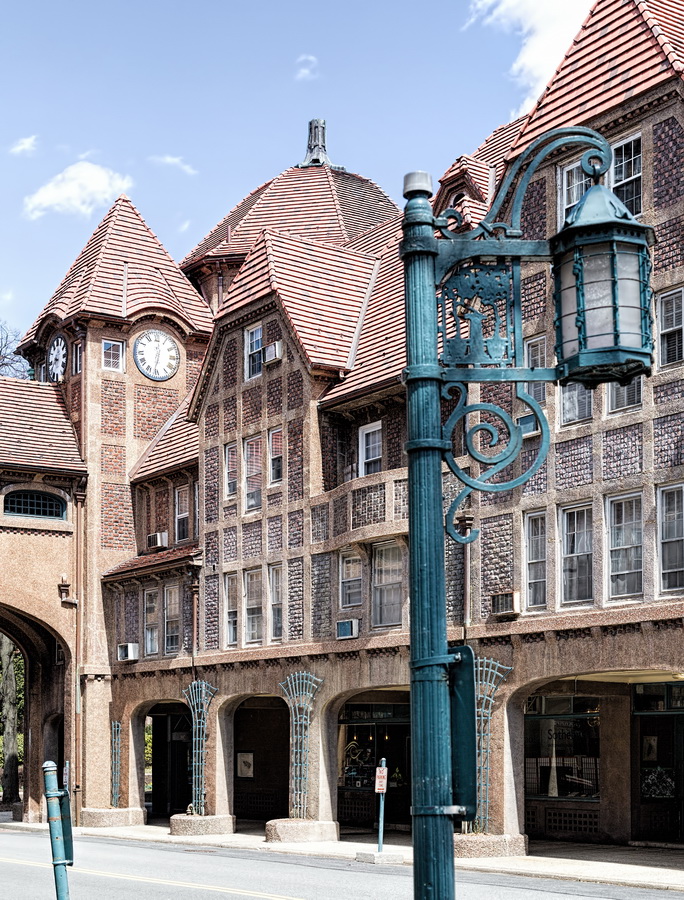
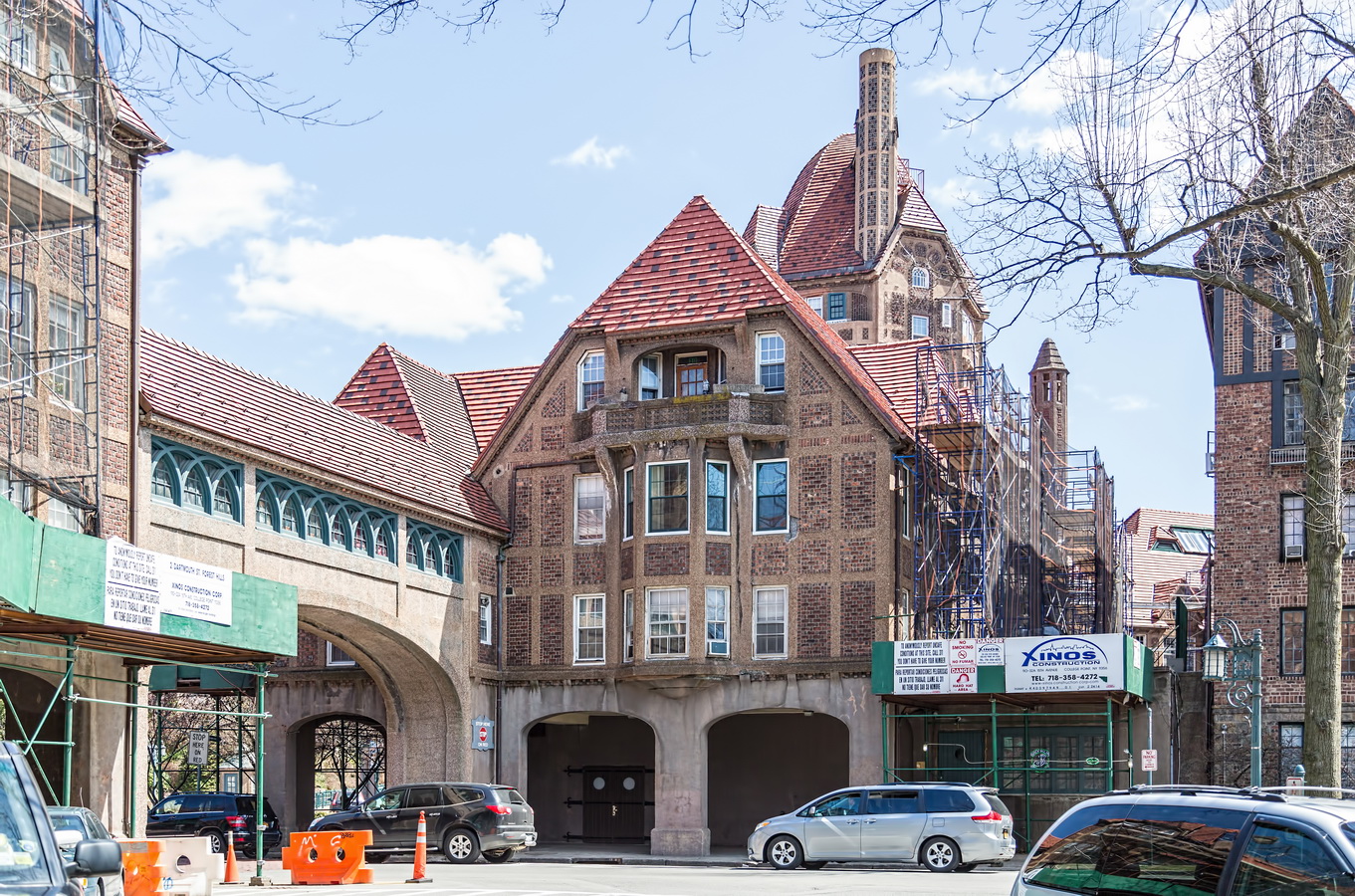
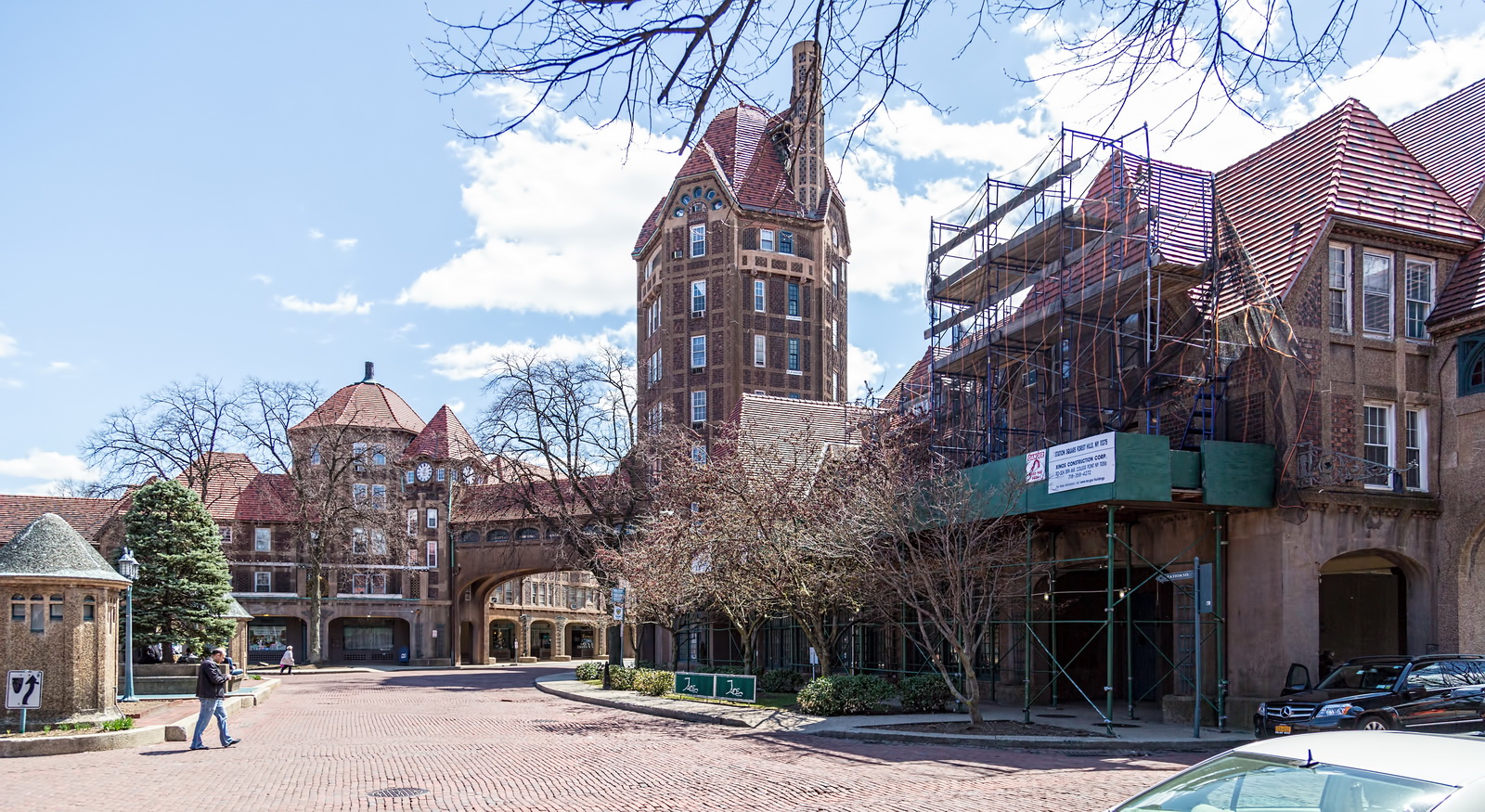
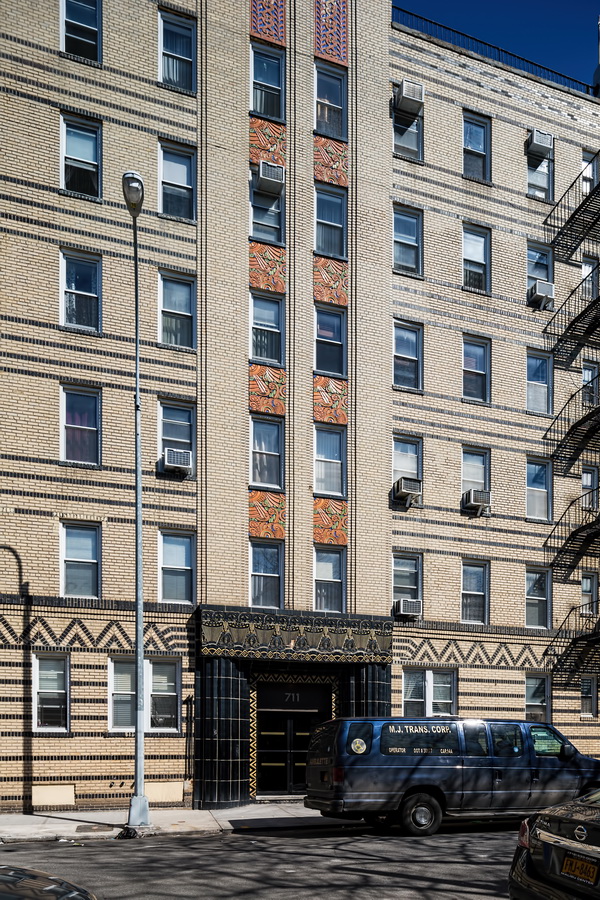
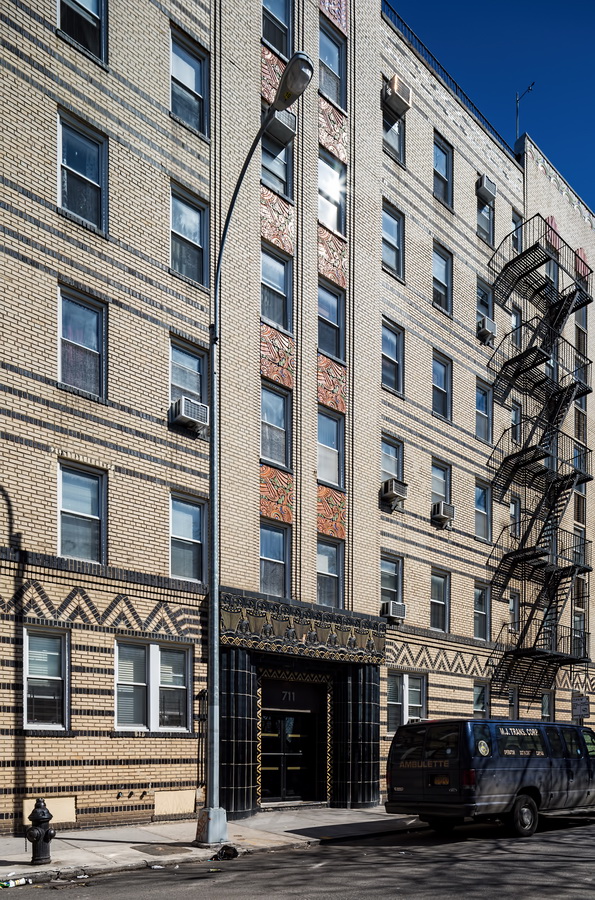
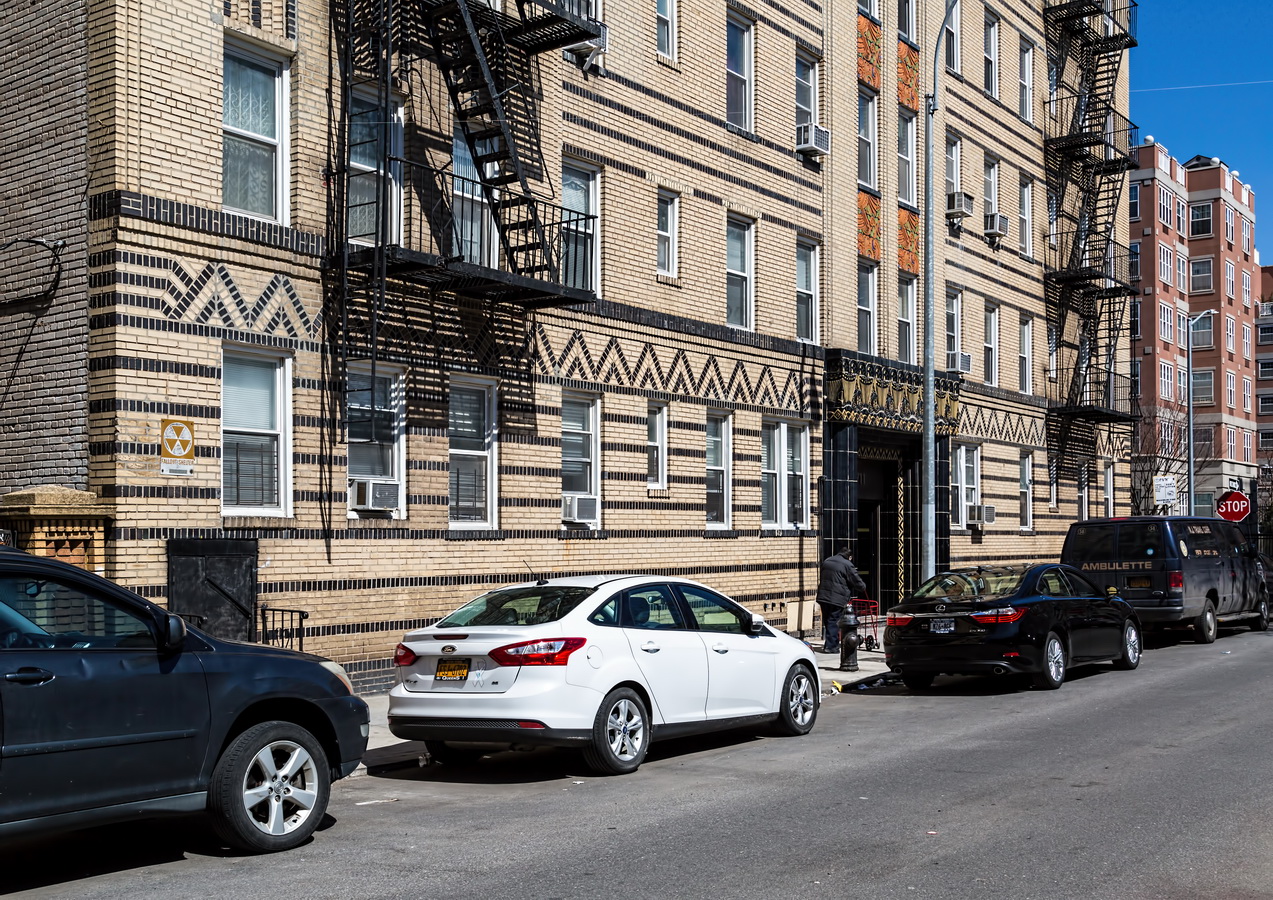
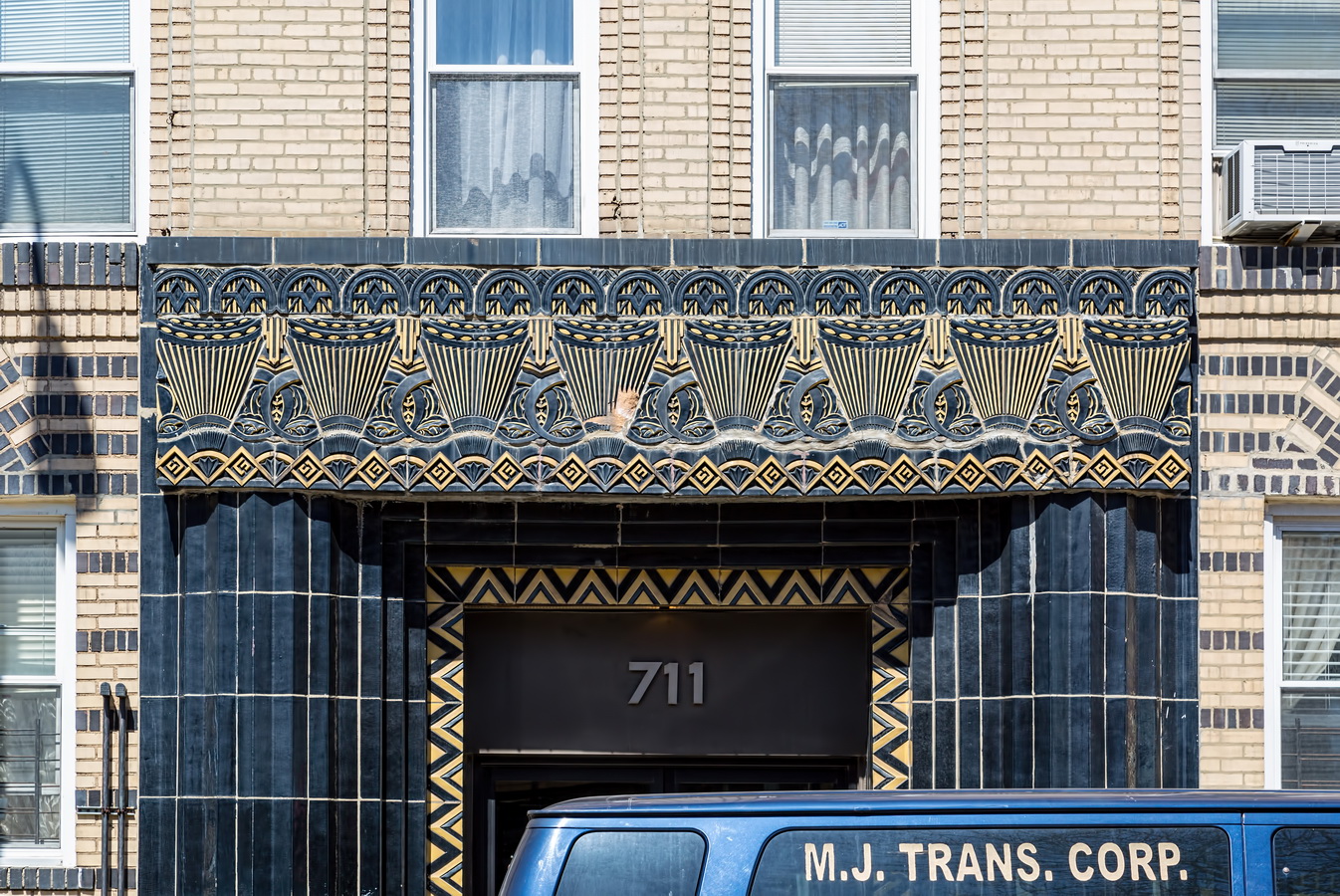
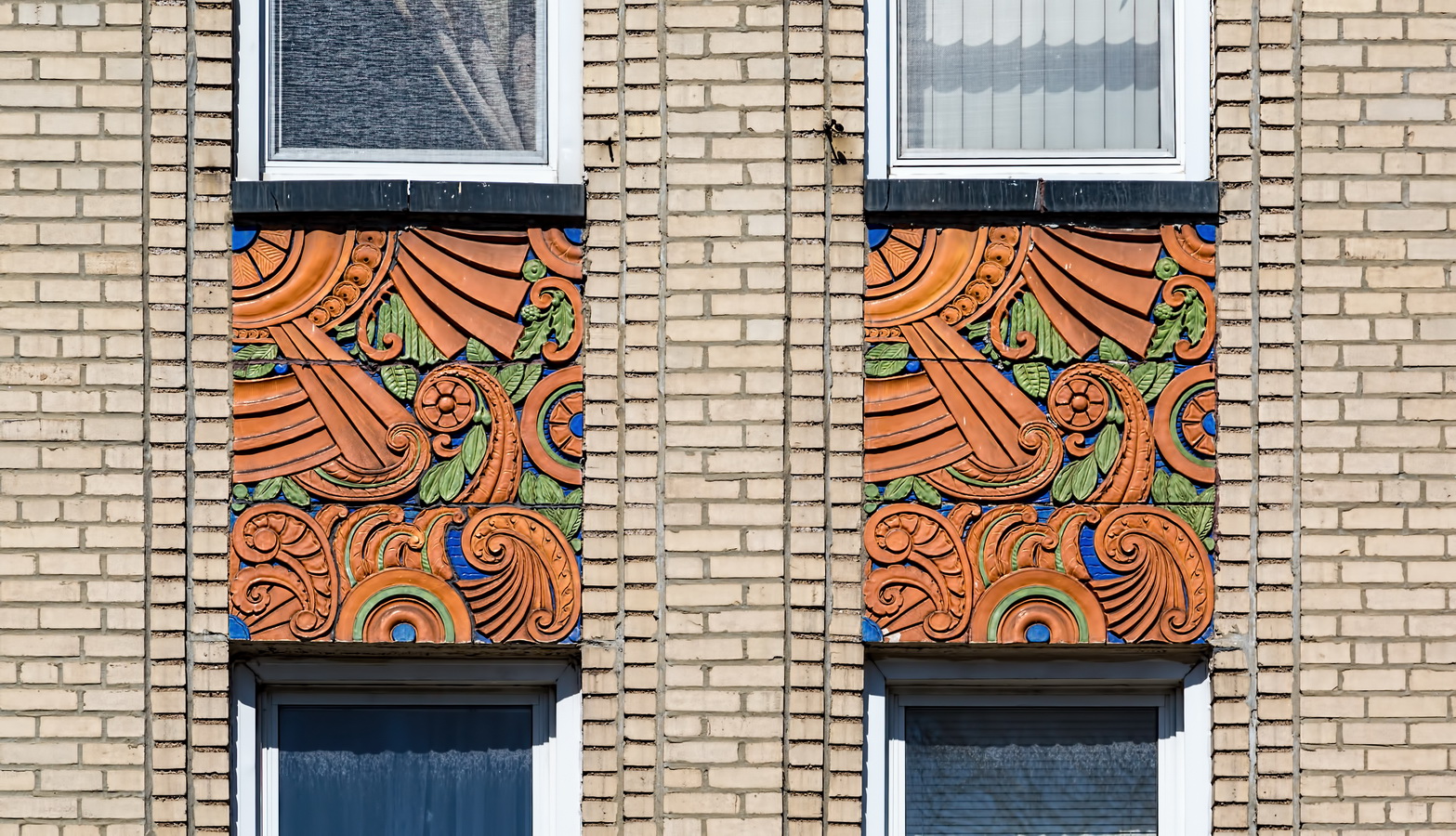
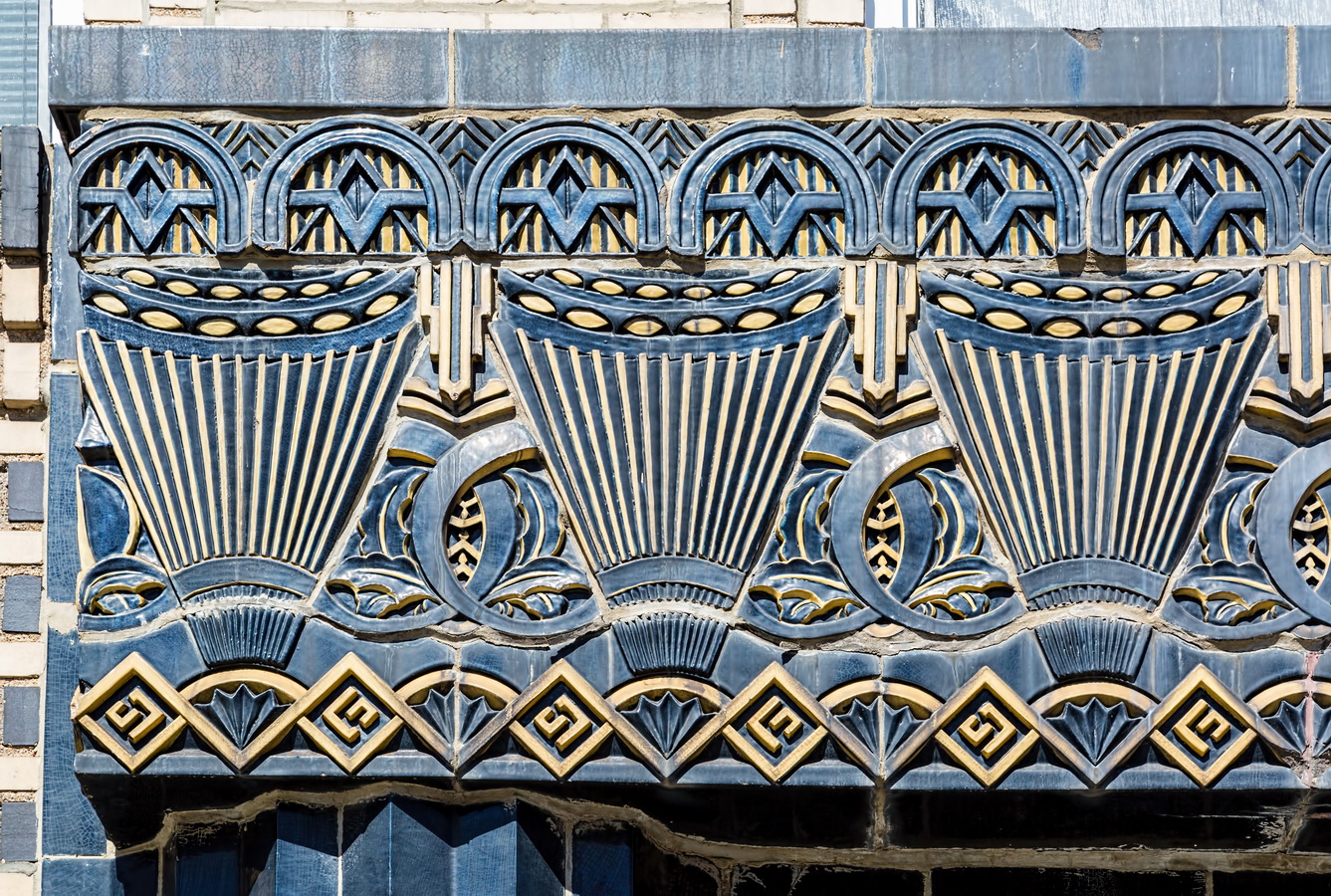
Here are some of the online maps that I’ve found particularly helpful for planning my explorations and researching buildings and neighborhoods. In the following samples, click the titles to open a new window with that map. Most links will load the location of 711 Brightwater Court in Brighton Beach, Brooklyn – a building that I was researching for a gallery.
This is my default map – it loads quickly, and searches intelligently in the areas I browse most frequently. Street View lets me see the lay of the land quickly, and helps me verify the location of buildings that I’ve photographed. When I’m scouting new areas or a particular landmark, Street View helps me find the best vantage points. Google’s Transportation layer shows subways and bus routes – even bus arrival times – a boon when planning a trip to an unfamiliar neighborhood. Just remember to double-check the MTA maps, because Google’s info is sometimes out of date.
Google Earth is like having a personal helicopter – without the noise. Unlike other online maps, you can change the orientation any way that you want: North doesn’t have to be at the top of the screen. And unlike other aerial maps, you can change your angle of view – you aren’t locked in to a two-dimensional straight-down view.
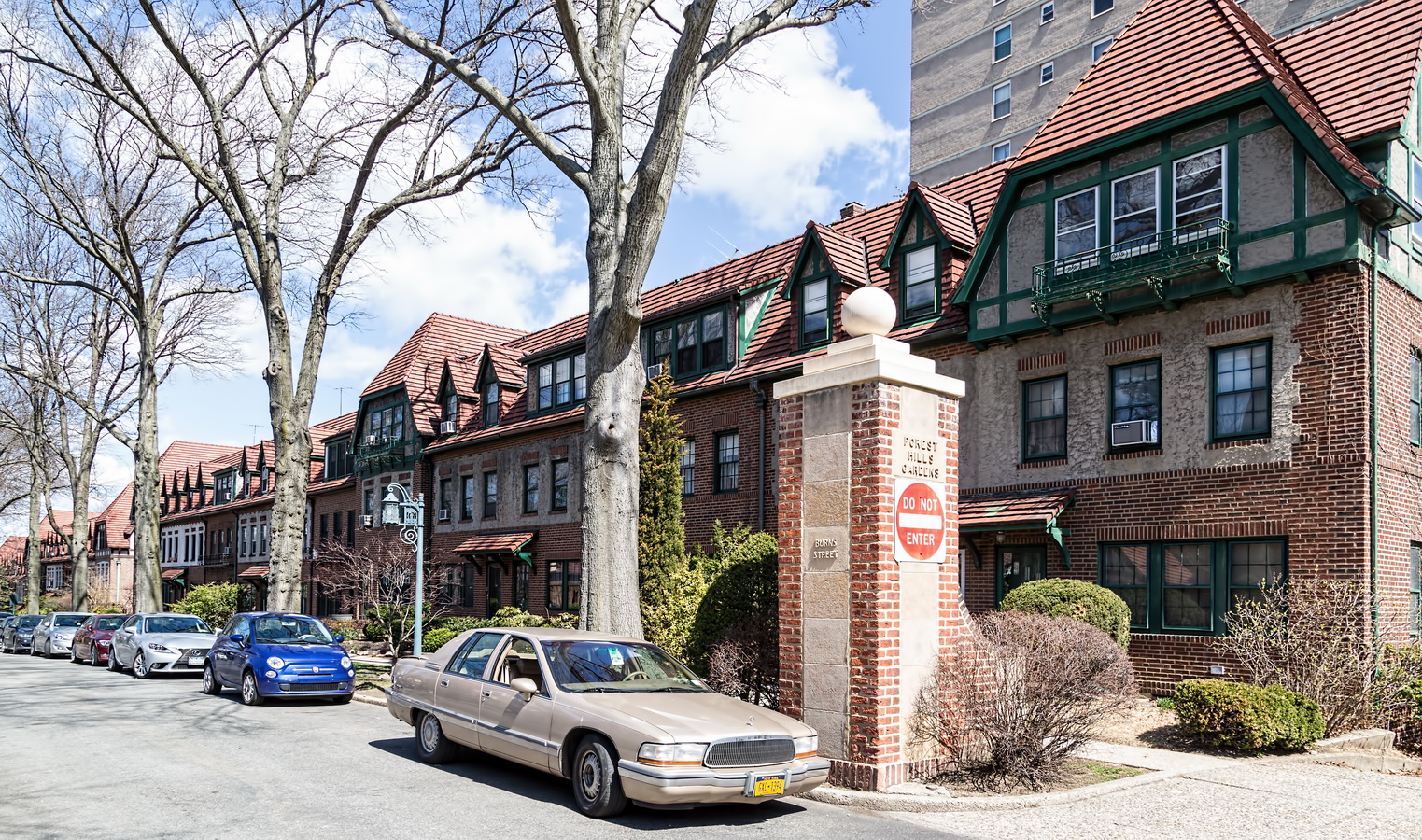
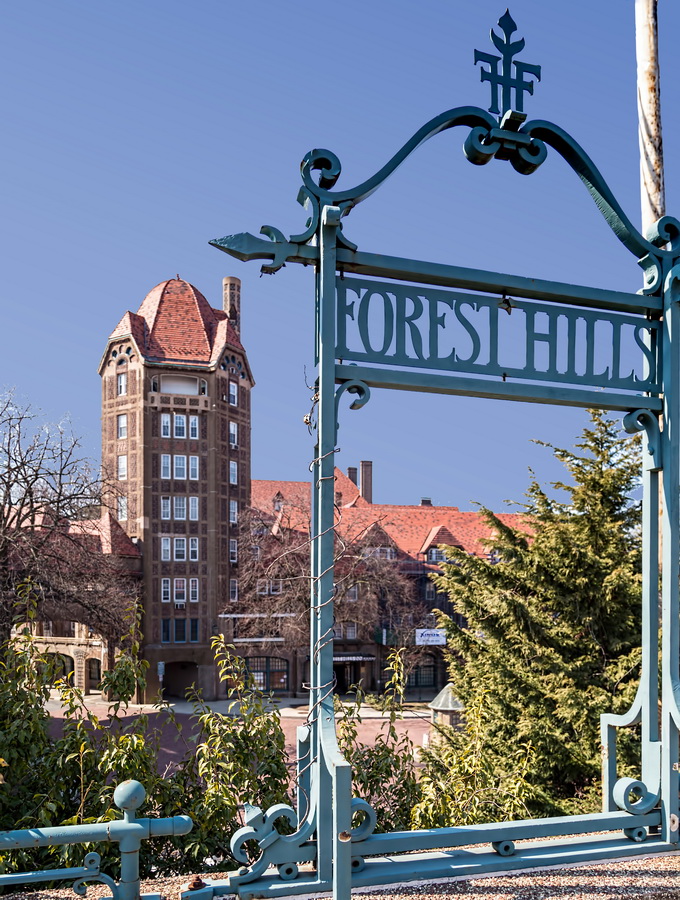
Open Street Map is a user-supported, open-source map. It contains details that you might not be able to find elsewhere. For example, I recently used this to find the boundaries of Forest Hills Gardens. (The development declined to provide a map, and my usual sources came up blank.)
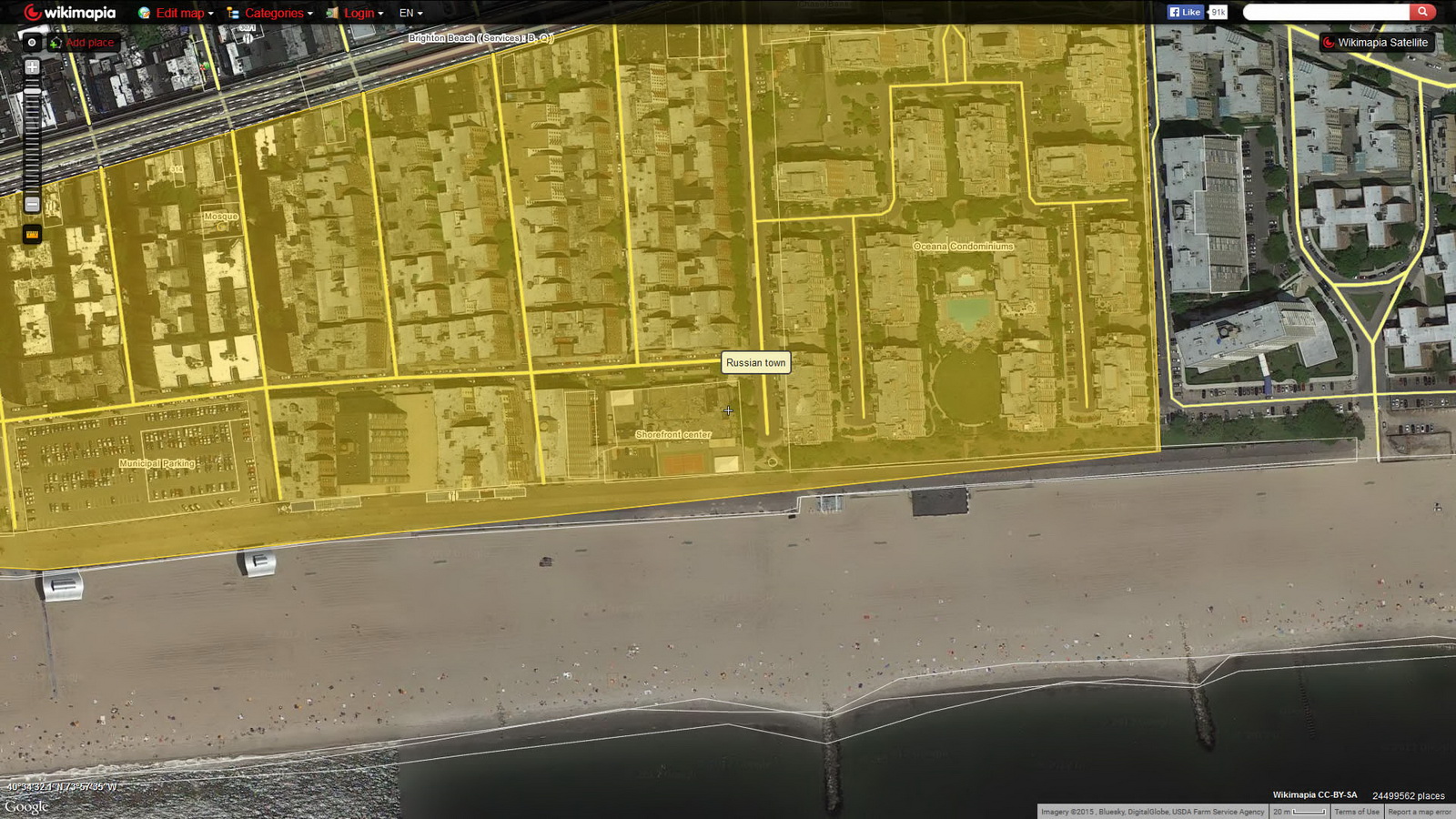
Like Open Street Map, WikiMapia is an open-source, user-supported map with lots of historical and architectural details, frequently including links to other sites. You can switch among 11 different interfaces (Google, Bing, OSM, etc.), making this easy to learn and use.
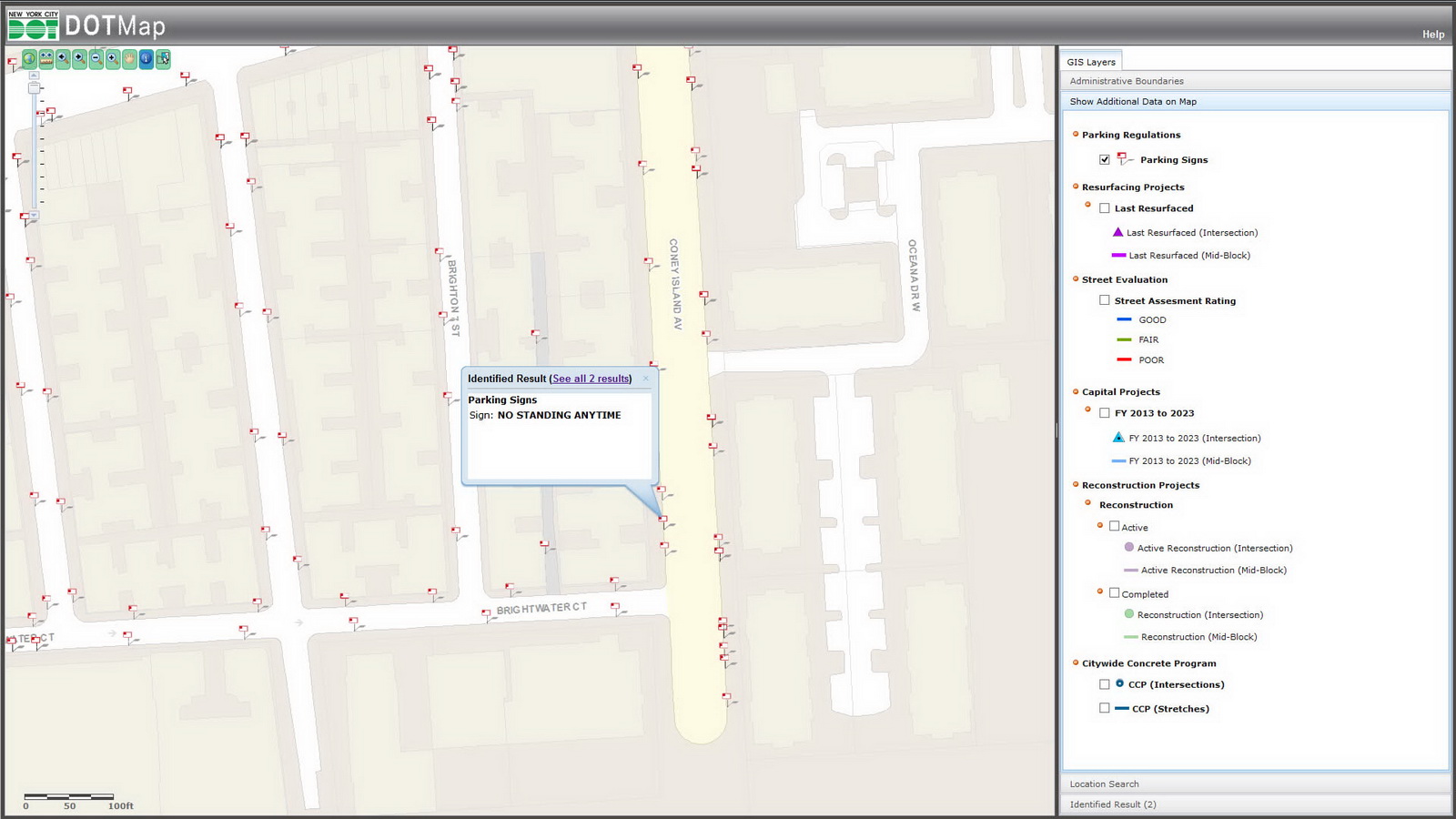
I refer to this whenever I want to find the best times for photographing a building without parked cars. This maps every traffic and parking sign in the city, so you can check to see when street-cleaning rules mandate “No Parking.”
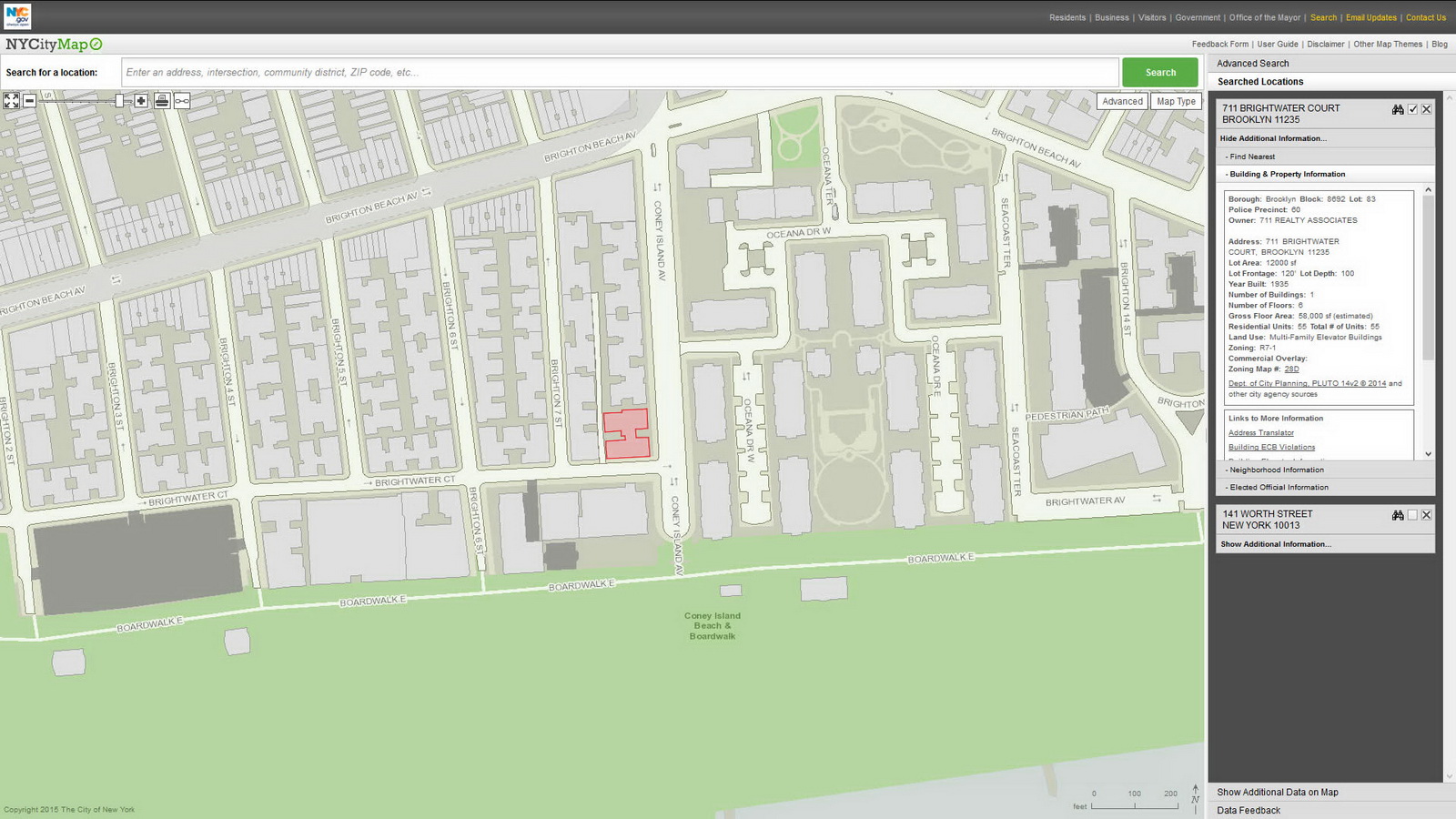
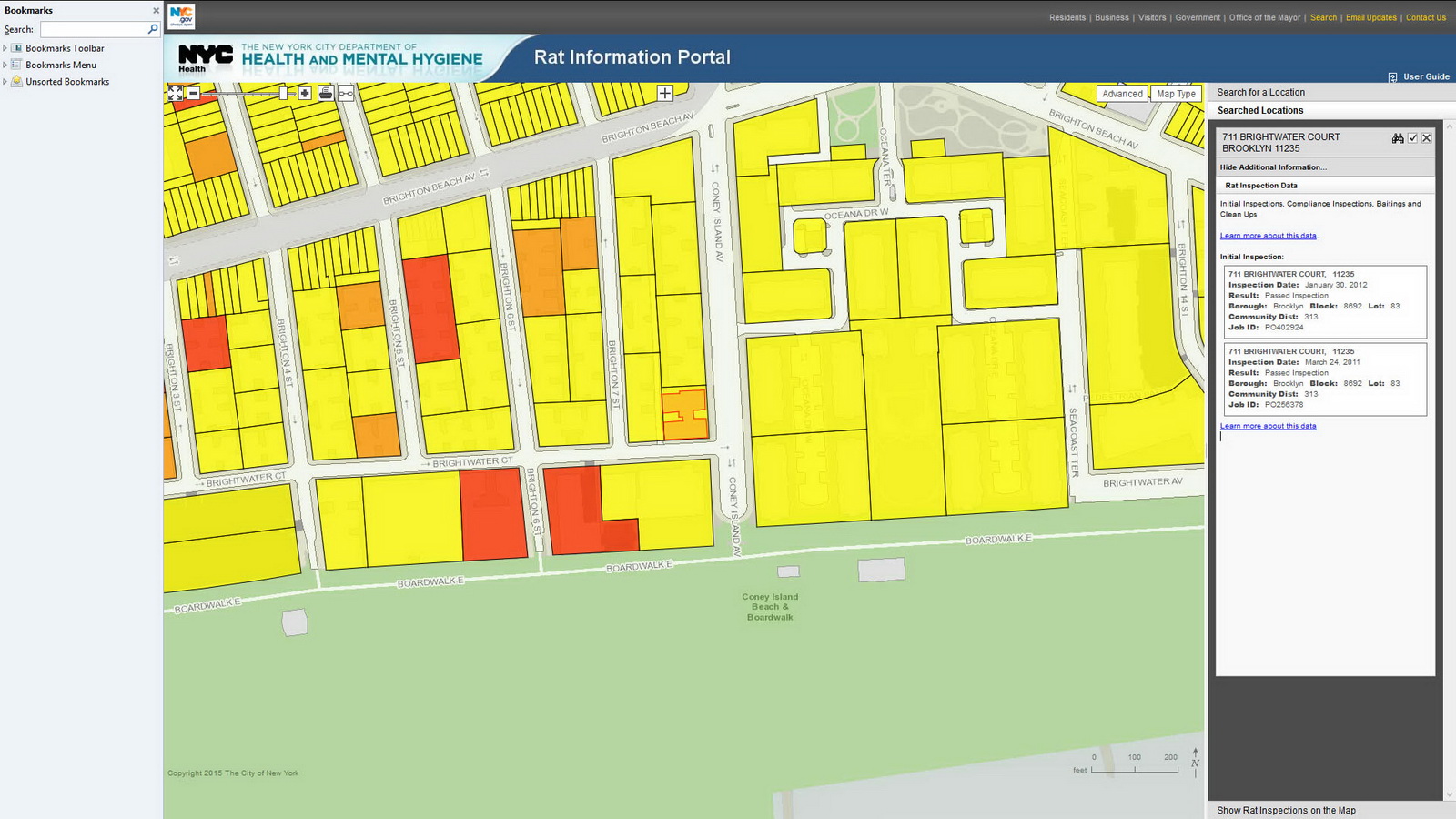
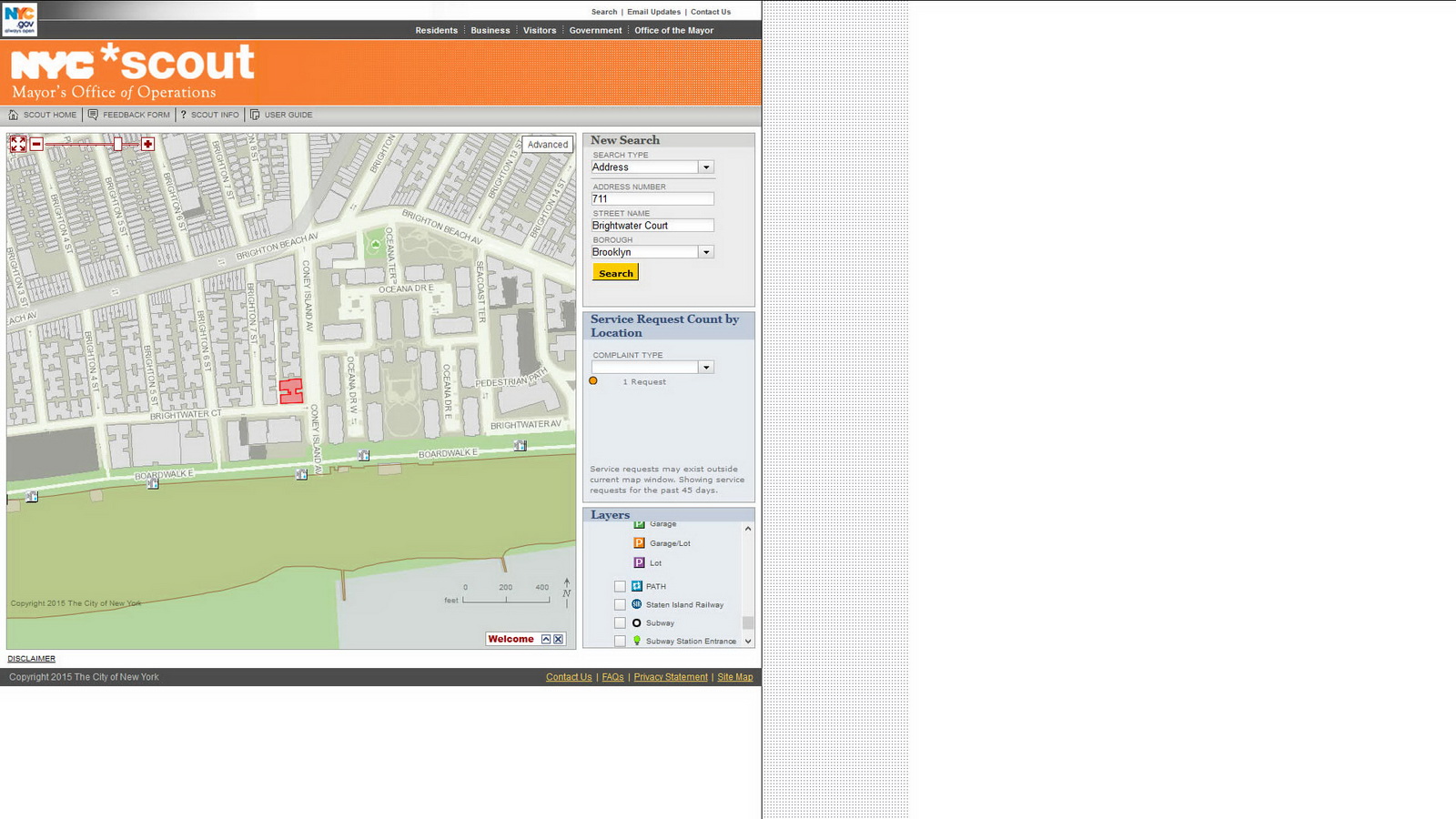
New York City Map is 12 maps in one! And it’s a time machine – just select one of the seven historic aerial views going back to 1924. The default view is linked to the Department of Buildings database, but 11 other map themes lead to 311 service requests, tax maps, census information, Green Infrastructure, NYC Parks, street closures, zoning and more. Before you buy a condo or sign a lease, you’ll want to check the Department of Buildings site for violations, and the Rat Information Portal to make sure that you don’t have any unexpected roommates!
There’s a crater in the middle of the street and you want to find out if it has been reported to 311? Here you go!
The Street Conditions Observation Unit (SCOUT) is a team of inspectors based in the Mayor’s Office of Operations. Their mission is to drive every City street once per month and report conditions that negatively impact quality of life to 311. SCOUT inspectors send reports of conditions they observe to the 311 system, and 311 assigns the conditions to the relevant agency for appropriate corrective action – the very same way that 311 handles complaints from the public.
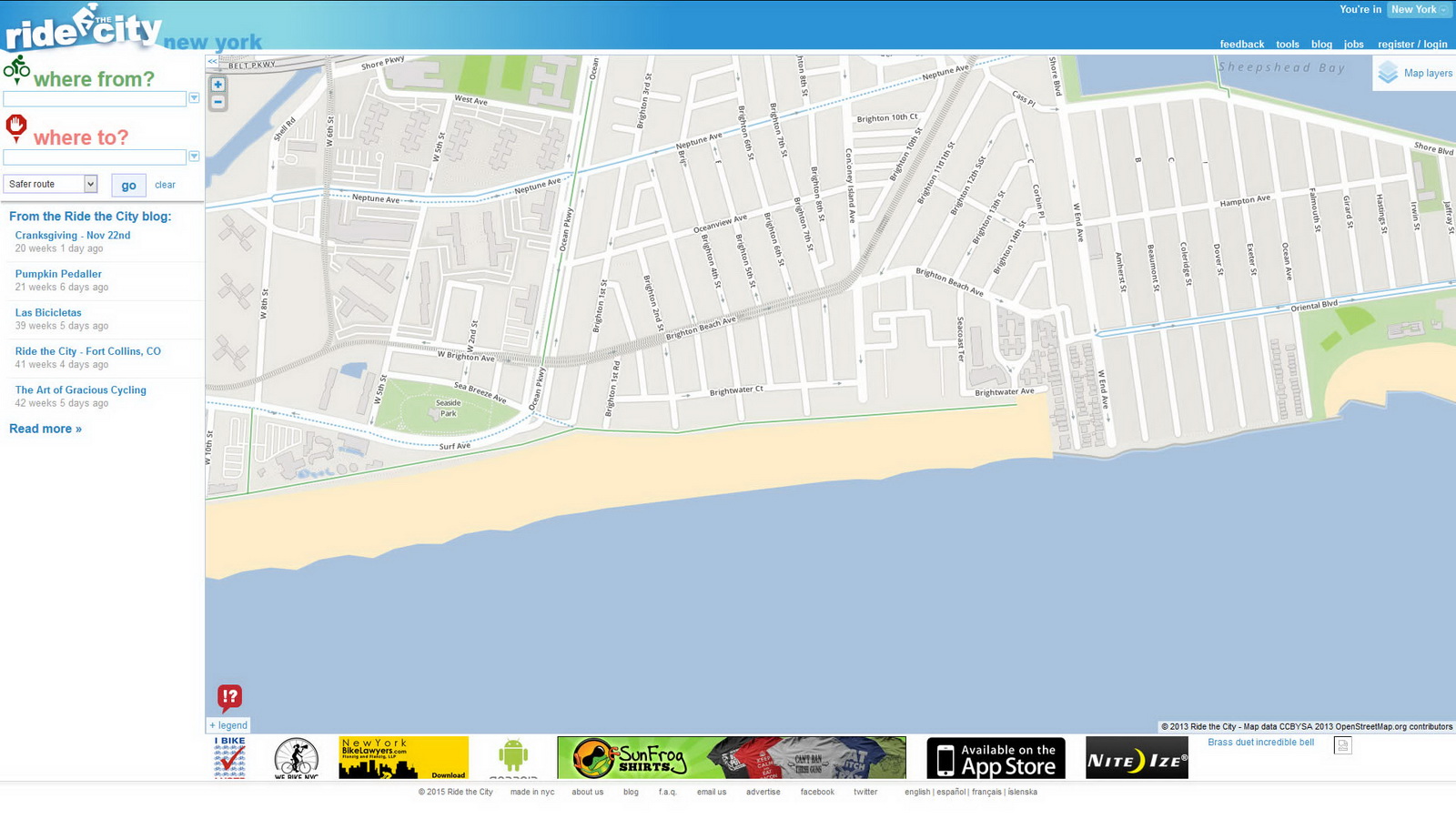
This map for bike riders will show you how to pedal from point A to point B – so its search function requires a starting and ending address. You can request the direct route, safe route, or safer route – select according to your skill and traffic comfort level.
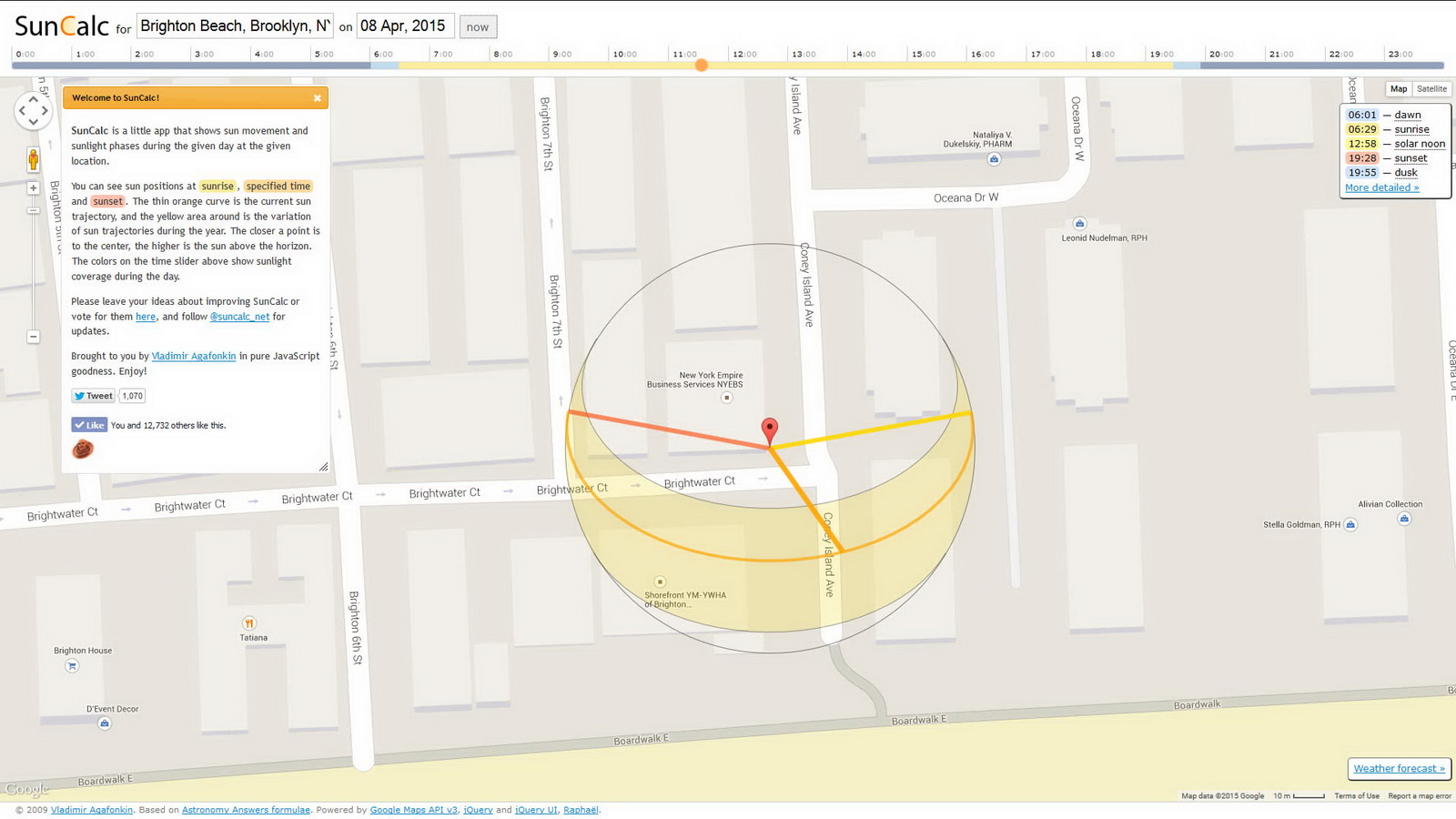
It doesn’t matter how much you spent on your camera. Your photos will only be as good as your light. Being in the right spot at the right time doesn’t have to be a matter of luck – you can predict the sun’s position with great accuracy using SunCalc. This is built on the Google Map interface, so it’s easy to navigate. Click on the landmark that you want to photograph, input the date (or click the NOW button) and drag the time slider to see how the sun angle changes during the day.
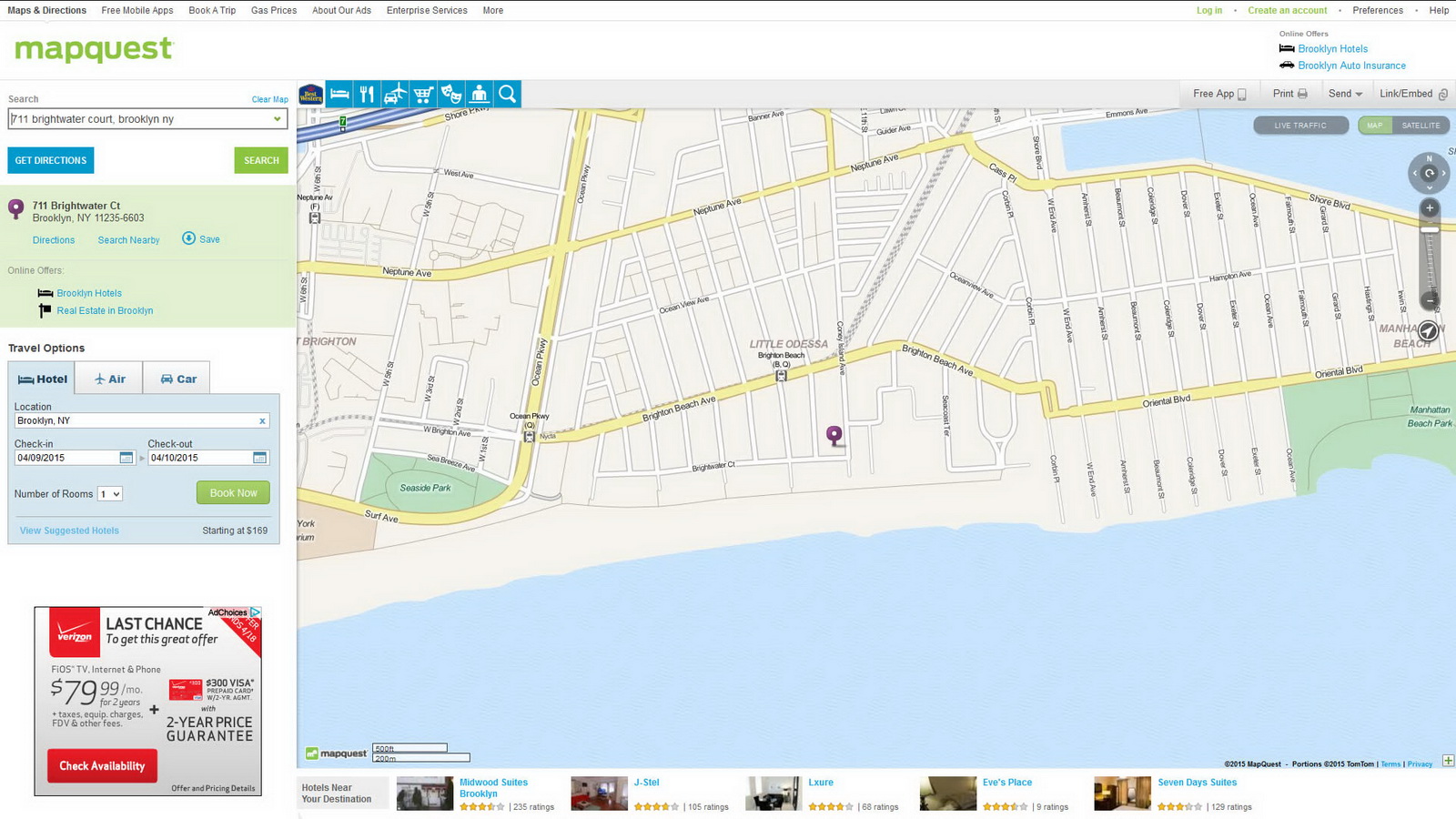
MapQuest is one of the earliest digital maps. It’s current claim to fame is travel – getting from point A to point B and finding a hotel and car rental when you get there.
MTA’s website, mta.info, is complicated but essential for anyone who wants to use public transit in New York, especially on weekends when maintenance is in full swing. The map is interactive, and you can also download a pdf version.
Each borough has its own bus map; the links above lead to pdf downloads.
Mapping New York City Recommended Reading